Lead-to-Cash, the cornerstone of your business
An efficient Lead-to-Cash process is a cornerstone of business success, influencing revenue, customer satisfaction, operational effectiveness, and overall competitiveness in the market. Businesses that prioritize and optimize this process can achieve sustained growth and resilience in a dynamic business environment.
The Lead-to-Cash (L2C) process is a comprehensive business workflow that spans from the initial generation of a sales lead to the collection of cash or payment for the goods or services provided. It encompasses various stages of the customer lifecycle and involves multiple departments within an organization.
The Lead to Cash process typically includes the following key areas:
- Lead management
- Product Data management
- Order Management and Procurement
- Account Receivables
- Account payables
- Customer onboarding and customer data management

Why ServiceNow?
ServiceNow can be used to manage most if not all parts of the Lead-to-Cash process. Here are some reasons to use ServiceNow:
- ServiceNow provides a unified platform that can integrate various business processes, including lead management, order fulfilment and customer support. Having a centralized system can streamline communication and data flow across different stages of the Lead-to-Cash process.
- ServiceNow excels at workflow automation. It can automate routine tasks, approvals and notifications, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency. Business logic can be added to automate purchase order creation to vendors and automated fulfilment of orders.
- ServiceNow is cconfigurable, allowing organizations to tailor it to their specific business needs. This adaptability can be advantageous for accommodating variations in the Lead-to-Cash process based on industry, business model, or specific requirements.
- ServiceNow can integrate with various third-party applications and systems, such as CRM tools, billing systems, and marketing platforms. This ensures a smooth flow of data between different stages of the Lead-to-Cash process and avoids data silos.
- ServiceNow’s service catalog and request management capabilities can be leveraged to streamline the ordering and fulfillment stages of the Lead-to-Cash process. This can include creating requests for new services, managing product configurations, approvals and tracking order status.
- ServiceNow provides analytics and reporting tools that can help organizations track key performance indicators (KPIs) related to the Lead-to-Cash process. This data-driven approach enables better decision-making and continuous process improvement.
At Sofigate we have implemented several projects related to different phases of the Lead-to-Cash process. Join us in our upcoming webinar , where we’ll show real-life examples and discuss the implementation of different phases of the Lead-to-Cash process. Depending on the license agreement, customers have different options on how to implement certain requirements, we will explain some of these in our webinar.
Olga Antonova is a Delivery Manager at Sofigate. Olga and her team specialize in helping IT and telecom service providers. Olga has been working with processes and service management tools for the last 15 years.
Related Insights

Diverse Paths, Shared Goals: Laura and Erkki show that different backgrounds create a great culture for learning

Public savings do not come from development cuts – but from investing in development

Managing DORA Compliance with ServiceNow

The Ultimate Guide to Understanding the Lead-to-Cash Cycle
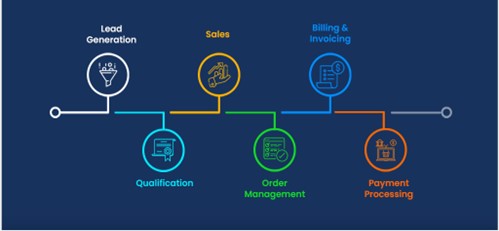
F or every business cash is the lifeblood and needs to generate enough cash from its activities so that it can meet its expenses. A Lead-to-cash cycle is essential for any business since it helps achieve efficient revenue generation by streamlining the entire sale process from start to finish. Grow Asia makes this end-to-end, top-level business cycle more resilient beginning with marketing and ending with revenue collection. This L2C cycle involves several key stages:
Lead Generation :
This is the initial stage where businesses identify and generate potential leads or prospects. Leads can come from various sources such as marketing campaigns, website visitors, social media, trade shows, or referrals.
Lead Generation
Lead Qualification :
Not all leads are equal. In this stage, businesses assess the quality and potential of each lead. This typically involves determining whether the lead has a genuine interest in the product or service and whether they meet the criteria of an ideal customer.
Lead Qualification
Sales Engagement :
Once a lead is qualified, it is handed over to the sales team. Sales representatives engage with the lead to nurture the relationship, provide information about the product or service, address questions and concerns, and ultimately persuade the lead to make a purchase.

Sales Engagement
Quote/Proposal and Negotiation :
In some cases, particularly in B2B (business-to-business) sales, a formal quote or proposal is generated for the lead. This document outlines the terms, pricing, and other details of the sale. Negotiations may occur at this stage as the lead and the sales team work out the specifics.

Closing the Deal :
This is the stage where the lead commits to making a purchase. It involves signing contracts or agreements, making payments, and formalizing the sale.

Closing the Deal
Order Fulfillment :
After the deal is closed, the business must fulfill the order. This could involve delivering a product, providing a service, or making the necessary arrangements based on the nature of the sale.

Order Fulfillment
Invoicing and Payment:
In this stage, the business issues an invoice to the customer, specifying the amount due and payment terms. Once the customer pays, the revenue is captured.

Invoicing and Payment
Customer Relationship Management (CRM):
Maintaining a good relationship with the customer is crucial for future sales and customer retention. This stage involves post-sale support, addressing customer inquiries, and ensuring a positive customer experience.

Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Revenue Recognition :
This is an accounting process where the revenue generated from the sale is recognized on the company’s financial statements. The timing of revenue recognition can vary based on accounting standards and the nature of the transaction.

Revenue Recognition
Analytics and Feedback :
Throughout the lead to cash cycle, data is collected and analyzed to improve the process. This includes tracking conversion rates, customer feedback, and other key performance indicators to identify areas for optimization.

Analytics and Feedback
Lead-to-Cash cycle is a comprehensive business process that encompasses the entire customer acquisition and revenue generation journey within an organization. A well-implemented process can optimize a business’s operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and contribute to the overall growth and profitability of the company.
Send us an email on [email protected] – we can help you work through this process.
Related items

Explore Offshoring 2.0
In today’s dynamic business landscape, companies harness offshoring to unlock global talen
Understanding the Key Components of the Record-to-Report Cycle
In today’s dynamic world, Record to Report is a key part of the financial management and r

