
The most distant human-made object
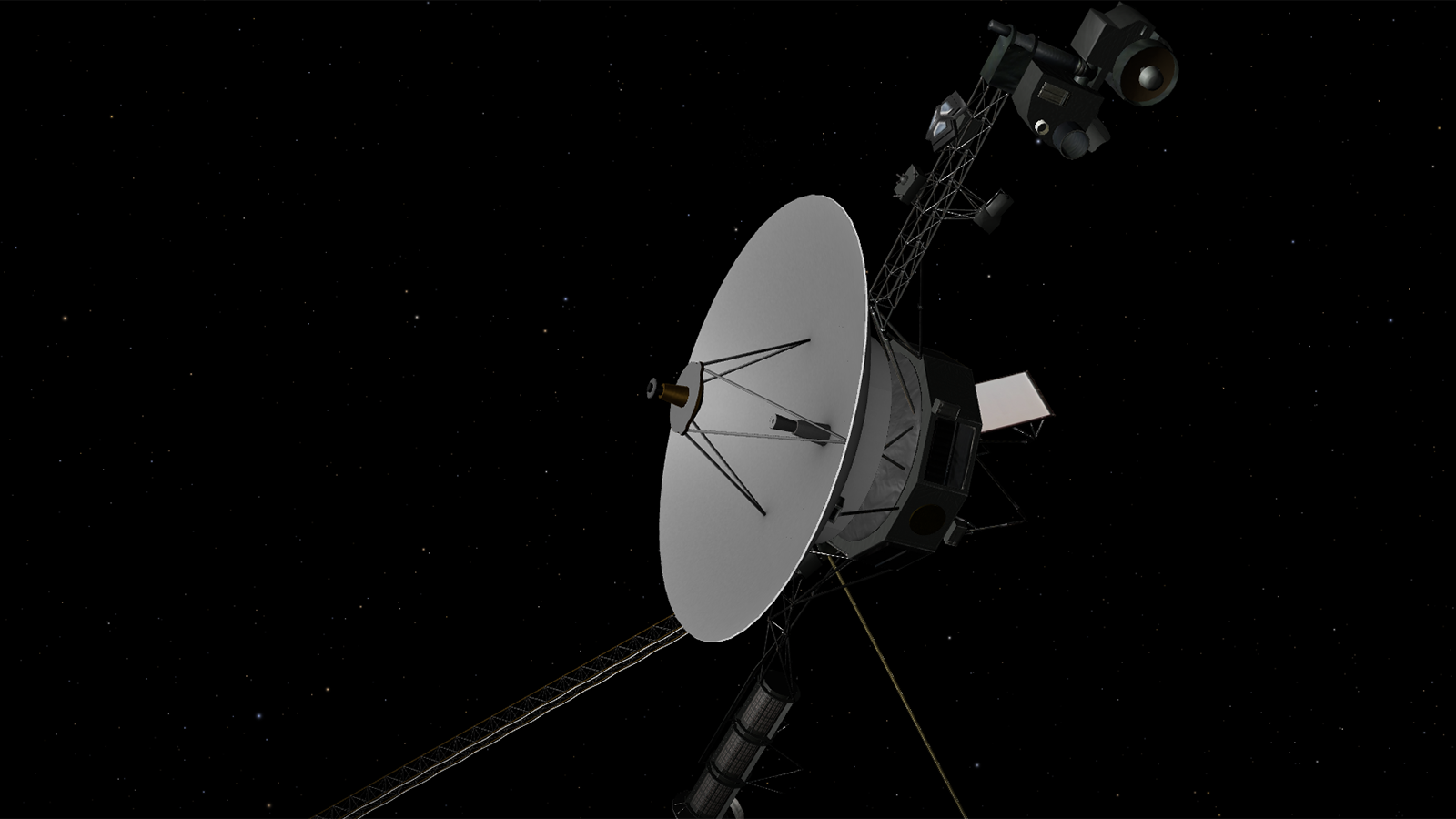

No spacecraft has gone farther than NASA's Voyager 1. Launched in 1977 to fly by Jupiter and Saturn, Voyager 1 crossed into interstellar space in August 2012 and continues to collect data.
Mission Type