Top 10 ways to develop a winning mindset for customer service and collection roles
Developing a winning mindset is essential for excelling in customer service, collections,
Write a Comment (Cancel reply)
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Lead to Cash
What is Lead to Cash?
The L2C process covers all aspects of customer interaction, from the first contact to the final payment.
It captures the entire B2B sales cycle, typically lasting four to seven months , and involves collaboration between numerous departments and personnel. It’s naturally complex, and challenges are embedded in every stage of the journey.
To build smoother, more efficient L2C processes, forward-thinking companies invest in innovative tools like Configure, Price, Quote (CPQ) software.
CPQ supports and enhances each step of L2C, delivering superior customer experiences and tightly aligned operations from sales to manufacturing.
A well-executed L2C strategy, augmented with the right technological solutions like CPQ, can be decisive in winning and retaining customers.
This article explores the L2C process in detail, alongside challenges and opportunities for transformation and improvement.
Introduction to the Lead to Cash (L2C) Process
The L2C process is integral to business operations.
It encompasses the entire journey from the first interaction with a potential customer to finalizing a sale and service delivery.
Here’s an overview of the critical steps:
1. Lead Generation and Qualification
Businesses kick off the L2C journey by identifying and capturing potential customer leads.
This involves diverse strategies like digital marketing, networking events, and leveraging social media platforms to generate a list of potential leads interested in the company's products or services.
Once leads are generated, they undergo a qualification process, considering criteria such as the potential customer's interest level, purchasing power, and compatibility with the product or service.
2. Lead Nurturing
Qualified leads are then nurtured , which means building and maintaining relationships pre-sale.
Nurtured leads have a 23% shorter sales cycle and tend to make larger purchases, so this step is crucial in converting leads into tangible sales opportunities.
Communication strategies like personalized emails, targeted content, and regular follow-ups keep the company's offerings at the forefront of the lead's mind.
3. Sales Quote and Proposal Creation
Here, the focus shifts to crafting persuasive proposals and quotes tailored to each potential customer's specific needs and requirements.
This step is crucial in convincing the leads about the value proposition of the company's offerings.
The more complex products are, the more critical accurate quotes and proposals become. They ensure alignment between customer expectations, the teams involved in bringing those to life, and the final product.
4. Negotiation and Contracting
Negotiation and contracting involve finalizing the terms and conditions of the sale.
This includes pricing agreements, delivery schedules, and other contractual details crucial for closing the deal. Close collaboration between sales and finance teams is vital.
5. Billing and Invoicing
Once a sale is agreed, the process moves to billing and invoicing. This phase ensures invoices are generated promptly and accurately reflect the details of the sale agreement.
Smooth and efficient billing processes are key to delivering a delightful customer experience. Hold-ups or errors are frustrating on the buyer side and can ruin an otherwise frictionless L2C process.
6. Payment Terms
This stage, involving accounts receivable, ensures invoice payment terms are agreed.
Payments are either settled pre- or post-production or delivery or split between stages depending on the business relationship, transaction/order volume, risk, and other factors.
7. Fulfillment and Delivery
After payment terms are agreed, the focus shifts to manufacturing, fulfilling, and delivering the product or service.
This includes all activities related to the preparation, shipping, and execution of services as per the agreement.
8. Customer Service and Support
The final stage, post-sale customer interaction and support, is vital for customer satisfaction and retention. Studies show that 85% of B2B buyers value quality customer service as much as the product's performance.
This after-sales phase cements long-term customer relationships by addressing needs that arise after purchase. It involves providing excellent service, responding to customer queries on time, and handling any feedback or complaints with care.
Challenges in the Lead-to-Cash Process
The L2C process is inherently complex, especially given the length of B2B sales cycles and the average number of stakeholders involved (which is 11, according to Gartner .)
Challenges are embedded within each process, from the initial generation of leads to aftercare support.
Let’s explore the leading L2C challenges companies face in detail.
Inefficiencies in Manual Processes
L2C involves collaboration and communication between numerous departments.
Typically, the sales team handles lead generation and nurturing before deals progress to design and product teams and, eventually, accounting, manufacturing, and after-sales support.
Manual tasks such as data entry, document processing, and manual tracking of sales and customer interactions can severely hamper the L2C pipeline at every juncture, leading to:
- Increased Error Rates : Manual entry and processing increase the risk of errors in customer data, order details, and financial transactions. Error rates are generally around 1% , which mounts up across the entire L2C pipeline.
- Delayed Responses : Manual handling of customer inquiries and order processing can result in slower response times, affecting customer satisfaction.
- Reduced Workflow Effectiveness : The reliance on manual tasks can lead to efficiency-killing bottlenecks.
- Higher Operational Costs : Manual processes require more labor and resources, which increase costs and come directly off a company's bottom line profits.
Data Management and Integration Issues
Effective data management and integration are crucial to building a slick L2C process.
Well-integrated systems furnish businesses with analytics and insights to improve processes. 67% of companies use data integration to support analytics and business intelligence (BI).
However, the majority struggle to manage integration efficiently or use their data effectively, which has negative impacts:
- Inconsistent Customer Data : Disjointed systems can result in erratic and incomplete customer profiles, affecting personalized service and sales strategies.
- Impaired Sales Forecasting : Lack of integrated data hampers accurate sales forecasting, essential for strategic planning and inventory management.
- Inefficient Order Processing : Poor data integration can lead to inefficiencies in order processing, from sales to fulfillment.
Navigating Varied Customer Preferences and Channels
Customer preferences are exceptionally diverse today, the impacts of which are felt throughout the L2C process. For instance, millennial buyers have increased by over 70% in recent years , driving a shift from in-person sales to their preferred online sales channels.
Catering to varied customer preferences across channels requires a balance between personalization and operational efficiency:
- Customization Needs : Addressing specific customer demands for product customization can complicate order management and production.
- Varied Pricing Structures : Offering flexible pricing options and catering to different customer segments while maintaining profitability introduces complexity.
- Cultural and Regional Differences : Navigating cultural and regional differences in customer behavior, compliance, and expectations presents communication challenges, particularly at the sales end.
Communication Breakdown in Custom or Complex Orders
Effective communication is fundamental to managing custom or complex orders within the L2C process.
Demand for custom orders has soared recently, with B2B buyers expecting in-depth product personalization. This increases product complexity, which in turn increases L2C complexity pre- and post-order.
Custom orders need to be effectively communicated between teams. Miscommunication, in particular, becomes a key issue that can slow the cycle down and lead to:
- Production Errors : Lack of clear communication can result in production errors, impacting the quality of the final product.
- Order Delays : Misunderstandings in order specifications can lead to delays in order fulfillment.
- Increased Costs : Inaccurate or incomplete communication can cause rework and waste, increasing production costs.
- Customer Dissatisfaction : Failures in accurately delivering custom orders can result in customer dissatisfaction and potential loss of future business.
Compliance and Security Concerns
The L2C process sends, receives, and processes sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII) data at almost every step. Failing to protect that data can lead to non-compliance and an increased risk of data breaches.
The vast majority of businesses state they wouldn’t purchase from a company they don’t trust with their data, so demonstrating trust and security credentials throughout the L2C process is paramount. This involves:
- Data Security : Implementing and continuously updating robust security measures is crucial to protect sensitive customer and transaction data from cyber threats.
- Regulatory Compliance : Businesses must adhere to a range of local and international regulations related to data privacy (like CCPA or GDPR), financial reporting, and industry-specific standards to ensure compliance.
- Audit Trails : Maintaining transparent and accurate records for auditing is vital. This involves using reliable systems that can track and document each step of the L2C process accurately.
- Secure Communication : Ensuring secure and confidential communication of customer details between personnel and teams is a major challenge without safe transmission protocols.
How CPQ Systems Address L2C Challenges
Configure, Price, Quote (CPQ) systems streamline the complex process of gathering customized orders from sales and shepherding them through manufacturing to fulfillment.
These tools simplify the intricate details required to produce and deliver products to each client's specifications by assisting in:
- Configuration : Helping sales teams or customers select suitable product options and features based on specific requirements, ensuring valid and feasible configurations.
- Pricing : Using an automated no-code engine to calculate prices, factoring in customizations, quantities, discounts, and special customer agreements.
- Quoting : Producing detailed and precise sales quotes with comprehensive information, including product descriptions, sales drawings, pricing, delivery schedules, and terms.
CPQ’s features combine to support the end-to-end L2C process, from collecting and quoting orders to manufacturing and after-sale data integration.
Let’s explore these benefits in detail and how they combat the challenges of L2C processes.
Enhancing Pricing and Quotation Accuracy
CPQ technology improves accuracy across pricing and quotations, some of the first processes handled in the L2C cycle.
Here, CPQ effectively manages complex pricing models, ensuring every quotation is accurate and consistent. This ensures alignment across the remainder of the cycle through to production.
- Handling Complex Pricing : CPQ systems adeptly navigate various pricing models, including bulk discounts and promotional offers.
- Consistent Quotation Accuracy : Ensuring consistent accuracy across all quotes, CPQ technology reduces errors and protects credibility.
Personalizing the Customer Experience
Robust CPQ systems elevate the customer experience by offering interactive and personalized sales features and guided selling. These tools allow customers to configure products visually in 3D and augmented reality alongside a sales rep or independently online.
Sales reps benefit from a visual product configured with in-built guided sales scripts, helping them serve the customer and meet the demand for complex, custom products with thousands of options.
Customers benefit from the ability to self-serve. They also gain a crystal clear visual understanding of their final product before committing to a purchase. This transparency reduces purchase anxiety and boosts conversion rates by 40% (the average for Epicor customers.)
Integrating for Efficient Data Management
By integrating with CRM, ERP, CAD, and other back-office systems, CPQ software slots right into modern enterprise workflows, supporting efficient data management across the L2C cycle. It bridges the communication gaps between sales, engineering, manufacturing, finance, and operations, building a seamless data flow.
- Bridging Departmental Gaps : CPQ integration connects various teams, ensuring consistent communication and collaboration.
- Real-Time Data Sharing : It facilitates real-time data exchange across departments, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making.
Reducing Manual Workloads
Automation is central to CPQ, streamlining processes from when a product is ordered to when it enters production.
For example, CPQ solutions like Epicor CPQ auto-create CAD drawings, bills of materials (BOMs), and other manufacturing information to ensure engineering and shop floor teams are readily equipped with the data they need to begin production.
Tight alignment between what the customer orders and the end product enables a more cohesive L2C cycle, as everyone has access to the same single source of truth they need to fulfill their tasks.
Additionally, automation across the L2C processes minimizes human errors, streamlines communication, and frees up valuable labor hours for strategic tasks.
- Minimizing Human Errors : By automating routine tasks, CPQ systems reduce the likelihood of costly mistakes.
- Freeing Up Staff for Strategic Tasks : Reducing manual workload allows staff to focus on more value-added activities, improving productivity and innovation.
Ensuring Compliance and Security
CPQ platforms are instrumental in maintaining compliance with industry regulations and data security standards, important commitments that many businesses grapple with.
By adopting cutting-edge CPQ with enterprise-grade security, businesses can build and retain customer trust in the sales process.
- Compliance with Industry Regulations : CPQ systems like Epicor CPQ are hosted in the cloud with best-in-class security, ensuring sensitive data is kept secure across the L2C cycle.
- Data Centralization : CPQ centralizes data into a single source of truth, protecting it as it passes through the L2C process from department to department. This minimizes data transfer via email, spreadsheets, or paperwork–which are potentially insecure.
Reporting and Analysis
In addition to integrating with CRM, ERP, and other back-office systems, CPQ produces data and supports analytics in its own right.
It arms businesses with actionable insights into customer behavior and product selections, driving continuous improvement. It also supports process mining initiatives, where repeated business processes are identified for optimization and automation.
- Reporting and Analysis: CPQ systems capture data that can feed into data analysis and business intelligence (BI) strategies. It provides insights into customer trends, operational bottlenecks, and efficiency opportunities.
- Predictive Analytics : By leveraging historical data, CPQ systems can offer predictive analytics, helping in strategic planning, inventory management, and targeted marketing efforts.
In Conclusion
The L2C process is more than just a series of operational steps. It's the heartbeat of customer engagement and business growth. As companies meet demand for complex, customizable products, the L2C cycle itself has evolved to adapt to new business processes.
Managing complex L2C pipelines, while challenging, offers an opportunity for businesses to go above and beyond in delivering impactful customer experiences. The key lies in optimizing the L2C process, leveraging advanced tools such as CPQ software.
These tools are not just solutions but transformative agents that redefine customer engagement and operational efficiency. A streamlined, efficient L2C process, equipped with tools like Epicor CPQ , is a powerful driver for customer satisfaction, loyalty, and repeat business.
What is the Lead to Cash (L2C) process, and how does it contribute to revenue growth?
The lead-to-cash process encompasses all the stages, from initial customer contact to final payment. It's integral for driving revenue growth as it streamlines the sales, billing, and fulfillment process, ensuring efficient and effective revenue generation.
How does revenue recognition work within the L2C process, especially for professional services?
In a business that provides professional services, like consulting or legal work, it's important to record the money earned (revenue) at the time the service is actually delivered. This helps match the money made with the time period when the work was performed, which is important for preparing accurate financial reports and following rules and regulations.
What are the common causes of revenue leakage in the L2C process, and how can they be addressed?
Revenue leakage often occurs due to inefficient processes, errors in billing, or missed sales opportunities. It can be addressed by adopting robust systems like Epicor CPQ , SAP Sales Cloud, or Salesforce CPQ that streamline the sales order and billing processes and provide better visibility and control over the entire L2C cycle.
How does integrating customer success strategies into the L2C process enhance customer experience and loyalty?
Integrating customer success strategies into the L2C process focuses a company’s efforts where they matter most: on long-term customer satisfaction.
This approach ensures customers receive continuous value from their purchases, fostering loyalty and leading to repeat business and referrals.
Can the L2C process benefit from automation, and if so, how?
Yes, automating the L2C process can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy, from lead generation to final invoicing.
Automation tools can help manage customer data, track sales orders, generate accurate quotes and invoices, and ensure timely follow-ups, all of which contribute to a smoother and more reliable process.
What role do CRM systems like SAP Customer Experience and Salesforce Sales Cloud play in the L2C process?
CRM systems like SAP Customer Experience, Salesforce Sales Cloud, and Epicor CPQ (which has built-in CRM capabilities) are critical in managing customer interactions and data throughout the L2C process.
They provide valuable insights into customer needs and behaviors, facilitate effective communication, and help track the progress of sales opportunities, all of which are key to optimizing the L2C cycle.
Free downloads

Featured Resource

Complimentary Nucleus Report

The Epicor CPQ Top 10

Choose another CPQ term
- 3D Configuration
- B2B eCommerce
- B2B Manufacturing
- CAD Automation
- Complex Product Configurator
- CPQ Implementation
- CPQ Product Rules
- CPQ Software
- Design Automation
- Digital Transformation
- Dynamic Pricing
- Engineer to Order
- Industry 4.0 and the 4th Industrial Revolution
- Make-to-Order (MTO) Manufacturing
- Manufacturing Automation
- Omnichannel Retailing
- Order to Cash
- Product Configuration
- Product Visualization and 3D Product Visualization
- Proposal Software
- Quote to Cash
- Sales Automation Software
- Salesforce CPQ
- Visual Configuration
Mapping the Service Business Processes to the Lead-to-Cash Process
After completing this lesson, you will be able to summarize the lead-to-cash – service process based on SAP Best Practices
Integrated Service Solution
The Bike Company implementation project is currently in the Realization phase, in which the end-to-end processes are tested by the project team.
You are already familiar with the detailed structures of the different areas, such as financial accounting, management accounting, human resources, purchasing, production, and sales. You will find out now how the Bike Company benefits from using the integrated service solution.
The selected scope items for all areas were assigned to the business processes of the Bike Company by Ivan. This enables the project team to understand which summarized scope items are used to represent a core process within the Bike Company.
Based on best practice scope items, Ivan has created a summarized business process for the Bike Company’s service process. The following is a high-level overview of the steps in the service process that Ivan created.
Please select the business process steps below or select Next to learn more.
Log in to track your progress & complete quizzes
What is Lead-to-Cash: Understanding the End-to-End Sales Process
- Under Business
- Be the 1st to leave a comment

In the business world, a smooth flow of cash is the lifeblood of any organization. But how do you convert a potential customer’s interest into that sweet, sweet revenue?
That’s where the concept of Lead-to-Cash (L2C) comes in.
What is Lead-to-Cash?
Lead to cash is a comprehensive end-to-end business process that encompasses the entire sales cycle, from initial customer interest to the final receipt of payment. It represents the journey of a lead (potential customer) as it moves through the stages of the sales funnel to become a cash-paying customer.
This process is critical for businesses as it directly impacts revenue generation and customer relationship management.
Understanding this process is critical for anyone involved in an organization. It ensures that your sales process is efficient and that all your systems work together seamlessly.
- Lead to cash
- Lead-to-cash cycle
- Lead-to-cash process
The lead-to-cash method not only enhances the internal workflow of a company but also maintains focus on the customer’s experience throughout their interaction with your business.