Latest News
Still Kickin’ Since the ’70s: NASA’s Voyager Mission Keeps Exploring

Un viaje poético a la luna Europa

Voyager 1 Team Accomplishes Tricky Thruster Swap

Voyager 1 Returning Science Data From All Four Instruments

Ed Stone, Former Director of JPL, Voyager Project Scientist, Dies
What is Voyager 1?
Voyager 1 has been exploring our solar system since 1977. The probe is now in interstellar space, the region outside the heliopause, or the bubble of energetic particles and magnetic fields from the Sun. Voyager 1 was launched after Voyager 2, but because of a faster route it exited the asteroid belt earlier than its twin, and it overtook Voyager 2 on Dec. 15, 1977.
- Voyager 1 discovered a thin ring around Jupiter and two new Jovian moons: Thebe and Metis.
- At Saturn, Voyager 1 found five new moons and a new ring called the G-ring.
- Voyager 1 was the first spacecraft to cross the heliosphere, the boundary where the influences from outside our solar system are stronger than those from our Sun.
- Voyager 1 is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space.
In Depth: Voyager 1
Voyager 1 launched after Voyager 2, but because of a faster route it exited the solar system earlier than its twin. Voyager 1 overtook Voyager 2 on Dec. 15, 1977.
Voyager 1 began studying Jupiter in April 1978 at a range of 165 million miles (265 million km). Images showed Jupiter’s atmosphere to be more turbulent than during the Pioneer 10 and 11 flybys. Voyager 1 took a picture every 96 seconds to create a timelapse movie of the approach.
In early 1979, Voyager 1 discovered a faint ring system around Jupiter. The spacecraft’s closest encounter with Jupiter was at 12:05 UT on March 5, 1979 at a range of 174,000 miles (280,000 km), It went on to encounter several of Jupiter’s moons, including Amalthea , Io , Europa , Ganymede , and Callisto . Spectacular close-up photos of the moons opened up completely new worlds for planetary scientists. The spacecraft discovered two new moons, Thebe and Metis .
Its flyby of the Saturn system in November 1979 was as spectacular as the Jupiter encounter. Voyager 1 found five new moons, a new ring, and complicated ring structures, including “shepherd moons” that keep some rings well-defined. The spacecraft photographed Saturn’s moons Titan , Mimas , Enceladus , Tethys , Dione , and Rhea . All the moons appeared to be composed largely of water ice.
Images of Titan showed a thick atmosphere that completely hid the surface . The spacecraft found that the Titan’s atmosphere was composed of 90% nitrogen. Nitrogen, methane, and more complex hydrocarbons indicated prebiotic chemical reactions might be possible on Titan.
Voyager 1’s closest approach to Saturn was at 23:46 UT on Nov. 12, 1980 at a range of about 78,000 miles (126,000 km).
After Saturn, Voyager 1 headed north out of the ecliptic plane at a speed of about 3.5 AU per year. Because of the specific requirements for the Titan flyby, the spacecraft was not directed to Uranus and Neptune .
Voyager 1’s final 64 images were a mosaic taken at a distance of 40 Astronomical Units (AU) from the Sun. This solar system family portrait included six planets (Mercury and Mars were not visible). The image of Earth inspired the “ Pale Blue Dot ” made famous by Voyager science team member Carl Sagan (1934-1996). These were the last of a total of 67,000 images taken by the two Voyagers.
The Voyager Interstellar Mission (VIM) began on Jan, 1, 1990. The goal was to extend exploration to the outer limits of the Sun’s sphere of influence and beyond.
- On Feb. 17, 1998, Voyager 1 became the most distant human-made object in existence when — at a distance of 69.4 AU from the Sun — it “overtook” Pioneer 10.
- On Dec. 16, 2004, Voyager 1 reached the termination shock and entered the heliosheath .
- On Aug. 25, 2012, the spacecraft became the first to exit the heliosphere and begin measuring the interstellar environment.
Voyager 1 continues to communicate with NASA’s Deep Space Network and send data back from four still-functioning instruments — the cosmic ray telescope, the low-energy charged particles experiment, the magnetometer, and the plasma waves experiment.
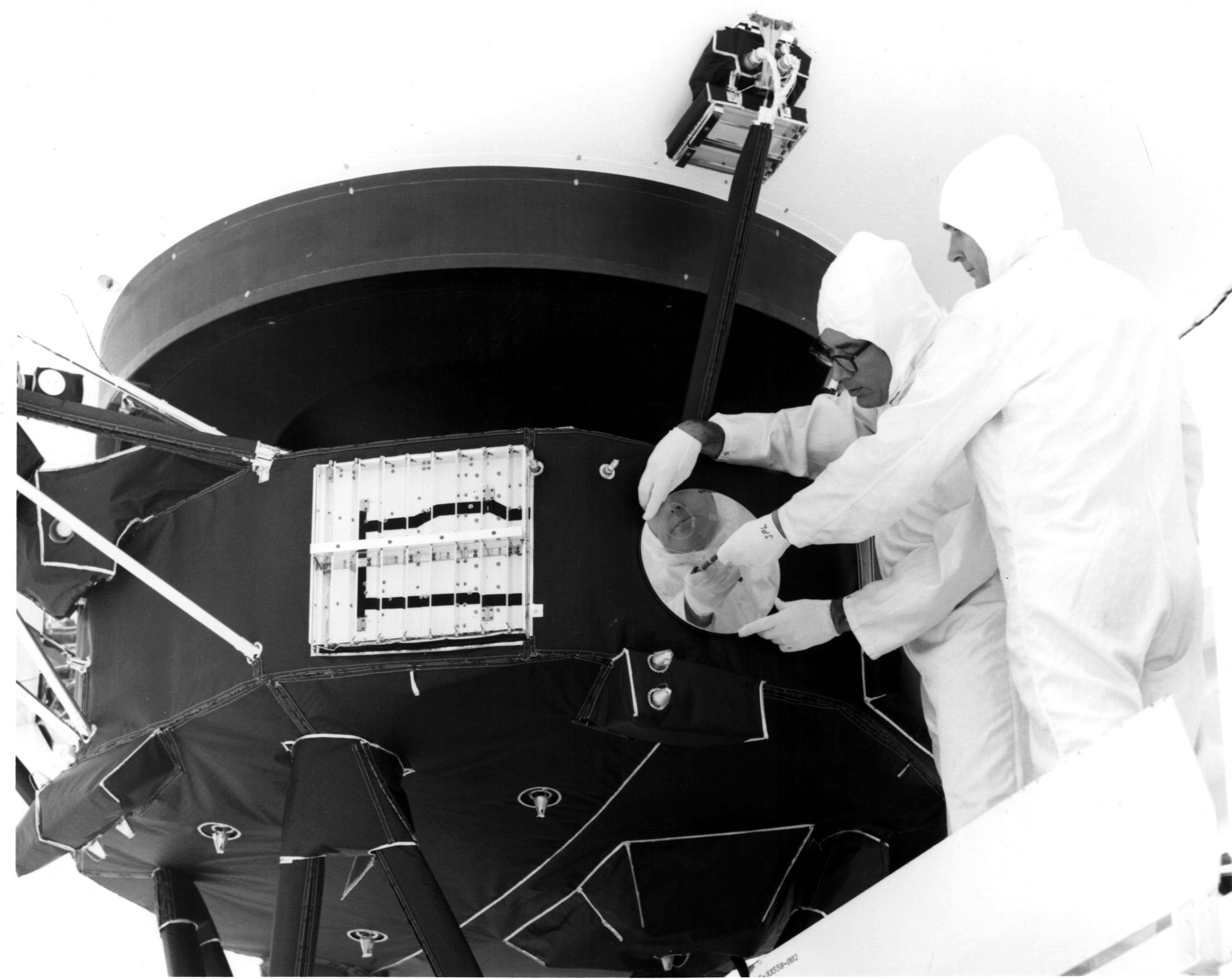