This process is deeply ingrained in the operations of any successful business and impacts numerous stakeholders across multiple departments. Sales, marketing, finance, and customer service teams must coordinate their efforts to navigate customers smoothly from point A to point B in your sales process.
Embracing the lead-to-cash framework can equip your organization with the agility needed to convert leads into revenue more effectively by using data-driven strategies and integrated systems.
Understanding the Lead to Cash Process (Workflow)
The lead to cash process typically includes the following stages:
1) lead generation
Lead generation marks the initiation of the lead-to-cash process. It’s about attracting potential customers to your product or service. Effective lead generation is pivotal, as it fills the sales funnel with prospects.
Here are key aspects:
- Channels and Strategies : Utilize a mix of digital marketing strategies including SEO, content marketing, social media advertising, and email campaigns to capture a wide audience.
- Content is King : Offer valuable and relevant content to solve problems or address the needs of your target audience, which can significantly increase lead generation rates.
- Landing Pages and Calls-to-Action : Design landing pages specifically for lead capture, ensuring they contain clear and compelling calls-to-action (CTAs) to encourage sign-ups or inquiries.
- Lead Magnets : Provide lead magnets like ebooks, webinars, or free trials, which offer value in exchange for contact information.
- Measurement and Optimization : Constantly analyze the performance of your lead generation efforts and optimize them for better outcomes.
2) Lead management
Once leads are generated, they enter the lead management stage. This phase is crucial for qualifying leads and preparing them for the sales process.
- Lead Scoring : Implement a lead scoring system to prioritize leads based on their engagement level and likelihood to purchase.
- Lead Nurturing : Use automated email marketing campaigns to nurture leads by providing further information, value, and engagement opportunities.
- CRM Integration : Ensure all lead data is captured in a CRM system for effective tracking and management.
- Sales and Marketing Alignment : Maintain constant communication between sales and marketing teams to ensure leads are appropriately managed and handed off.
- Feedback Loop : Establish a feedback loop to refine the lead management process based on the sales team’s experiences and conversion rates.
3) Quote to order
The next phase involves transforming interested leads into actual sales opportunities. This is where salesforce effectiveness really comes into play. Quotes are carefully crafted with detailed pricing , discounts , and proposals .
Tools like Salesforce CPQ (Configure, Price, Quote) streamline this process with automation , making creating personalized quotes efficient.
- Customized Quoting : Generate personalized quotes based on the specific needs and preferences of the lead, using CRM data to tailor the offer.
- Approval Processes : Set up an efficient approval process for quotes to ensure they meet pricing and discount policies.
- Follow-up Strategies : Implement systematic follow-ups on quotes to address concerns and adjust offers as necessary.
- Automation Tools : Use automation tools to streamline the quote creation process, reducing errors and saving time.
- Conversion Tracking : Monitor the conversion rate from quotes to orders to identify areas for improvement in the sales process.
4) Order management
Order Management involves the processing and fulfillment of orders. This step is key to ensuring customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
- Order Processing : Implement an automated system for order entry, validation, and processing to minimize delays.
- Inventory Management : Keep real-time track of inventory levels to ensure product availability and timely order fulfillment.
- Delivery and Fulfillment : Coordinate with logistics to ensure timely and accurate product delivery. Provide customers with tracking information.
- Change Management : Allow for order modifications while maintaining efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Issue Resolution : Establish a clear process for handling order issues, ensuring quick resolution to maintain customer trust.
5) Billing and invoicing
The Billing and Invoicing step is where the company’s efforts are translated into revenue. It’s crucial for cash flow and customer satisfaction.
- Automated Invoicing : Utilize software to automate the creation and distribution of invoices, ensuring accuracy and timeliness.
- Flexible Payment Options : Offer multiple payment methods to accommodate customer preferences, improving the payment experience.
- Compliance and Accuracy : Ensure invoices comply with local tax laws and regulations. Double-check for accuracy to avoid disputes.
- Dispute Management : Implement a process for efficiently resolving billing disputes to maintain customer satisfaction.
- Follow-up and Collections : Establish polite but persistent follow-up procedures for late payments to maintain positive cash flow.
6) Payment management
In the Payment Management phase, businesses oversee the receipt and processing of payments from customers, crucial for maintaining healthy cash flow.
- Secure Payment Processing : Employ secure, reliable payment gateways to protect customer information and ensure transaction safety.
- Reconciliation : Regularly reconcile payments received with invoices issued to ensure accuracy in accounts receivable.
- Late Payment Strategies : Implement strategies for managing late payments, including reminders, fees, and payment plans.
- Customer Communication : Maintain clear communication with customers regarding payment statuses and issues to foster trust and transparency.
- Financial Reporting : Integrate payment data into financial reports for accurate revenue tracking and forecasting.
7) Revenue recognition
Revenue Recognition is the final step, focusing on accurately recording revenue in the financial statements. It’s crucial for financial reporting and compliance.
- Compliance with Standards : Ensure that revenue recognition practices comply with applicable accounting standards (e.g., GAAP, IFRS).
- Timing and Criteria : Recognize revenue when the product is delivered or the service is performed, and all criteria for revenue recognition are met.
- Contract Management : Review contracts to determine the appropriate revenue recognition method based on delivery and performance obligations.
- Automation for Accuracy : Use automated systems to track and recognize revenue, reducing manual errors and ensuring consistency.
- Audit and Review : Regularly audit revenue recognition practices to ensure compliance and identify areas for improvement.
By carefully managing each of these stages, businesses can optimize their lead-to-cash process, enhancing efficiency, customer satisfaction, and revenue growth.
8) Post-sale service and analysis
After the sale, your focus should shift to providing excellent customer service to ensure customer satisfaction and encourage repeat business. Also, data analysis and reporting are vital to evaluate the process, identify bottlenecks or data silos , and improve the overall efficiency of the Lead to Cash cycle.
What is the difference between order-to-cash and lead to cash?
The difference between order-to-cash (OTC) and lead-to-cash (LTC) lies in the scope of the processes they cover. Order-to-cash is a subset of the broader lead-to-cash process.
Order-to-Cash (OTC) focuses on the processes that take place after a customer places an order. It includes the steps involved in order management, fulfillment, shipping, invoicing, payment collection, and accounts receivable. Essentially, OTC encompasses the backend processes that occur from the moment an order is received until the payment is collected and recorded.
It is a critical component of a company’s revenue cycle management and is concerned with executing and managing the order effectively and efficiently.
Lead-to-Cash (LTC) , on the other hand, is a more comprehensive end-to-end process that begins much earlier in the sales cycle. It starts with the initial customer engagement (lead generation) and includes every step through to the final receipt of payment. LTC covers lead generation, lead qualification, lead nurturing, opportunity management, quoting, order management (which includes the OTC process), invoicing, payment processing, and customer service.
It also involves strategies for customer retention and repeat business.
So while order-to-cash is specifically about fulfilling and monetizing orders, lead-to-cash is about the entire customer acquisition and retention cycle, including the order-to-cash process within it.
Enhancing Lead to Cash Through Technology
By leveraging technology, you can streamline your lead-to-cash process. This improves the collaboration between sales and finance, enhances efficiency with automation, utilizes analytics for better forecasting, and maintains a customer-centric approach for superior service.
Integrating Sales and Finance
Integrating your sales and finance operations is critical. An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system can act as a bridge, ensuring that the moment a sales opportunity is identified, both your sales force and your finance team are aligned. This real-time connection helps avoid discrepancies and fosters more accurate quotes and financial forecasting.
Automation for Efficiency and Accuracy
Automation plays a vital role in reducing manual processes and improving accuracy . From generating quotes to order processing, automation ensures that every step is conducted with precision. By implementing a robust lead-to-cash solution , repetitive tasks are minimized, and your team can focus on more strategic activities.
Analytics and Forecasting for Strategic Decisions
Employing analytics and forecasting tools within your CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system can reveal important trends and enable data-driven strategic decisions. You’ll understand customer behaviors and preferences, which is essential for customer acquisition , loyalty , and tailoring customer experiences .
Customer-Centric Approach
A customer-centric strategy prioritizes customer experiences at each step of the lead-to-cash process. Utilize marketing automation to deliver tailored messages and offers that resonate with your customer base. This approach not only enhances loyalty but also optimizes the efficiency of your customer acquisition strategies.
Lead to Cash FAQs
How does the lead-to-cash process enhance sales performance.
The lead-to-cash process enhances sales performance by creating a streamlined pathway from initial customer inquiry to final payment, improving efficiency and providing a better customer experience.
What are the key stages of the lead-to-cash cycle in a business?
Key stages of the lead-to-cash cycle include lead generation, customer acquisition, sales order processing, delivery of goods or services, and payment collection, ensuring that each step is optimized for faster conversion and revenue recognition.
What benefits do telecom companies experience from implementing lead-to-cash systems?
Telecom companies experience significant benefits from implementing lead to cash systems, including improved customer satisfaction, reduced time-to-market for services, and streamlined billing processes.
How do Salesforce and SAP platforms facilitate the lead to cash process?
Platforms like Salesforce and SAP facilitate the lead to cash process by offering integrated solutions that manage customer interactions and transactions, thus improving data accuracy and operational efficiency.
Can you detail the transformative impact of lead to cash on customer relationship management?
Lead to cash can transform customer relationship management. It enables personalized customer engagements and delivers insights that inform targeted and effective sales strategies.

About Moneyspace
Main topics:, latest articles.
Forex Trading in Kenya (Quick Guide)
How to Start Trading in Kenya: A Beginner’s Guide
The New KFC Menu Prices (Updated for 2024

- Oracle Billing and Revenue Management
- Oracle Digital Experience
- Unified Orchestration and Assurance(OSS)
- Oracle Cloud Applications
- Multi cloud deployment, orchestration and Management Services
- DevSecOps, Observability and Monitoring
- Application Management and Support
- Generative AI
- Smart Cities
- Adptx TM Cloud
- Adptx TM Suite
- Adptx TM Comm
- Adptx TM Utilities
- Financial Services
- Communications, Media & Technology
- Energy & Utilities
- Public Services
- Brand Story
- Vision & Mission
- Connecting to Roots - CSR Initiatives
- Digital Transformation
- Oracle Breakthroughs
- Case Studies
- Whitepapers

Unlocking Success: The Contract to Cash Journey in the Lead to Cash Cycle

In today’s dynamic business landscape, optimizing operations and maximizing efficiency are critical for sustainable success. At the heart of the sales cycle lies the contract to cash (C2C) process, a pivotal driver in converting leads into revenue. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the contract to cash process, highlighting its definition, key features, and its remarkable ability to resolve common pain points faced by businesses. By fully embracing C2C, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction, expedite revenue generation, and achieve optimal operational effectiveness.
Defining the Contract to Cash Journey:
Contract to cash encompasses a seamless end-to-end business process that guides organizations from initial sales agreements to the realization of revenue. It is a vital component of the lead to cash (L2C) cycle, representing the transformation from signed contracts to cash collection. This comprehensive process involves managing contract terms, fulfilling orders, generating accurate invoices, recognizing revenue, and efficiently collecting payments. By aligning sales, finance, and operations, the contract to cash process ensures a smooth transition from customer acquisition to revenue realization.
Key Features Empowering Contract to Cash:
1. Streamlined Contract Management:
Effective contract management sets the foundation for C2C success. By automating contract creation and approval workflows, businesses can minimize errors and expedite the contract negotiation process, enhancing efficiency and reducing bottlenecks.
2. Efficient Order Fulfillment:
Once the contract is in place, the order fulfillment phase begins. This critical step involves coordinating product delivery or service provision while ensuring adherence to contractual obligations. Streamlining this process reduces delays, boosts customer satisfaction, and prevents revenue leakage.
3. Accurate Invoicing and Revenue Recognition:
Timely and precise invoicing is paramount for revenue recognition. C2C systems automate invoice generation and delivery, guaranteeing accuracy and mitigating the risk of errors. Proper revenue recognition ensures financial transparency and compliance with accounting standards.
4. Optimal Payment Collection:
The final stage of the C2C process revolves around collecting payments promptly. Organizations leverage automated payment methods, such as online portals or electronic funds transfer (EFT), to accelerate cash flow and reduce payment delays. Efficient payment collection minimizes bad debt risks and optimizes working capital management.
Resolving Common Pain Points with Contract to Cash:
The contract to cash process effectively resolves several prevalent pain points encountered by businesses:
- Streamlining Manual and Disconnected Processes : Traditional manual processes are prone to errors, delays, and communication breakdowns. C2C streamlines workflows by integrating sales, finance, and operations, fostering collaboration, eliminating redundancy, and enhancing overall process efficiency.
- Mitigating Revenue Leakage: Incomplete or inaccurate contracts, delays in order fulfillment, and invoicing errors can lead to revenue leakage. The comprehensive nature of C2C ensures end-to-end visibility and control over the revenue generation process, minimizing revenue leakage and maximizing profitability.
- Optimizing Cash Flow: Sluggish payment collection negatively impacts cash flow, hindering business growth and financial stability. Through C2C implementation, organizations can automate payment collection processes, facilitating faster and more efficient cash flow. This optimization is vital for sustaining operations, investing in growth initiatives, and managing working capital effectively.
- Ensuring Compliance and Audit Readiness: Inadequate contract management and revenue recognition practices expose businesses to compliance and audit risks. By implementing a robust C2C process, organizations can ensure adherence to regulatory requirements, minimize audit exposure, and maintain a clean audit trail.
Conclusion:
In today’s competitive business landscape, unlocking the full potential of the lead to cash cycle is vital. The contract to cash process serves as a powerful catalyst, enabling organizations to streamline operations, optimize revenue realization, and deliver enhanced customer satisfaction. By embracing C2C, businesses can achieve operational excellence, foster sustainable growth, and secure a distinct competitive advantage.
Get in touch with us to know more.
Facebook | Linkedin | Twitter | Instagram

The Rising Tide of Household Debt and the Importance of Credit History
In recent times, household debt has reached alarming levels, with a total of $17.06 trillion in Q2 2023, as reported by the New York Federal Reserve. One significant factor contributing to this surge is the increase in credit card balances, which have hit a record high of $1.03 trillion. While mortgage balances have remained stable … Continue reading “The Rising Tide of Household Debt and the Importance of Credit History”

Achieving Efficiency and Growth Potential through Standardization in the Quote-to-Cash Process
In order to fully realize the potential of a B2B subscription business, it is essential to implement standardization within the Quote-to-Cash (QTC) process. By adopting standardization practices, businesses can unlock greater efficiency and drive sustainable growth. In this article, we will explore the various strategies that can be employed to achieve this goal. 1. Streamlined … Continue reading “Achieving Efficiency and Growth Potential through Standardization in the Quote-to-Cash Process”

Achieving Quote to Cash Excellence for B2B Subscription Businesses
In today’s dynamic business landscape, B2B subscription businesses face unique challenges in driving growth and ensuring customer satisfaction. One critical aspect that plays a pivotal role in their success is the quote to cash (QTC) process. QTC encompasses the entire customer journey, from generating a quote to receiving payment, and it can significantly impact a … Continue reading “Achieving Quote to Cash Excellence for B2B Subscription Businesses”

Aarav Solutions announces Bhavin Patel as new Chief Operating Officer
Exciting news at Aarav Solutions! We’re thrilled to announce Bhavin Patel as our new Chief Operating Officer (COO). Bhavin’s promotion is a testament to his exceptional leadership, strategic thinking, and industry expertise. As COO, he’ll lead operational initiatives, driving growth, customer success, and fostering a high-performing team. Raj Darji, our CEO, highlighted Bhavin’s … Continue reading “Aarav Solutions announces Bhavin Patel as new Chief Operating Officer”

Application Readiness Assessment – Paving the Path to Seamless Cloud Migration
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the cloud emerges as a pivotal catalyst for successful transformation. Yet, the journey to cloud migration is far from a mere lift-and-shift affair. In this article, we embark on a comprehensive exploration of the essential factors that demand consideration before migrating your applications to the cloud, ensuring a … Continue reading “Application Readiness Assessment – Paving the Path to Seamless Cloud Migration”

What is Regression Testing and Its Types?
In the dynamic landscape of software development, change is constant. Applications are frequently modified to introduce new features, address bugs, or improve performance. However, these changes can inadvertently disrupt existing functionality, leading to broken features and poor performance. This is where the importance of regression testing comes into play. In this article, we’ll delve into … Continue reading “What is Regression Testing and Its Types?”

Join our mailing list to receive monthly updates on the latest insights on emerging technology and critical issues that global businesses are facing.
Welcome Aboard! Thank You for subscribing to our newsletter.
email has been subscribed to
Thank you for your interest!
Your digital treasure is on its way to your inbox - keep an eye out for an email from Aarav Solutions. Happy exploring!
Your resource is on the way, please check your inbox.
Your digital treasure is on its way to your inbox – keep an eye out for an email from Aarav Solutions. Happy exploring!

Lead to cash / Order to cash
We deliver end-to-end customer experiences that build sales.
- How we can help you
- Experiences with clients
What’s on our mind
What our clients say, meet the experts.
At the core of every business are the set of end-to-end steps a customer goes through when purchasing, paying for and receiving a product. Lead-to-cash (L2C) or Order-to-cash (O2C) refers to the processes, technology and capabilities an organisation utilises to enable that customer journey. At Clarasys, we understand how our clients can optimise their lead-to-cash processes to create excellent customer experiences and maximise revenue.
We work with you to innovate and transform your L2C / O2C journey – from the initial strategy, right through to implementation. We track your progress, improve employee experience and help you deliver go-to-market solutions. We do this by:
- Analysing your existing end-to-end journey
- Understanding your pain points on cost, revenue or CX
- Identifying opportunities to improve based on our knowledge of what works
If you're thinking about SAP S/4HANA and its role in L2C / O2C, read more about our services here.
Lead-to-cash / Order-to-cash helps to enhance customer experiences, and achieve better business performance.
At Clarasys, our role is to diagnose the symptoms of L2C / O2C issues, identify root causes and define a path to sustained improvement. We use the Clarasys Agile Method (CAM), taking the principles of Agile project management and applying them across the entire organisation.
A CAM-centred approach allows us to work with you to identify the pain points that matter, prioritise customer scenarios and create a roadmap for future change.
GROW & BUILD RESILIENCE WITH SUBSCRIPTION PRODUCTS
Is your business making the move to a subscription model?
Experiences with clients.

Taking a strategic pause: Why you should prioritise a SAP S/4HANA upgrade over other business initiatives
The relentless pursuit of growth and innovation can put pressure on businesses to rush forward, chasing the latest technological advancements. But, as you stand on the brink of introducing SAP...

SAP S/4HANA: What's the big deal? A closer look at its role in ERP & order to cash
In the dynamic, fast-paced world of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), SAP S/4HANA has emerged as a revolutionary force that is reshaping how businesses operate. This advanced ERP solution is...
TESTIMONIALS
In a very short period of time, and really efficiently with a really low level of intrusion on the daily working of the team, Clarasys were able to deliver a project in exactly the form that they said it would be delivered…they delivered a finished product exactly as promised.
We had a really good chemistry with the Clarasys guys. They came in, no airs and graces. They talked to the people who really mattered at the front line which you don’t necessarily get, I find, when talking to other consultants.
Swinton Insurance
Anthony mclaughlin.
Ben has over 11 years of cross-industry consulting experience having joined Clarasys from Accenture in 2015. Ben has a broad range of project and CRM experience across the lifecycle including project/delivery management, business analysis and implementation. He is comfortable managing onshore and offshore teams through complex releases with strong stakeholder management skills and is able to translate functional and technical issues into a clear direction. Ben applies agile principles and innovation/expertise to projects. Ben spends lots of his time away from work participating in and watching an array of sports.
Matt Brooks
Matt is an experienced business consultant with expertise in the implementation and improvement of CRM and subscription billing technologies and processes. His specialisms include supporting clients in the adoption of subscription business models and supporting technologies, with a focus on improving their customer experience. Most recently, he has worked on the agile delivery of a subscription billing platform for a global education publishing and assessment company, who were looking to transition their legacy business model to a subscription-based offering.
Richard Hibbert
Business leader that excels at discovering ways to improve CX and save cost. Works with C-suite stakeholders to uncover options for transformation, evaluate trade-offs and deliver against strategy. Over 15 years experience at consulting firms and in industry - so able to offer “real world” experience as well as a consultative approach to change. Focus and specialisms: customer-facing processes, including sales and service; operational discovery; data analysis and visualisation, contact centres; customer experience; cost transformation; Information services & media.
Find out how we can make your business [ thrive ]
Stay up to date with notifications from The Independent
Notifications can be managed in browser preferences.
UK Edition Change
- UK Politics
- News Videos
- Paris 2024 Olympics
- Rugby Union
- Sport Videos
- John Rentoul
- Mary Dejevsky
- Andrew Grice
- Sean O’Grady
- Photography
- Theatre & Dance
- Culture Videos
- Fitness & Wellbeing
- Food & Drink
- Health & Families
- Royal Family
- Electric Vehicles
- Car Insurance Deals
- Lifestyle Videos
- Hotel Reviews
- News & Advice
- Simon Calder
- Australia & New Zealand
- South America
- C. America & Caribbean
- Middle East
- Politics Explained
- News Analysis
- Today’s Edition
- Home & Garden
- Broadband deals
- Fashion & Beauty
- Travel & Outdoors
- Sports & Fitness
- Climate 100
- Sustainable Living
- Climate Videos
- Solar Panels
- Behind The Headlines
- On The Ground
- Decomplicated
- You Ask The Questions
- Binge Watch
- Travel Smart
- Watch on your TV
- Crosswords & Puzzles
- Most Commented
- Newsletters
- Ask Me Anything
- Virtual Events
- Wine Offers
- Betting Sites
Thank you for registering
Please refresh the page or navigate to another page on the site to be automatically logged in Please refresh your browser to be logged in
From leads to cash: the crucial business process you need to streamline now
The articles on these pages are produced by business reporter, which takes sole responsibility for the contents.