Each of the Voyagers contain a message to potential extraterrestrials in the form of a 30-centimeter diameter gold-plated copper disc. Like the plaques on Pioneers 10 and 11, the Voyager Golden Record has inscribed symbols that show the location of Earth relative to several pulsars. The record includes instructions to play it similar to a vinyl record player.
Audio on the disc includes greetings in 55 languages, 35 sounds from life on Earth (such as whale songs, laughter, etc.), 90 minutes of music including everything from Mozart and Bach to Chuck Berry and Blind Willie Johnson. It also includes 115 images of life on Earth and recorded greetings from then U.S. President Jimmy Carter and then-UN Secretary-General Kurt Waldheim.
As of Aug. 21, 2024, Voyager 1 was 164.7 AU from Earth — the farthest object created by humans — moving at a velocity of 38,026.79 mph (17.0 km/second) relative to the Sun.
Adapted from Asif A. Saddiqi’s “ Beyond Earth: A Chronicle of Deep Space Exploration ,” NASA History Office, 2018.

National Space Science Data Center: Voyager 1
A library of technical details and historic perspective.

Beyond Earth: A Chronicle of Deep Space Exploration
A comprehensive history of missions sent to explore beyond Earth.
Discover More Topics From NASA

Our Solar System


Interstellar Mission
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence.

Mission Statistics
Launch Date
Sept. 5, 1977
About the mission
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
Voyagers 1 and 2 were designed to take advantage of a rare planetary alignment that occurs only once in 176 years and remain the most well traveled spacecraft in history. Both spacecraft carry a sort of time capsule called the Golden Record, a 12-inch gold-plated copper disk containing sounds and images selected to portray the story of our world to extraterrestrials.
Instruments
- Imaging system
- Infrared interferometer spectrometer
- Ultraviolet spectrometer
- Triaxial fluxgate magnetometer
- Plasma spectrometer
- Low-energy charged particles detectors
- Cosmic Ray System (CRS)
- Photopolarimeter System (PPS)
- Plasma Wave System (PWS)
Mission Highlights
Sept. 1, 2013

Interactive 3D model of Voyager 1. View the full interactive experience at Eyes on the Solar System .
- › Mission Website
- › Fact Sheet
- › JPL History
- › Voyager 1 Information on Solar System Exploration
- › NASA Mission Page
- › Voyager 2 Information on National Space Science Data Center
Voyager turns 45: What the iconic mission taught us and what's next
Can the first probe to visit Neptune and Uranus make it to its 50th anniversary?

Forty-five years ago, on Aug. 20, 1977, NASA's Voyager 2 spacecraft launched from Cape Canaveral, Florida, on a Titan III-Centaur rocket, embarking on a "grand tour" of the solar system that would include visits to the Jupiter and Saturn systems and would make it the first spacecraft to visit the ice giants Uranus and Neptune and their moons.
Voyager 2 is now 12.1 billion miles (19.5 billion kilometers) away and still sending back data on the distant and unknown heliopause, and scientists are beginning to wonder how long the iconic space probe can keep going.
Designed to take advantage of a once-every-176-years alignment in the 1970s that made it possible for spacecraft to take gravity-assist slingshots from planet to planet across the solar system , the Voyager mission consisted of two probes. Voyager 2 was the first to launch, with Voyager 1 following two weeks later. Both carried the famous " Golden Record ," a 12-inch gold-plated copper disc containing sounds and images portraying the diversity of life and culture on Earth .
Now over 14.5 billion miles (23.3 billion km) away, Voyager 1 is the farthest artificial object from Earth. But Voyager 2 is arguably more iconic because of its incredible multidecade tour of the giant planets.
- NASA's twin Voyager probes are nearly 45 — and facing some hard decisions
- After 45 years, the 5-billion-year legacy of the Voyager 2 interstellar probe is just beginning
Related: Celebrate 45 years of Voyager with these amazing images of our solar system (gallery)
Voyager's "grand tour"
Though it launched second, Voyager 1 was so called because it was to reach Jupiter and Saturn first — in March 1979 and November 1980, respectively — before exiting the plane of the planets where it took the famous "Pale Blue Dot" photo . Voyager 2 visited four planets: Jupiter in July 1979, Saturn in August 1981, Uranus in January 1986 and Neptune in August 1989.
"Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 provided tremendous legacies for planetary exploration," Jonathan Lunine, a planetary scientist and physicist at Cornell University who is working on the Juno , Europa Clipper and James Webb Space Telescope missions, told Space.com. "Not only in what they accomplished in terms of science, but also demonstrating that it was really possible to explore the outer solar system with a couple of spacecraft."
Get the Space.com Newsletter
Breaking space news, the latest updates on rocket launches, skywatching events and more!