Article bookmarked
Find your bookmarks in your Independent Premium section, under my profile

Enigen is a Business Reporter client.
“Outperformers achieve higher growth by carefully considering the sales journey and balancing rigourous process discipline with the flexibility to meet individual customer needs.” – McKinsey & Company
According to McKinsey, “Outperformers” focus on optimising their Lead-to-Cash (L2C) process by implementing tools and strategies that improve efficiency, customer satisfaction, and connected data.
In recent years, there has been a growing trend among businesses to optimise their L2C process. This is largely driven by the increasing demand for faster, more efficient sales processes that can deliver better customer experiences and improve revenue growth.
When it comes to L2C, the adoption of digital technologies is key. By investing in the right technologies, businesses can streamline their sales processes, improve customer engagement, and automate the manual tasks involved in lead generation and sales. Too often overlooked is the integration of the sales and finance functions. By aligning these two areas of the business, companies can achieve greater visibility into their sales performance, improve cash flow, and reduce the risk of errors and disputes.
To remain competitive in today’s fast-paced and digitally driven marketplace, businesses must adopt and innovate with modern technology supporting the whole L2C process, from start to finish. Businesses need a solution that is designed to be flexible and scalable so that connecting departments and applications do not become convoluted as the enterprise grows. As well as this, clients need to be afforded the power to orchestrate complex orders and collect the cash at the right time – empowering the customer while driving improved efficiency, accuracy, and process automation across the lifecycle of the order.
Digital consultancy, Enigen has been working in Business Transformation with Oracle technology for over 13 years, partnering with some of the world’s most customer-centric businesses to give them the technology they need to deliver and exceed expectations.
Enigen has seen first-hand the challenges businesses have with retaining transparency and consistency and that without effective integration across departments, these businesses risk incurring significant costs. Alex Love, Managing Director of Enigen, has mentioned: “There is a real tangle of on and off systems working in this area that costs businesses huge sums of money in efficiency and human error. Getting it synchronised, automated, and data-driven helps improve those challenges and makes you more competitive and faster to react to client needs which drives a better customer experience”.
Enigen has designed a comprehensive single-platform solution built entirely on Oracle that encompasses the full spectrum of Lead Acquisition, Opportunity Management, Quote Production, Order Management, and Finance.
By leveraging components of Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications Suite, Enigen offers a solution that is reliable, efficient, and easy to manage.
Siobhan Wilson, senior vice president applications, Oracle EMEA and UK Country Leader, said “Enigen’s approach to addressing Lead-to-Cash is an excellent example of how Oracle Fusion Cloud Applications can increase productivity, improve controls, gain better insights and reduce costs. By leveraging the power of Oracle Cloud, Enigen can offer a solution to our joint customers that is both robust and scalable, providing businesses with the flexibility they need to adapt and grow in a rapidly changing market".
By carefully considering the sales journey and balancing rigorous process discipline with the flexibility to meet individual customer needs, businesses can achieve higher growth and outperform their competitors.
To see more on Enigen’s lead-to-cash solution in action, check out the video: To begin your journey, get in contact with Enigen at www.enigen.co.uk or email Aja at [email protected] .
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.
New to The Independent?
Or if you would prefer:
Hi {{indy.fullName}}
- My Independent Premium
- Account details
- Help centre
Revenue Hub
Accelerate revenue execution
CPQ (Configure Price Quote)
Automate quotes & subscriptions
CLM (Contract Lifecycle Management)
Streamline contract signings
Manage revenue lifecycle
Subscriptions
Unlock recurring revenue
Expert Implementation & Success
Top integrations, top features.
Revenue Operations Events
Revenue Operations Jobs
Revenue Operations Podcast
Revenue Operations Swag
Revenue Operations Terms
Trending Topics
- Infographics
- Customer Portal
- Pricing & Plans
- Feature Comparison
- Request a Demo
- Request a demo

Lead-to-Order (L2O)

Table of Contents
What is lead-to-order .
Lead-to-Order (L2O) is an end-to-end approach to managing the customer lifecycle. It integrates Sales, Order Management, and Product Delivery for a seamless customer experience and efficient sales and fulfillment cycle. Implementing lead-to-order management ensures effective measurement of business performance throughout the customer lifecycle and insights into inefficiencies that may impact revenue growth.
- Lead-to-order management
- Sales cycle
Lead-to-Order Management
Managing lead-to-order as an end-to-end business process helps organizations manage leads, improve conversion rates, and generate more accurate quotes that convert to closed-won deals . An integrated system ensures companies can track their sales performance and its impact on revenue. It also helps measure the efficiency and effectiveness of marketing, sales, and finance operations.
Below is the lead-to-order process flow that connects the stages of the customer lifecycle:
Sales Opportunity Management
The L2O process begins with acquiring and qualifying leads. After the lead has been qualified and the sales rep determines that an opportunity exists to close a deal successfully, the prospect moves to the Opportunity stage of the pipeline. The potential customer is then nurtured throughout the opportunity management process.
Configure-Price-Quote
In the course of sales conversations, the prospect discusses their budget, purchase timeline, and product/service requirements with the sales rep. The salesperson then prepares a quote and generates a formal proposal or digital sales room . The negotiation and approval stage may involve many stakeholders on both sides of the deal; however, automated workflows within CPQ software and templated sales proposals and contracts can streamline the process.
Order Management
Once the deal is closed-won, the order desk verifies the order details, BOM, CAD drawings, or other product configuration requirements from the quote. The order is then placed and sent to fulfillment or engineering if it’s a custom-manufactured product.
Once the order is placed, an invoice can be created and sent to the customer. Within the billing platform, invoices can be tracked, subscriptions can be managed, and accounts receivable can follow up on late invoices
Service or Product Delivery
An end-to-end L2O process also manages service or product delivery based on the product or service configuration, customer specifications, and order details.
Lead-to-Order KPIs
Lead-to-order KPIs are performance metrics used to measure a company’s effectiveness in turning leads into orders. These KPIs provide insight into the success of a company’s sales, marketing, and customer service teams in converting prospective customers into paying customers. By tracking these key performance indicators, companies can assess their effectiveness in targeting potential customers and delivering on their promises.
Some common lead-to-order KPIs include:
- Lead response time: This measures the time it takes for a sales or customer service representative to respond to an inquiry from a potential customer. Keeping this metric as low as possible indicates that representatives are responding quickly and efficiently, which will lead to higher conversion rates.
- Lead conversion rate: This is the ratio of total leads received compared to total orders generated over a certain period of time. A high conversion rate shows that the company is effectively targeting its prospects and ensuring they become customers. This also implies that the sales team is effectively closing deals with prospects.
- Customer acquisition cost (CAC): This metric measures the total cost associated with acquiring new customers over a given period of time. It includes any expenses associated with marketing campaigns or other initiatives to generate new leads or drive sales from existing ones. CAC is critical because it helps companies understand how much they spend on acquiring new customers compared to revenue generated from them.
These three key performance indicators help companies assess their performance in generating orders from prospective customers, enabling them to make informed decisions about their sales, marketing, and customer service strategies. Using this data helps companies optimize their processes to maximize conversions while minimizing operational costs. In addition, evaluating formative behavior, such as website clicks and social media engagements, can also provide further insights into buyer behavior and preferences, which helps improve L2O KPIs even further.
Why Businesses Need Lead-to-Order Process Automation
B2B businesses often find it difficult to connect the stages of their lead-to-order process through a unified platform that will provide sales and revenue intelligence to maximize business efficiency while ensuring a positive customer experience. Therefore, L2O technology has been developed to mitigate the following challenges businesses face:
- Support for omnichannel selling
- Building complex product configurations
- Quoting based on array of pricing models
- Disconnected sales and finance technology
- Poor tracking of sales and revenue KPIs relevant to the lead-to-order process
Automating the L2O process streamlines how businesses qualify leads and convert them into customers while also providing valuable insights into the success of their sales efforts. By setting clear lead qualification criteria upfront and creating automated workflows for capturing data accurately throughout each stage, businesses can save valuable time without compromising on customer satisfaction levels or sacrificing any potential revenue from qualified sales opportunities.
Lead-to-Order Management Systems
Lead-to-order management systems enable businesses to bring all their lead, opportunity, quote, order, and billing systems into one platform.
Connecting lead qualification, opportunity management, quote generation, order placement, and automated billing streamlines the sales process, from the initial customer inquiry to the order fulfillment.
In addition, the software provides a comprehensive overview of customer inquiries and orders, allowing sales teams to quickly identify what customers are interested in, what products they are looking for, and what orders they have placed.
This data can then be used to target potential customer prospects and develop more efficient strategies for responding to inquiries and fulfilling orders.
Lead-to-order management systems typically include features such as tracking customer inquiries, allowing customers to place orders online, managing payment information and setting up automatic follow-up emails or messages regarding order status.
This automation helps improve efficiency by removing manual processes and reduces errors that might occur during the ordering process.
Additionally, it enables businesses to quickly analyze customer patterns that can be used for marketing purposes or to understand better what leads are likely to convert into sales.
People Also Ask
What is the lead-to-cash process.
The lead-to-cash process is a customer’s journey from the initial inquiry of a product or service to making the final payment. It includes a variety of activities, both online and offline, that aim to convert leads into paying customers. The lead-to-cash process typically starts with qualifying leads. This step involves researching potential customers to identify those who have the greatest likelihood of becoming paying customers. Once qualified leads are identified, businesses can begin nurturing them by providing relevant content and opportunities for engagement with their products or services. This often includes conducting outreach via phone calls or emails to explain further how their offering may benefit customers. In addition to nurturing leads, businesses should also focus on creating strong relationships with them throughout the lead-to-cash process. This could involve enhancing customer support capabilities so that any queries or concerns are quickly addressed in an efficient manner. Moreover, companies should also monitor how their various offerings fare among different market segments to adjust their strategy when it comes time for customers to make payments. Finally, companies need effective methods for collecting payments once all necessary steps have been taken and customers are ready to purchase products or services. Secure payment gateways should be used to ensure that all transactions take place safely and efficiently without any issues arising during processing time frames. At every stage of the lead-to-cash process, businesses should remember that it is essential for them to not only attract new customers but also retain existing ones by providing positive experiences with their products or services throughout each interaction, including invoicing and payment.
What is the difference between lead-to-order and order-to-cash?
Lead-to-order and order-to-cash are business processes often used in organizations to manage customer orders. Lead-to-order is the process of capturing customer interest, converting it into an opportunity, and ultimately turning it into a sales order. It involves gathering information, generating quotations, and closing sales. On the other hand, order-to-cash is a process that starts with receiving an order and ends with receiving payment from the customer. It involves verifying the purchase order, scheduling deliveries or services, invoicing, and collecting payments. The main difference between lead-to-order and order-to-cash is that lead-to-order focuses on converting potential customers into sales orders. In contrast, order-to-cash focuses on fulfilling orders and collecting payments for them. Another key difference is that lead-to-order typically deals with prospects or leads who may have yet to purchase from the organization while order-to-cash generally deals with existing customers who have already made a purchase before. Additionally, lead-to-order requires more marketing efforts and customer relationship management ( CRM ) processes, while order-to-cash requires more operational workflows and financial management processes.
Multistep request a demo popup
- Turn emails from customers & suppliers into fast, accurate digital transactions.
- AI-powered Sales Order Automation so you can ship more perfect orders.
- Maximize touchless automation to deliver more perfect orders.
- Eliminate the errors and CSR effort from repetitive order exceptions.
- Rapid-deploy deep integration with all leading ERPs.
- Empower your Customer Service team within Salesforce.
- Anti-phishing security layer helps protect against breaches and ransomware.
- Deliver an Amazon-like digital order experience to more customers.
- Cut costs and earn more discounts from your suppliers.
- Increase real-time visibility into order status for your customers.
- Manufacturers
- Distributors
2.5 Billion Dollar Chemical Company
- Automating 1,2000 trading partners across 14 countries.
- Re-deployed staff to spend more time serving customers.
- Automating 200,000 lines monthly to improve order response time.
- Discover why our customers process orders from 95,000 trading partners using Conexiom.
AI-Powered Strategies to Maximize Profitability and Sales Efficiency
- Best practices and trends to deliver exceptional customer experiences.
- Real-life examples and case studies to guide your automation journey.
- Chat with our experts at an upcoming in-person or digital event.
- Build your business case for order automation.
- Calculate ROI of Order Digitization
- Learn about Conexiom's mission and meet our leadership team.
- Come work with us on revolutionizing order automation.
- Stay updated with the latest industry trends, insights, and developments.

What Is the Order-to-Cash Process and What Are its 8 Stages?
June 10, 2024 |, pierce smith.
Managing cash flow from orders to payments is a complex balancing act of satisfying customers and optimizing resource allocation for sustainable growth. Yet many companies struggle with inefficiencies that disrupt operations and compromise financial stability. The solution is to implement a robust order-to-cash (O2C) process.
Your customer service team stands at the epicenter of a complex ecosystem, where each order sets off a chain reaction through your manufacturing and distribution channels. But beneath the hum of machinery and the whir of conveyor belts lurks an unseen threat: a fragmented order-to-cash process silently siphoning away your profits and customer goodwill.
While you're focused on optimizing production lines and streamlining logistics, could you be overlooking a critical weak link in your operational chain?
As industry margins tighten and customer expectations soar, one pivotal question emerges: How can you transform your order-to-cash cycle from a liability into a catalyst for efficiency and customer loyalty? The answer may revolutionize not just your bottom line, but your entire approach to customer service in manufacturing and distribution.
Read on to learn how effectively managing cash flow from start to finish can boost efficiency and speed up cash conversion.

The TL;DR Version
Cross-functional Workflow: The Order-to-Cash (O2C) process is a comprehensive cycle that starts with a customer order and ends with payment receipt, involving multiple departments like sales, finance, and logistics.
Strategic Importance: In B2B manufacturing and distribution, the O2C process is crucial for maintaining regulatory compliance, financial accuracy, and strong business relationships, enhancing strategic planning and trustworthiness.
Automation Benefits: Implementing technology to optimize the O2C process reduces manual errors, speeds up transactions, and supports scalability, providing significant competitive advantages.
Key Benefits of Optimization: Enhances customer satisfaction, accelerates cash conversion cycles, improves data visibility and analytics, reduces operational costs, and supports business growth.
Stages of O2C: Includes Order Entry and Validation, Processing and Fulfillment, Shipping and Delivery, Invoicing, Account Receivables Management, Cash Application and Payment Reconciliation, Credit Management, and Performance Measurement and Analytics.
What is the order-to-cash process?
The Order-to-Cash (O2C) process is a cross-functional workflow that begins when a customer places an order and ends with the final receipt of payment . This comprehensive cycle not only drives the operational workflow but also significantly impacts customer satisfaction and the company's cash flow management.
For leaders in customer service and operations, a deep understanding of the O2C process is essential. It involves coordinating multiple departments — including sales, finance, logistics, and customer support — to work in harmony. The efficiency of your O2C process has a direct impact on the speed and accuracy of order processing, fulfillment, and payment, which ultimately affects the overall state of the company and the management of customer relationships.
To stay competitive in a market that values fulfillment speed, order accuracy, product availability, and real-time order data, it's crucial for businesses to identify and address potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies within their O2C process.
Why is the order-to-cash process important in B2B manufacturing and distribution?
In the complex landscape of B2B manufacturing and distribution, the efficiency and integrity of the order-to-cash (O2C) process are not just operational necessities but strategic assets. A well-orchestrated O2C process can significantly influence a company's regulatory compliance, financial accuracy, business relationships, strategic planning, and trustworthiness.
Automation reduces manual errors, speeds up transaction times, and allows for better scalability as the business grows. For B2B manufacturers and distributors, investing in technology to optimize the O2C process can result in significant competitive advantages, enabling them to respond more swiftly to market changes and customer needs.
Here are five key benefits that underscore the importance of optimizing the O2C process in any robust business operation:
- Ensuring Regulatory Compliance — A standardized workflow makes adhering to financial reporting rules easier. Proper records also facilitate compliance with tax laws and accounting standards, reducing audit risks.
- Maintaining Accurate Records — Systematizing order entry, fulfillment, billing, and payment collection helps keep your books organized, contributing to the overall integrity of financial reporting.
- Enhancing Partnerships — By smoothly processing orders, deliveries, and invoices according to agreed-upon terms, you build a reputation as a low-risk, customer-centric partner in your business network. This builds durable, mutually beneficial relationships.
- Improving Planning — Evaluating order trends and collection patterns over time provides insight into demand cycles. You can then forecast requirements and allocate capital more prudently based on a solid understanding of historical sales patterns.
- Bolstering Trust — Demonstrating financial integrity through a well-run order handling process convinces enterprise and individual customers that your operations are conducted transparently, and transactions are managed responsibly, enhancing your credibility and reputation among stakeholders.
Order-to-Cash vs. Quote-to-Cash
Understanding the nuances between Order-to-Cash (O2C) and Quote-to-Cash (Q2C) is crucial before changing anything in either process. While both are integral to the sales cycle, they cater to different stages of customer interaction and completion of a sale.
The Order-to-Cash process begins once a customer places an order. It encompasses everything from order management, fulfillment, and shipping, to invoicing and payment collection. The primary focus here is on efficiently fulfilling orders and ensuring timely payments, which directly impacts cash flow and revenue recognition for the company.
On the other hand, Quote-to-Cash extends further upstream and starts earlier in the sales cycle. This process includes everything from the initial customer inquiry and quote generation to the final payment collection. Q2C is more comprehensive as it not only involves the O2C components but also encompasses pricing configurations, quote creation, and contract negotiations. This process is crucial for aligning customer expectations with the company’s offerings and capabilities, ensuring all terms are agreed upon before an order is even placed.
What Are the Top 5 Benefits of Optimizing the Order to Cash Process?
Optimizing your company's order-to-cash (O2C) process can lead to significant improvements across key areas of your business. By replacing manual work with intelligent systems, you can streamline operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and boost your bottom line. Here are the top 5 benefits of optimizing your O2C process:

1. Improved Customer Satisfaction and Retention
An efficient Order to Cash process contributes to a positive customer experience by delivering accurate and timely invoices, providing convenient payment options, and resolving billing inquiries promptly, fostering customer loyalty and repeat business.
2. Accelerated Cash Conversion Cycles
A streamlined Order to Cash process enables businesses to reduce the time between delivering products or services and receiving payments, accelerating cash conversion cycles and improving liquidity.
3. Enhanced Data Visibility and Analytics
By capturing and analyzing data throughout the order-to-cash cycle, businesses can gain valuable insights into customer behaviors, process bottlenecks, and areas for improvement, enabling data-driven decision-making and continuous process optimization.
4. Reduced Operational Costs and Errors
Automating and optimizing the Order to Cash process can significantly reduce manual work, minimize errors, and lower associated operational costs, improving overall efficiency and profitability.
5. Facilitates Operational Scaling and Growth
A well-defined and efficient O2C process is essential for handling increased order volumes, ensuring consistent service delivery, and maintaining operational efficiency during periods of business expansion or growth.
Woodhill Supply, a one-stop wholesaler for pipe, valve, fitting, plumbing, HVAC/R, and tool needs, partnered with Conexiom to automate the invoicing stage of their order-to-cash process. By implementing Conexiom's solution, Woodhill Supply was able to efficiently enter accounts payable invoices into their Epicor Eclipse system with minimal effort, reallocate staff to more value-added tasks, and see a return on investment in just four weeks .
What Are the 8 Stages of Order to Cash Processing?
Implementing an effective order-to-cash process involves a structured, multi-step approach that encompasses the following eight stages:
1. Order Entry and Validation
The process starts with accurately capturing customer orders. Verify important details like product specs, quantities, pricing, and delivery needs.
2. Order Processing and Fulfillment
Once validated, the order progresses to processing and fulfillment. Check inventory availability before allocating stock, picking, packing, and shipping the order.
3. Shipping and Delivery
This stage involves coordinating with logistics providers to ensure timely and accurate delivery of the order to the customer's specified location, adhering to agreed-upon service levels, and handling any potential exceptions or delays.
4. Invoicing
After successful delivery, generate invoices containing all important commercial details, such as descriptions, quantities, pricing, taxes, and payment terms, for compliance and transparency.
5. Account Receivables Management
Effective account receivables management is crucial for monitoring outstanding invoices, managing customer credit limits, and ensuring timely payment collection, minimizing the risk of bad debts and cash flow disruptions.
6. Cash Application and Payment Reconciliation
As payments are received, this stage involves accurately applying the funds to the corresponding invoices, reconciling accounts, and resolving any discrepancies or disputes that may arise.
7. Credit Management
Continuous credit management is essential for evaluating customer creditworthiness, setting appropriate credit limits, and identifying potential risks, enabling proactive measures to mitigate financial exposure.
8. Performance Measurement and Analytics
The final stage involves analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics throughout the O2C cycle, such as cycle times, error rates, and cash conversion cycles, enabling data-driven decision-making and continuous process improvement.
What Are the Challenges in the Order to Cash Process?
While an efficient O2C cycle is important, many companies face hurdles in optimizing the process. Here are some key issues:
- Manual document handling: Around half of O2C documents are still emailed, requiring staff to manually enter orders, invoices, and payment details. This data re-entry is time-consuming and error-prone.
- Scalability issues: If O2C relies on manual work, order processing speed depends on headcount. During busy periods, fulfillment can slow, worsening customer response times. Manual workflows also hinder handling increased volumes as the business grows.
- High error rates : Rekeying information introduces opportunities for many errors , such as incorrect pricing or shipment details. Mistakes and their consequences then need fixing, wasting further resources and potentially damaging customer satisfaction.
- Slow order processing: If order details pass between departments manually, this lengthens overall processing timelines. Customers face delays in receiving fulfilled orders or issue resolutions.
- Extended cash conversion: the manual steps in order processing and invoicing increase days sales outstanding. This ties up cash flow and impacts liquidity as payments are received later.
- Limited visibility: Without centralized order data, it's tough to analyze metrics, find inefficiencies, or address recurring issues promptly. Bottlenecks may go unnoticed.
How Conexiom Can Help Optimize Your Order-to-Cash Process
Many companies find their O2C process bogged down by inefficient, manual tasks. Staff spend hours rekeying order data, invoices, and other documents instead of focusing on customers. This leads to delays, errors, and higher costs.
Conexiom provides you with a powerful automated approach to streamlining this complex O2C process. Our innovative platform harnesses the power of artificial intelligence to reduce manual work.
By leveraging AI, Conexiom can:
- Pre-fill order records with accuracy by intelligently extracting key details from various documents.
- Integrates seamlessly with major ERP systems to keep data synchronized across all stages.
- Achieve automation rates up to 80%, freeing staff to focus on higher-value customer needs.
- Shorten cash conversion cycles by accelerating processing times at each step.
- Provide new visibility into performance with data-driven analytics.
- Ensure smooth customer and vendor experiences through consistent, error-free processing.
Request a demo today to explore how Conexiom can transform your O2C process, streamline operations, and drive business growth.
.png)
Subscribe to the Conexiom newsletter
"> "> receive platform tips, release updates, news and more, recent posts, top digital transformation examples, webinar recap: how gems setra slashed order processing time by 65% with ai order automation, you might also be interested in.
Digital Transformation
Perfect Order
What Is Perfect Order in Logistics?
Looking for more content, looking for more content get updates sent to your inbox.
Order Fulfillment Explained: Process, Strategies, Costs, Metrics & More
Find out everything you need to know about order fulfillment. This guide covers its history, integral sales processes, various types, logistics, global-to-local strategies, key performance metrics, and emerging trends