What did the Voyager probes reveal?
Voyager's discoveries are the stuff of legend among planetary scientists, many of whom still rely on the unique images from the spacecraft's wide-angle and narrow-angle cameras. The probes spotted volcanoes on Jupiter's moon Io , discovered that Jupiter's Great Red Spot is an Earth-size storm and found that the gas giant has faint rings. They studied Saturn's rings ; saw the giant moon Titan's thick, Earth-like atmosphere; and revealed the tiny moon Enceladus to be geologically active.
Voyager 2 alone then visited Uranus and Neptune. The spacecraft's first-ever images of Uranus revealed dark rings, the planet's tilted magnetic field and its geologically active moon Miranda. Neptune, meanwhile, was also discovered to have rings and many more moons than scientists initially thought. We also got to see Triton , a geologically active moon that is orbiting "backward" and, like Pluto , is now believed to be a captured dwarf planet from the Kuiper Belt .

Voyager as a catalyst
In addition to making groundbreaking discoveries, the Voyager mission helped scientists determine what merited deeper exploration. The mission revealed Jupiter to be an incredibly complex planet, thus spurring NASA to launch the Galileo mission in 1989 and the Juno mission in 2011. The Voyager probes' work also helped to inspire the iconic Cassini mission to Saturn.
"Voyager 1's close flyby of Titan was the catalyst for the wonderful Cassini mission to Saturn and its Huygens probe," Lunine said. The Huygens probe landed on the surface of Titan in 2005 and sent back an incredible video .
Voyager 2 has also been a catalyst for investigations into the role of the ice giant planets — not only in the solar system but also in distant star systems, since most of the exoplanets found so far are roughly the size of Neptune and Uranus.

Voyager and NASA today
NASA has spent decades following up on the Voyager missions, and those efforts continue today. The space agency's Dragonfly mission will reach Titan, Saturn's largest moon, in 2034, while Europa Clipper will study Jupiter's ocean moon, first imaged by Voyager, starting in 2030. In April, the National Academies Planetary Science Decadal Survey recommended that NASA send a $4.2 billion Uranus Orbiter and Probe mission to unveil the mysterious ice giant planet and its moons in the 2040s.
It's the latest mission that's a direct consequence of Voyager 2's brief visit to the Uranus system in January 1986. "Voyager 2's flyby of Uranus was a bull's-eye — it went directly through the plane of the moons' orbits because of the orientation of Uranus' axis to the sun ," Lunine said. That made it unlike flybys at other planets, where the probes were able to visit one moon after another. "Voyager 2 got very brief images from these moons, so they're largely unexplored," Lunine said.
Ariel and Miranda, in particular, are thought to be ocean worlds and so would be specifically targeted by the Uranus Orbiter and Probe. "It's been 45 years since the launch of Voyager 1 and Voyager 2, and here we are now finally talking about a Uranus Orbiter and Probe mission," Lunine said. "It seems like a long time because these missions take so long to conceive of, fund, build, launch and execute, but it all comes from the intriguing peeks that we got from Voyager 2."

How long will Voyager last?
Both Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 still communicate with NASA's Deep Space Network (which itself was created to communicate with Voyager 2 at Uranus and Neptune), receiving routine commands and occasionally transmitting data to Earth. "We are still getting data from Voyager," Stamatios Krimigis, principal investigator for the Voyager 1 and 2 probes and the Voyager Interstellar Mission, said during a news conference held at COSPAR 22 in July. "We're looking forward to getting data for probably another five or six years."
— What's next for NASA's Voyager 2 in interstellar space?
— Scientists' predictions for the long-term future of the Voyager Golden Records will blow your mind
— NASA's twin Voyager probes are nearly 45 — and facing some hard decisions
Around the mid- to late 2020s , the probes' scientific instruments will be entirely switched off, and eventually, the spacecraft will go cold and silent — but their journeys into interstellar space will continue indefinitely. "My motto is, I want to be here after Voyager passes on," said Krimigis, who is in his 80s. "But I'm not sure that's going to happen."
In around 300 years, Voyager 1 and 2 will enter the Oort cloud , the sphere of comets surrounding the solar system. About 30,000 years later, they'll exit the neighborhood and silently orbit the center of the Milky Way for millions of years.
Their scientific work may be almost over, but the Voyager spacecraft have only just begun their journeys into the cosmos.
Follow us on Twitter @Spacedotcom and on Facebook .
Join our Space Forums to keep talking space on the latest missions, night sky and more! And if you have a news tip, correction or comment, let us know at: [email protected].
Jamie is an experienced science, technology and travel journalist and stargazer who writes about exploring the night sky, solar and lunar eclipses, moon-gazing, astro-travel, astronomy and space exploration. He is the editor of WhenIsTheNextEclipse.com and author of A Stargazing Program For Beginners , and is a senior contributor at Forbes. His special skill is turning tech-babble into plain English.
Galaxies get tangled up in 'the queen's hair' in new Hubble Telescope image
Black holes that form in 'reverse Big Bang replays' could account for dark energy
'Star Trek: Lower Decks' Season 5 episode 5: What's the problem with Starbase 80?
Most Popular
- 2 Blue Origin stacks huge New Glenn rocket ahead of 1st launch (photo)
- 3 Could a supernova ever destroy Earth?
- 4 SpaceX launches 24 Starlink satellites on 2nd leg of spaceflight doubleheader (video)
- 5 All astronauts still in good health on ISS, NASA flight surgeon says amid new tabloid rumors