What is Order Fulfillment?
Order fulfillment is the process through which businesses manage and fulfill customer orders, from receiving an order to delivering the product to the end customer. The order fulfillment pipeline bridges crucial touchpoints like — inventory management, picking, packing, shipping, and even potential returns.
Starting at the factory, goods are produced and then stored in warehouses. Upon receiving an order, these goods are retrieved from the warehouse, prepared for shipment, and then sent to distribution centers or directly to retail locations. In some cases, especially in e-commerce, the items are shipped directly to the end consumer. Each step is crucial in ensuring that the right product reaches the right recipient promptly and efficiently.
The decision on managing order fulfillment processes— in-house or outsourced—varies by company and their specific needs. In-house order fulfillment definition means a company handles all aspects of the order fulfillment process using its resources, offering direct control over operations, inventory, and quality. In contrast, outsourced order fulfillment meaning involves partnering with third-party logistics providers (3PLs) specializing in these operations.
The History of Modern Order Fulfillment
The evolution of order fulfillment over the years has been closely connected to changing consumer behaviors. As shopping methods shifted from physical stores to online platforms and now a blend of both, businesses had to adapt swiftly to keep pace.
- Traditional Fulfillment (Pre-Internet Era): In the years before the Internet, the order fulfillment meaning was very straightforward. Manufacturers would produce goods, which were then stored in bulk at warehouses. These goods would later be shipped in large quantities to physical retail outlets where consumers would make purchases. The model was predominantly linear, with little to no room for variation.
- Advent of Mail Ordering: Mail ordering provided consumers with the ability to shop from the comfort of their homes. Combined with the deregulation of motor carriers in the United States, these circumstances required businesses to develop direct-to-consumer fulfillment processes, where individual orders were picked, packed, and shipped based on catalog orders received by mail or over the phone.
- Rise of E-commerce: With the onset of the Internet, online shopping portals began to emerge. This shift demanded a new framework for order fulfillment. Warehouses had to adapt to picking and shipping individual items directly to consumers rather than bulk shipping to physical retailers. The need for efficient inventory management, rapid shipping, and return-handling processes became evident.
- Omni-channel Retailing: Omni-channel retailing emerged as a blend of physical and online shopping experiences. Consumers could order online and pick it up in-store or buy in-store and return it online. This approach required businesses to integrate their physical and digital order fulfillment processes seamlessly.
- The Amazon Effect: In order to meet heightened consumer expectations, Amazon introduced Prime - ushering in the era of same-day delivery. This phenomenon, known as the "Amazon Effect", forever changed the landscape of order fulfillment. This compelled retailers worldwide to fine-tune their supply chains and utilize data analytics to expedite order fulfillment.
- Eco-Conscious Fulfillment: The modern consumer is informed, conscientious, and shows deep concern for sustainable consumption. This shift has shifted retailers' focus into eco-responsible practices, like green packaging, ethically sourced materials, and reducing carbon footprints. Sustainability has become a crucial part of brand integrity and customer appeal. The current fulfillment strategies reflect this, underscoring the importance of responsible practices in building consumer trust and long-term loyalty making sustainability a competitive differentiator in the crowded retail space.
With the convenience provided by online giants like Amazon, consumer expectations have skyrocketed. The demand for same-day or next-day delivery has now become standard, forcing businesses to address supply chain complexities and shipping delays. For example, a study by Deloitte reveals that 59% of responding manufacturing companies have faced shipping delays due to truck driver shortages and congested ports in the past 12–18 months.
As we move forward, consumers are increasingly valuing personalization and sustainability. This means delivering products quickly and ensuring packaging is personalized and eco-friendly. It’s not just about speed anymore but about the entire experience, from placing an order to the unboxing experience itself.

Order Fulfillment Processes
The order fulfillment cycle encompasses several key stages, each crucial to ensuring that products reach customers efficiently and accurately. While these stages form the backbone of fulfillment across various sales channels and business models, their implementation can differ significantly based on the specific operational demands of each channel.
Inventory Management
Order processing, returns processing, customer service.
Each of these processes requires integration based on the sales channel and business model in question. They're interconnected, and efficiency in one process often means efficiency across the whole fulfillment cycle. Each sales channel has unique requirements, customer expectations, and operational frameworks, and the way orders are fulfilled must align with these specifics to ensure customer satisfaction and maintain operational efficiency.
Dissecting Sales Channels
The order fulfillment cycle varies depending on the sales channels.
Traditional Retail
In traditional retail, encompassing physical stores, pop-up shops, and trade shows, order fulfillment processes predominantly revolve around ensuring that products are available on shelves for direct customer purchase. The process is less about individual order shipping and more about efficient inventory management, restocking, and in-store customer service.
There are three primary categories:
- Big-box (e.g., Walmart, Target, Kroger): These retailers operate on a massive scale, requiring sophisticated supply chain management systems to keep their numerous stores stocked. They leverage robust data analytics to predict consumer behavior and ensure product availability. Big-box stores often have their distribution centers, allowing for efficient inventory management and distribution to their many outlets.
- Mid-size (e.g., Petco, Barnes and Noble, American Eagle): While they operate on a smaller scale than big-box retailers, mid-size stores also rely on data-driven supply chains and often utilize a mix of centralized and direct-to-store delivery models for replenishment. They might not have the same bargaining power with suppliers as big-box stores but focus on supplier relationships and niche market strategies to maintain inventory efficiency.
- Mom and Pop (Local neighborhood stores and Delis): These smaller, often family-owned stores typically have a more straightforward supply chain, sourcing goods from local suppliers of wholesale distributors. Order fulfillment management might be more manual, and the ordering process is often based on observed demand rather than complex predictive analysis. Personalized customer service, boutique experiences, and community connections are their unique strengths. The United States Census Bureau estimates there were 7,936,977 small business establishments in 2019.
Across all these traditional retail categories, the common goal is to avoid stockouts while minimizing overstock. The scale of operations, resources, technological integration, and supplier relationships are the key differentiators in how these retailers approach order fulfillment. According to a survey by DHL, 40% of respondents are insourcing order fulfillment while 48% are pursuing a hybrid approach.
Online Marketplaces
Online marketplaces such as Amazon, eBay, Walmart, and various regional alternatives have significantly reshaped the retail landscape, offering consumers a one-stop-shop experience with a wide variety of products from multiple sellers. Consumers tend to migrate towards these marketplaces due to several triggers:
- Convenience : These platforms provide unparalleled ease of shopping, with multiple brands and products available in one place, easy checkout processes, and quick delivery options.
- Variety : The vast array of products and brands gives consumers the power to compare and choose items that best fit their needs and budgets.
- Trust : The established reputation of these marketplaces often translates to consumer trust, especially concerning secure payment processes and reliable customer reviews.
- Competitive Pricing : Regular discounts, deals, and the ability to compare prices drive cost-conscious consumers to these platforms.
Order fulfillment meaning in these marketplaces can take various forms, significantly impacting both the seller's operations and the customer's shopping experience.
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and Walmart Fulfillment Services (WFS) : These order fulfillment services, offered by Amazon and Walmart respectively, allow merchants to leverage the marketplace's vast logistic networks. Sellers send their products to Amazon's or Walmart's fulfillment centers, and the rest (storage, packing, shipping, customer service, and returns) are handled by the marketplace. Amazon’s FBA or WFS allow sellers to scale their business, access prime customers, and offer faster shipping, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction.
Fulfilled by Merchant (FBM) : In this model, sellers list their products on the marketplace but handle the fulfillment process themselves. Fulfillment by merchants gives sellers more control over their inventory, order fulfillment logistics, and shipping costs, which can be advantageous for niche products, fragile items, or when the merchants have an efficient fulfillment system in place. According to a survey by Shippo, two-thirds of respondents said they wouldn’t consider purchasing from a retailer that didn’t offer free shipping.
The changing consumer behavior towards online marketplaces highlights the need for sellers to adapt their order fulfillment strategies accordingly. Whether opting for FBA, WFS , or FBM, sellers must consider factors like cost, control, scalability, and customer expectations.
Ecommerce Platforms
For ecommerce platforms like Shopify, Magento, WooCommerce, and BigCommerce, order fulfillment takes on a direct-to-consumer (DTC) approach that requires a seamless blend of efficiency, speed, and adaptability. Unlike traditional retail, where the focus is on shelf availability, DTC fulfillment emphasizes the accurate, swift, and reliable delivery of products straight to customers' doorsteps.
The process involves:
- Order Receipt and Processing: When a customer places an order online, the seller receives it via their ecommerce platform tools . The order must be quickly processed, necessitating real-time inventory visibility to ensure stock levels are accurate across all sales channels, preventing order cancellations due to stockouts.
- Picking, Packing, and Shipping: Orders then move to the fulfillment center or warehouse where items are picked from shelves, securely packaged, and labeled for shipping. Given that consumers now expect fast, often free shipping, e-commerce businesses must strategically choose courier services and optimize delivery routes or maintain partnerships with multiple carriers to meet various shipping preferences and speeds.
- Returns Management: E-commerce typically sees higher return rates than brick-and-mortar retail, making an efficient returns process essential. This involves not just receiving and processing returned items, but also managing reverse logistics, which can be complex and cost-intensive.
- Customer Communication: Throughout this process, proactive customer communication is key. This includes providing order confirmations, shipping updates, tracking information, and easy access to customer service. Such transparency is crucial for building customer trust and satisfaction.