Suggested Searches
- Climate Change
- Expedition 64
- Mars perseverance
- SpaceX Crew-2
- International Space Station
- View All Topics A-Z
Humans in Space
Earth & climate, the solar system, the universe, aeronautics, learning resources, news & events.
Six Ways Supercomputing Advances Our Understanding of the Universe

NASA’s Hubble Sees Aftermath of Galaxy’s Scrape with Milky Way

What’s Up: November 2024 Skywatching Tips from NASA
- Search All NASA Missions
- A to Z List of Missions
- Upcoming Launches and Landings
- Spaceships and Rockets
- Communicating with Missions
- James Webb Space Telescope
- Hubble Space Telescope
- Why Go to Space
- Commercial Space
- Destinations
- Living in Space
- Explore Earth Science
- Earth, Our Planet
- Earth Science in Action
- Earth Multimedia
- Earth Science Researchers
- Pluto & Dwarf Planets
- Asteroids, Comets & Meteors
- The Kuiper Belt
- The Oort Cloud
- Skywatching
- The Search for Life in the Universe
- Black Holes
- The Big Bang
- Dark Energy & Dark Matter
- Earth Science
- Planetary Science
- Astrophysics & Space Science
- The Sun & Heliophysics
- Biological & Physical Sciences
- Lunar Science
- Citizen Science
- Astromaterials
- Aeronautics Research
- Human Space Travel Research
- Science in the Air
- NASA Aircraft
- Flight Innovation
- Supersonic Flight
- Air Traffic Solutions
- Green Aviation Tech
- Drones & You
- Technology Transfer & Spinoffs
- Space Travel Technology
- Technology Living in Space
- Manufacturing and Materials
- Science Instruments
- For Kids and Students
- For Educators
- For Colleges and Universities
- For Professionals
- Science for Everyone
- Requests for Exhibits, Artifacts, or Speakers
- STEM Engagement at NASA
- NASA's Impacts
- Centers and Facilities
- Directorates
- Organizations
- People of NASA
- Internships
- Our History
- Doing Business with NASA
- Get Involved

NASA en Español
- Aeronáutica
- Ciencias Terrestres
- Sistema Solar
- All NASA News
- Video Series on NASA+
- Newsletters
- Social Media
- Media Resources
- Upcoming Launches & Landings
- Virtual Guest Program
- Image of the Day
- Sounds and Ringtones
- Interactives
- STEM Multimedia
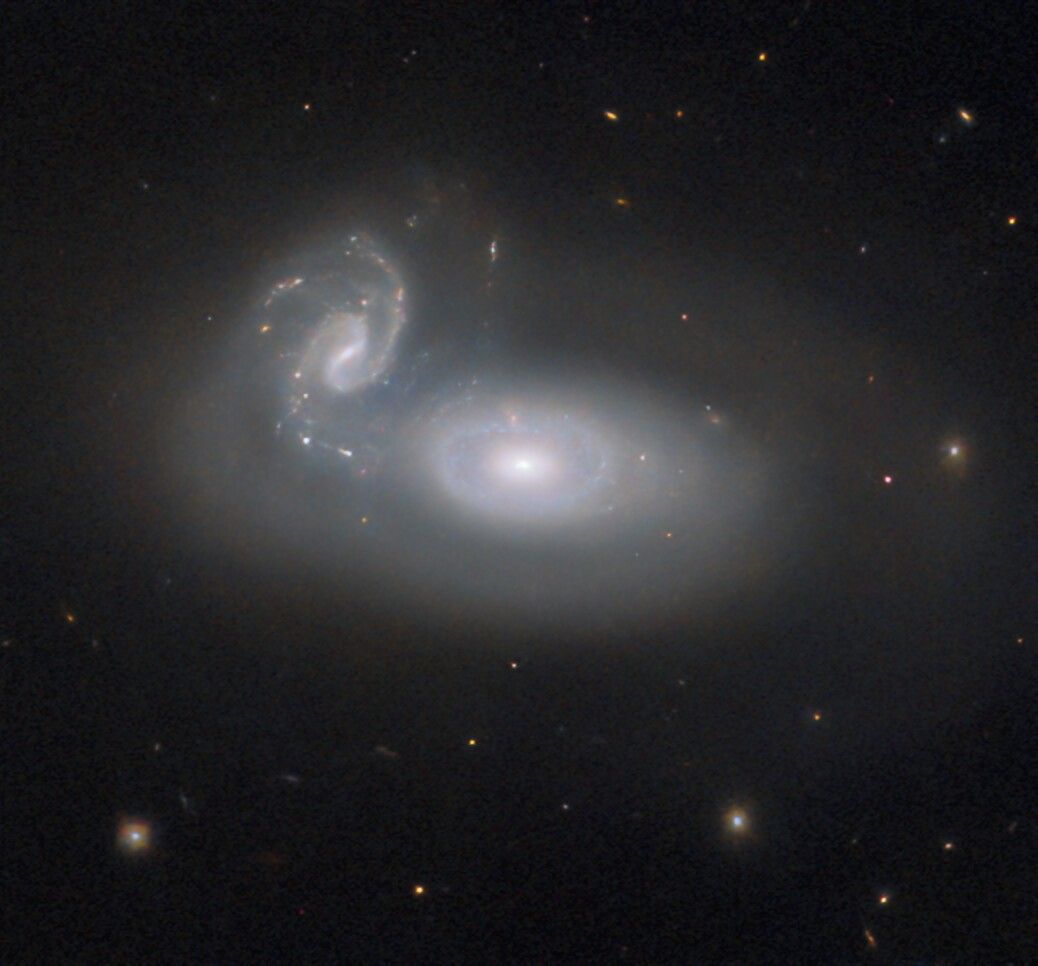

Hubble Takes a Look at Tangled Galaxies
NASA’s EMIT Will Explore Diverse Science Questions on Extended Mission
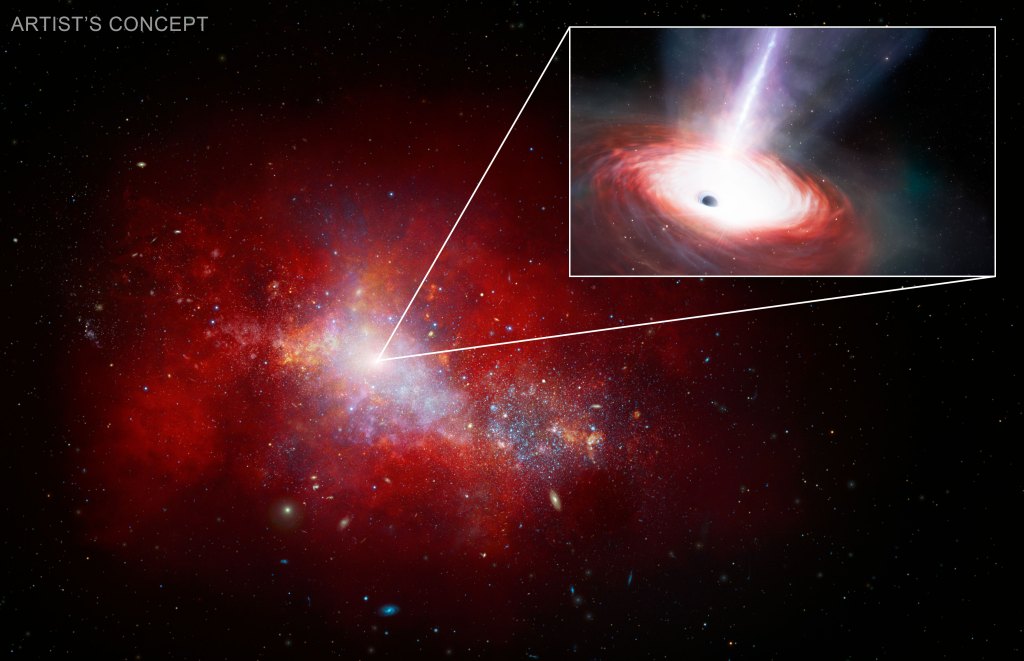

Astronomers Find Early Fast-Feeding Black Hole Using NASA Telescopes

Wearable Tech for Space Station Research

Station Science Top News: Nov. 8, 2024

NASA Shares Space Food Insight with Commercial Food Industry
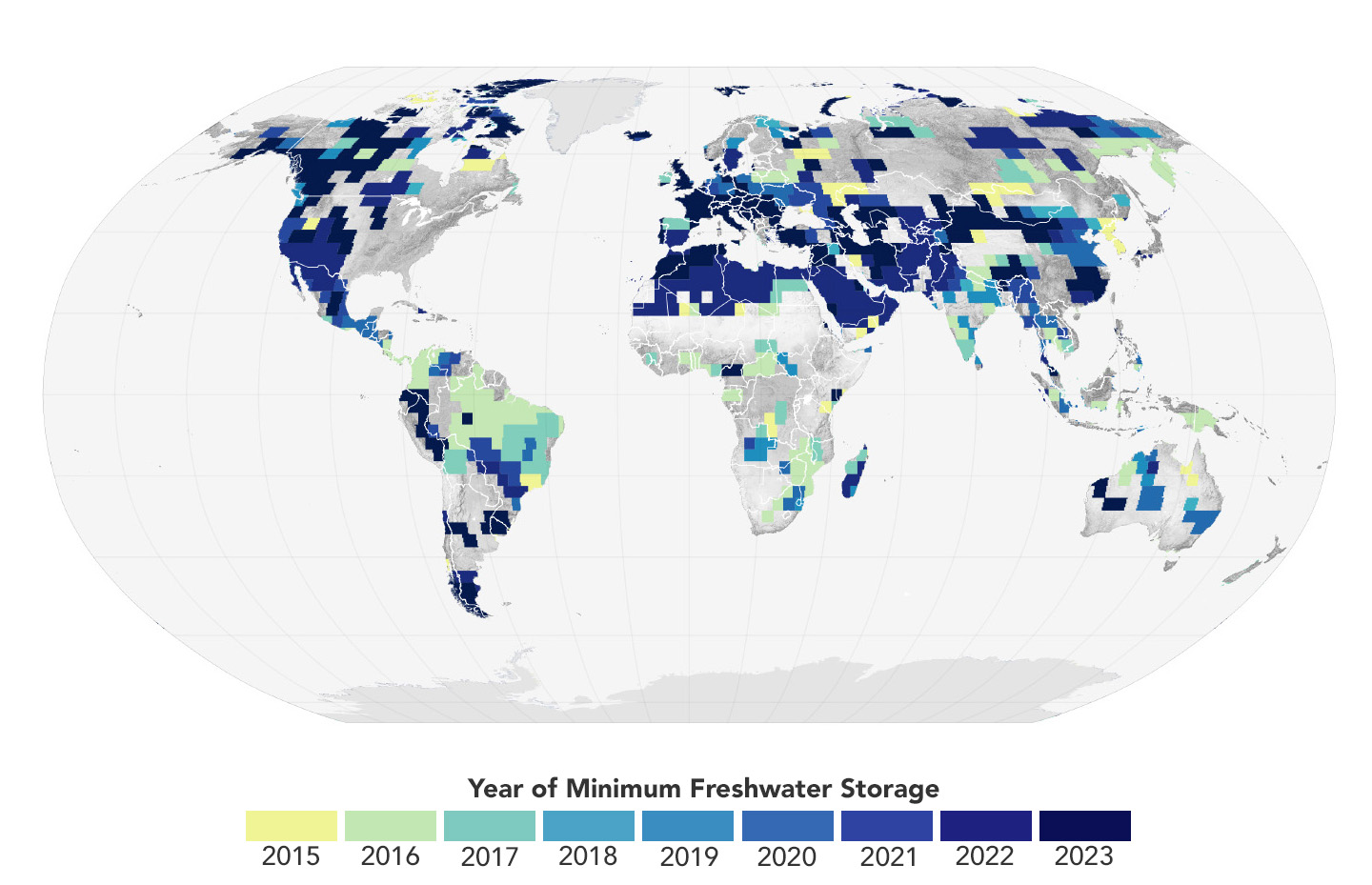
NASA Satellites Reveal Abrupt Drop in Global Freshwater Levels

NASA Data Helps International Community Prepare for Sea Level Rise

F.12 Artemis IV Deployed Instruments Program Final Text and Due Dates Released.

Amendment 51: F.13 Lunar Terrain Vehicle Instruments Program Correction.

OSDR Chats with Dr Robert Reynolds

Dynamic Spin Rig Publications
Speed publications.

NASA Goddard Lidar Team Receives Center Innovation Award for Advancements

Precision Pointing Goes the Distance on NASA Experiment

Math, Mentorship, Motherhood: Behind the Scenes with NASA Engineers

Student-Built Capsules Endure Heat of Re-entry for NASA Science

Power to Explore STEM Writing Challenge

NASA Seeks Options for Future Headquarters Building

55 Years Ago: Apollo 12 Makes a Pinpoint Landing on the Moon

El X-59 enciende su motor por primera vez rumbo al despegue

La NASA lleva un dron y un rover espacial a un espectáculo aéreo

Destacado de la NASA: Felipe Valdez, un ingeniero inspirador
Nasa spacecraft embarks on historic journey into interstellar space.

NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft officially is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. The 36-year-old probe is about 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometers) from our sun.
New and unexpected data indicate Voyager 1 has been traveling for about one year through plasma, or ionized gas, present in the space between stars. Voyager is in a transitional region immediately outside the solar bubble, where some effects from our sun are still evident. A report on the analysis of this new data, an effort led by Don Gurnett and the plasma wave science team at the University of Iowa, Iowa City, is published in Thursday’s edition of the journal Science.
“Now that we have new, key data, we believe this is mankind’s historic leap into interstellar space,” said Ed Stone, Voyager project scientist based at the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena. “The Voyager team needed time to analyze those observations and make sense of them. But we can now answer the question we’ve all been asking — ‘Are we there yet?’ Yes, we are.”
Voyager 1 first detected the increased pressure of interstellar space on the heliosphere, the bubble of charged particles surrounding the sun that reaches far beyond the outer planets, in 2004. Scientists then ramped up their search for evidence of the spacecraft’s interstellar arrival, knowing the data analysis and interpretation could take months or years.
Voyager 1 does not have a working plasma sensor, so scientists needed a different way to measure the spacecraft’s plasma environment to make a definitive determination of its location. A coronal mass ejection, or a massive burst of solar wind and magnetic fields, that erupted from the sun in March 2012 provided scientists the data they needed. When this unexpected gift from the sun eventually arrived at Voyager 1’s location 13 months later, in April 2013, the plasma around the spacecraft began to vibrate like a violin string. On April 9, Voyager 1’s plasma wave instrument detected the movement. The pitch of the oscillations helped scientists determine the density of the plasma. The particular oscillations meant the spacecraft was bathed in plasma more than 40 times denser than what they had encountered in the outer layer of the heliosphere. Density of this sort is to be expected in interstellar space.
The plasma wave science team reviewed its data and found an earlier, fainter set of oscillations in October and November 2012. Through extrapolation of measured plasma densities from both events, the team determined Voyager 1 first entered interstellar space in August 2012.
“We literally jumped out of our seats when we saw these oscillations in our data — they showed us the spacecraft was in an entirely new region, comparable to what was expected in interstellar space, and totally different than in the solar bubble,” Gurnett said. “Clearly we had passed through the heliopause, which is the long-hypothesized boundary between the solar plasma and the interstellar plasma.”
The new plasma data suggested a timeframe consistent with abrupt, durable changes in the density of energetic particles that were first detected on Aug. 25, 2012. The Voyager team generally accepts this date as the date of interstellar arrival. The charged particle and plasma changes were what would have been expected during a crossing of the heliopause.
“The team’s hard work to build durable spacecraft and carefully manage the Voyager spacecraft’s limited resources paid off in another first for NASA and humanity,” said Suzanne Dodd, Voyager project manager, based at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), Pasadena, Calif. “We expect the fields and particles science instruments on Voyager will continue to send back data through at least 2020. We can’t wait to see what the Voyager instruments show us next about deep space.”
Voyager 1 and its twin, Voyager 2, were launched 16 days apart in 1977. Both spacecraft flew by Jupiter and Saturn. Voyager 2 also flew by Uranus and Neptune. Voyager 2, launched before Voyager 1, is the longest continuously operated spacecraft. It is about 9.5 billion miles (15 billion kilometers) away from our sun.
Voyager mission controllers still talk to or receive data from Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 every day, though the emitted signals are currently very dim, at about 23 watts — the power of a refrigerator light bulb. By the time the signals get to Earth, they are a fraction of a billion-billionth of a watt. Data from Voyager 1’s instruments are transmitted to Earth typically at 160 bits per second, and captured by 34- and 70-meter NASA Deep Space Network (DSN) stations. Traveling at the speed of light, a signal from Voyager 1 takes about 17 hours to travel to Earth. After the data are transmitted to JPL and processed by the science teams, Voyager data are made publicly available.
“Voyager has boldly gone where no probe has gone before, marking one of the most significant technological achievements in the annals of the history of science, and adding a new chapter in human scientific dreams and endeavors,” said John Grunsfeld, NASA’s associate administrator for science in Washington. “Perhaps some future deep space explorers will catch up with Voyager, our first interstellar envoy, and reflect on how this intrepid spacecraft helped enable their journey.”
Scientists do not know when Voyager 1 will reach the undisturbed part of interstellar space where there is no influence from our sun. They also are not certain when Voyager 2 is expected to cross into interstellar space, but they believe it is not very far behind.
JPL built and operates the twin Voyager spacecraft. The Voyagers Interstellar Mission is a part of NASA’s Heliophysics System Observatory, sponsored by the Heliophysics Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. NASA’s DSN, managed by JPL, is an international network of antennas that supports interplanetary spacecraft missions and radio and radar astronomy observations for the exploration of the solar system and the universe. The network also supports selected Earth-orbiting missions.
The cost of the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 missions — including launch, mission operations and the spacecraft’s nuclear batteries, which were provided by the Department of Energy — is about $988 million through September.
For a sound file of the oscillations detected by Voyager in interstellar space, animations and other information, visit:
For an image of the radio signal from Voyager 1 on Feb. 21 by the National Radio Astronomy Observatory’s Very Long Baseline Array, which links telescopes from Hawaii to St. Croix, visit:
Protected: Milky Way’s Black Hole Was “Birth Cry” of Radio Astronomy
Dwayne Brown Headquarters, Washington 202-358-1726 [email protected] Jia-Rui C. Cook Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, Calif. 818-354-0850 [email protected]

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Eyes on Voyager. This near real-time 3D data visualization uses actual spacecraft and planet positions to show the location of both Voyager 1 and 2 and many other spacecraft exploring our galactic neighborhood. Voyager 1's position in October 2024.
In August 2012, Voyager 1 made the historic entry into interstellar space, the region between stars, filled with material ejected by the death of nearby stars millions of years ago. Voyager 2 entered interstellar space on Nov. 5, 2018 and scientists hope to learn more about this region.
Voyager 1 has been exploring our solar system since 1977. The probe is now in interstellar space, the region outside the heliopause, or the bubble of energetic particles and magnetic fields from the Sun. Voyager 1 was launched after Voyager 2, but because of a faster route it exited the asteroid belt earlier than its twin, and it overtook Voyager 2 on Dec. 15, 1977.
Voyager 1 is a little under 15.4 billion miles from Earth, according to NASA. This makes it the most distant human-made object ever. For context, Voyager 1 is about 165 times farther away from us ...
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar probes, Voyager 1 and Voyager 2. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable planetary alignment to explore the two gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and potentially also the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune - to fly near them while collecting data for ...
Voyager 1 reached interstellar space in August 2012 and is the most distant human-made object in existence. Launched just shortly after its twin spacecraft, Voyager 2, in 1977, Voyager 1 explored the Jovian and Saturnian systems discovering new moons, active volcanoes and a wealth of data about the outer solar system.
Now over 14.5 billion miles (23.3 billion km) away, Voyager 1 is the farthest artificial object from Earth. But Voyager 2 is arguably more iconic because of its incredible multidecade tour of the ...
Launched in 1977, the twin Voyager probes are NASA’s longest-operating mission and the only spacecraft ever to explore interstellar space. NASA’s twin Voyager probes have become, in some ways, time capsules of their era: They each carry an eight-track tape player for recording data, they have about 3 million times less memory than modern cellphones, and they transmit data about 38,000 ...
NASA. Sep 12, 2013. RELEASE 13-280. NASA’s Voyager 1 spacecraft officially is the first human-made object to venture into interstellar space. The 36-year-old probe is about 12 billion miles (19 billion kilometers) from our sun. New and unexpected data indicate Voyager 1 has been traveling for about one year through plasma, or ionized gas ...
Contact restored. That was the message relieved NASA officials shared after the agency regained full contact with the Voyager 1 space probe, the most distant human-made object in the universe ...