DTC fulfillment demands an integrated approach that ties production, inventory, and distribution into a single, responsive ecosystem. Leveraging the capabilities of e-commerce platforms, businesses can automate many aspects of the fulfillment process, synchronizing inventory data, tracking orders in real time, and analyzing sales patterns to forecast demand.
B2B Sales Channels and Order Fulfillment
B2B sales, traditionally dominated by wholesale, direct sales, and enterprise procurement, involve sales between businesses, such as a manufacturer to wholesaler or wholesaler to retailer. These transactions are typically characterized by larger order volumes, recurring orders, and long-standing relationships between businesses.
However, the landscape is changing with the emergence of B2B e-commerce, where business buyers expect a shopping experience akin to B2C, driven by convenience, efficiency, and transparency. This shift is leading to a transformation in B2B order fulfillment:
- Wholesale: Traditionally, wholesalers might have ordered via sales reps or direct ordering systems. With B2B e-commerce, wholesalers are now shopping in online marketplaces or through supplier websites with customer-like interfaces, necessitating real-time inventory data, easy order placements, and customer service – aspects previously reserved for B2C.
- Direct Sales: For manufacturers selling directly to large retailers or other businesses, e-commerce platforms allow for streamlined ordering processes, often integrated with the buyer's procurement systems. Fulfillment requires coordination of large, regular shipments, often with strict delivery windows and compliance standards.
- Enterprise Procurement: Large corporations procuring supplies typically have complex, rule-based purchasing systems. B2B e-commerce is simplifying this process, allowing for online catalogs, easy reordering, and spend tracking. Fulfillment must be precise, as businesses rely on the timely delivery of the right goods for their operations.
Across these channels, B2B order fulfillment must deal with unique challenges, such as:
- Volume and Complexity: Orders are often large and might include a wide variety of items, requiring meticulous order fulfillment management and logistical planning.
- Customer Expectations: B2B buyers expect a level of service similar to what they experience as individual consumers, including fast shipping, order accuracy, and easy returns.
- Regulatory Compliance: Especially for cross-border transactions, B2B shipments might need to comply with a range of regulations, requiring detailed documentation and compliance checks.
The evolution of B2B e-commerce is pushing businesses to modernize their systems, adopt advanced supply chain technologies, and enhance their order fulfillment strategies to meet heightened customer expectations. This transformation, while challenging, presents an opportunity for businesses to improve efficiency and order fulfillment rates, forge stronger relationships with partners, and tap into new markets.
Omnichannel Fulfillment
The omnichannel approach has emerged as a critical strategy for brands aiming to provide a seamless customer experience across multiple sales channels. This approach recognizes that customers interact with brands in a variety of ways — online through e-commerce platforms, social media, mobile apps, and offline in physical stores or pop-up shops — and expects consistency, convenience, and personalized engagement across all these touchpoints. According to a study by Insider Intelligence, an estimated 50% of US Gen Z and millennial social users make purchases on social media , compared to 38% of US adults overall.
Channels are indeed converging, and customers no longer see a distinction between a brand's online presence and its physical store—they view it as one entity and expect the experience to be continuous. For instance, they might want to browse products online, try them in-store, and later purchase via an app with home delivery. Alternatively, they might buy online and pick up in-store (BOPIS), a trend that surged especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
However, omnichannel fulfillment also brings complexities to order fulfillment:
- Inventory Visibility: Real-time, accurate inventory data is paramount, as customers expect items seen online to be available immediately for purchase or in-store pickup.
- Flexible Fulfillment: Brands need the capability for varied fulfillment options, like BOPIS, ship-from-store, or same-day delivery, necessitating agile and responsive supply chains.
- Consistent Experience: Whether it's the purchase process, product pricing, or returns policy, consistency across channels is crucial to maintain customer trust and satisfaction.
- Data Integration: Collecting and analyzing data from all touchpoints allows for personalized marketing, improved forecasting, and responsive replenishment, creating a smooth back-end operation that supports the front-end customer experience.
Implementing an effective omnichannel strategy requires significant investment in technology, logistics, and personnel training. It involves integrating disparate systems for inventory management, order processing, customer relationship management, and more.
However, the payoff is substantial—brands that successfully execute an omnichannel approach see improved customer loyalty, order fulfillment rates, higher average order values, and increased revenue, as they can engage customers at multiple points along their shopping journey, thereby maximizing opportunities for conversion. In a landscape where customer expectations continue to rise, an omnichannel approach is becoming less of an option and more of a necessity for brands looking to thrive in the long term.
Unpacking Various Order Fulfillment Types
There are various types of order fulfillment approaches that businesses can implement depending on a business's size, resources, expertise, and strategic goals. Here's a breakdown of several common types:
1. Self-fulfillment
For self-fulfillment or insourced order management, the business manages every step of the order fulfillment process in-house, rather than outsourcing to third-party logistics (3PL) providers or using dropshipping methods
Pros: Complete control over the fulfillment process, direct handling of inventory, packaging, and shipping, and closer customer relationship management.
Cons: Requires substantial investment in storage space, staff, technology, and logistics, and can be challenging to scale during peak periods.
It is Ideal for startups, small businesses, or those with unique products that require special handling or branding experiences.
2. Third-party Logistics (3PL)
3PLs handle the order fulfillment logistics of storage, picking, packing, and shipping, allowing businesses to focus on core competencies like product development and marketing.
Pros: Offers expertise in logistics and order fulfillment management, provides scalability, and reduces the need for physical storage space and staffing.
Cons: Less control over the fulfillment process, the potential for miscommunication, and reliance on the 3PL's system reliability and performance.
Third-party partnerships can provide access to advanced technology, wider distribution networks, and volume shipping discounts but require careful management, clear communication, and trust.
3. Dropshipping
Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where a store doesn't keep the products it sells in stock. Instead, when a store sells a product using the dropshipping model, it purchases the item from a third party — usually a wholesaler or manufacturer — and has it shipped directly to the customer.
Pros: Eliminates the need for inventory management and upfront investment in products, and offers virtually unlimited inventory.
Cons: Less control over inventory, longer delivery times, reliance on supplier’s stock and performance, and potential for inventory issues.
4. Cross-docking and JIT (Just-In-Time) Fulfillment
Products are quickly transferred between transport vehicles without long-term warehousing (cross-docking) or are manufactured/received as needed (JIT), reducing storage, product handling, and overall order fulfillment costs.
Pros: Reduces inventory holding costs, less space requirement, and quicker delivery to customers.
Cons: Requires precise coordination, reliable suppliers, and accurate forecasting to prevent stockouts or delays.
5. BOPIS (Buy Online, Pick-up In-Store)
BOPIS, or "Buy Online, Pick-up In-Store," is a hybrid retail model that blends online shopping with traditional brick-and-mortar experiences. For example, Walmart leverages its physical stores as distribution points where customers can pick up online orders. This order fulfillment strategy merges the digital and physical shopping experiences, offering customers convenience, no shipping fees, and immediate gratification while driving additional in-store purchases.
Pros: Increases customer convenience, reduces shipping costs and time, and leverages existing physical infrastructure.
Cons: Requires accurate inventory tracking, dedicated storage space for pick-up items, and additional staff training.
6. Hybrid Order Fulfillment Solutions
Businesses often use a mix of self-fulfillment, 3PL, dropshipping, and other methods based on their product types, sales volume, geographic reach, and growth strategies. This approach offers greater flexibility, optimizes order fulfillment costs, and ensures better risk management.
For instance, a business might handle fulfillment in-house in its primary market to maintain control and customer experience but use 3PLs in new or distant markets to reduce shipping times and navigate the challenges of local order fulfillment logistics.
The choice of a hybrid model can be influenced by various factors, such as the desire to test new markets, the need for specialized handling or storage, seasonality, international shipping complexities, or expansion plans.
Ultimately, the choice among these order fulfillment strategies depends on the business’s size, resources, market demand, product nature, and long-term goals. Each method comes with its own set of requirements and order fulfillment challenges , and businesses must evaluate their capabilities, conduct cost-benefit analyses, and possibly consult with supply chain experts to determine the most suitable approach.
Understanding Fulfillment Center Logistics
At its core, all order fulfillment logistics require a combination of warehouse organization, picking and packing products, and reverse logistics.
1. Warehouse Organization: SKUs, Shelving, and Space Optimization
Warehouses and fulfillment centers are the backbone of the supply chain, and their organization significantly impacts order processing efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction. Warehouse organization is structured around stock keeping units (SKUs), which are unique identifiers for each distinct product. The arrangement of SKUs, shelving, and the overall use of space are often tailored to the type of fulfillment, sales channels, and products involved.
For instance, a warehouse serving a traditional retail channel might have pallets of the same product (ideal for bulk shipping), whereas a direct-to-consumer e-commerce warehouse would need individual bins for a broad array of SKUs (facilitating single-item orders). Similarly, facilities handling perishable goods or large, heavy items would require specialized storage, handling, and order fulfillment solutions.
Space optimization, often facilitated by warehouse management systems (WMS) , involves strategic shelving (like high-density storage for fast-moving items), and layout designs to minimize picking time and accommodate varying inventory levels, thereby enhancing throughput and efficiency.
2. Picking Methodologies: Wave, Batch, Zone, and More
The picking and packing process is central to order fulfillment, directly affecting the speed and accuracy of customer order deliveries. You can choose from various approaches depending on warehouse size, order types, and volume to overcome picking challenges :
- Wave Picking: Orders are grouped into waves based on specific criteria (like shipping carrier or destination), and picked at scheduled times, optimizing workflow and reducing shipping times.
- Batch Picking: Multiple orders are picked simultaneously to minimize trips to the same location, ideal for warehouses with a wide variety of SKUs and smaller orders.
- Zone Picking: The warehouse is divided into zones, with workers assigned to each. Products are picked within zones and then consolidated, suitable for large warehouses with high-volume orders.
- Discrete Picking: One order is picked at a time, simple but less efficient for larger operations.
Each method impacts fulfillment speed, accuracy, and workforce requirements differently. For example, while batch and wave picking can increase efficiency, they may also require more complex coordination and a robust WMS to handle order grouping and routing.
3. Returns Processing
Returns are an inevitable aspect of the sales process, more so with the rise of e-commerce, where return rates are significantly higher than in traditional retail. Reverse logistics, or the flow of returned items back into the inventory poses challenges in sorting, assessing, restoring, and repackaging products.
In the digital age, consumers expect smooth return processes; thus, an efficient returns management system needs to be in place. This involves designated areas within the warehouse for returns, skilled staff to assess and refurbish products, and technology to update inventory levels in real time. Additionally, a proactive approach, including data analysis, can help businesses understand return reasons and patterns, potentially leading to reduced return rates over time.
Ultimately, a strategic approach to warehouse organization, picking methodologies, and returns processing can greatly improve order fulfillment efficiency , accuracy, and customer satisfaction, directly contributing to a company's bottom line.
Global Fulfillment: From Local to Global
Addressing regional nuances in domestic fulfillment.
Domestic fulfillment is subject to local regulations, consumer preferences, and logistical infrastructures. In the U.S., for instance, domestic fulfillment involves navigating a vast geographic area with diverse regional demands, requiring a strong distribution network for timely deliveries. Meanwhile, businesses must also comply with local tax laws, environmental regulations, and consumer product safety laws which can vary from one state or region to another.
Cross-Border Fulfillment: Expanding Globally Without Hiccups
Cross-border fulfillment involves selling products internationally, which involves navigating various legal frameworks, shipping protocols, and cultural nuances. According to Shopify, consumers are increasingly looking beyond their home country as 57% of respondents say they’ve recently made an international online purchase .
A common challenge includes navigating the complexities of international shipping logistics, such as longer shipping times and the need for multi-language support. Additionally, consumer expectations regarding shipping costs and times can vary widely, necessitating a clear communication strategy. A survey by Voxware reveals that 69% of respondents are unlikely to shop with a retailer if their delivery is delayed by more than two days.
Duty and Customs Management to Avoiding International Bottlenecks
Successful global fulfillment requires adept handling of duties and customs. Incorrect paperwork, underestimating duties, or not adhering to international trade agreements can lead to delays, additional order fulfillment costs , and negative customer experiences. For instance, the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), now replaced by the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), has significantly influenced trade and fulfillment operations among these countries, affecting tariffs, regulations, and supply chain strategies.
The trade tensions between the U.S. and China, highlighted by increased tariffs, have prompted many businesses to consider near-shoring — shifting their supply chains to closer countries like Mexico. This change allows companies to reduce order fulfillment costs, have more control over the manufacturing process, and provide faster fulfillment due to proximity.
Brexit is another prime example, causing disruptions in trade between the United Kingdom and the European Union. Post-Brexit, many EU-based businesses are now compelled to establish a presence in the UK to avoid increased shipping times and costs, and to navigate new tax and duty requirements efficiently.
International 3PLs and Localized Fulfillment Centers
Using international third-party logistics (3PLs) providers or localized fulfillment centers can be advantageous for global operations. Ecommerce 3PLs often have a deeper understanding of local markets, regulations, and consumer behavior, providing businesses with strategic storage locations, reduced shipping times, and costs, and helping to manage complex international logistics.
By utilizing a network of international fulfillment centers, businesses can store products closer to their customers, significantly reducing shipping times and logistics costs while increasing customer satisfaction.
Technology's Role in Seamless Fulfillment
Technology plays a key role in optimizing and streamlining order fulfillment processes, directly improving efficiency, accuracy, and customer satisfaction.
1. Order Fulfillment Software and Multichannel Order Fulfillment Management
Businesses can leverage the right technology to manage orders from multiple sales channels (e-commerce platforms, marketplaces, and physical stores) through a single interface. This software enhances visibility, accuracy, and efficiency by automating tasks like inventory tracking, order routing, and shipment tracking. In addition, multichannel order management systems allow businesses to synchronize inventory and sales data across various platforms, ensuring consistent information and smoother operations.
2. Distributed Order Routing
Distributed order management systems determine the most cost-effective and efficient way to fulfill orders by analyzing variables such as inventory levels across locations, shipment times, and costs. These systems help businesses optimize their supply chains and improve customer satisfaction through quicker deliveries.
3. Warehouse Management System (WMS) Essentials
Modern Warehouse management systems (WMS) solutions offer far more than traditional inventory tracking. They provide real-time tracking of products within the warehouse and en route to customers, sophisticated forecasting tools to anticipate inventory needs and analytics to monitor KPIs and optimize operations. These systems are critical for businesses looking to scale, offering insights into potential bottlenecks or inefficiencies.
4. Integrations
Integrating a WMS with other systems like e-commerce platforms, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software allow for seamless data exchange and streamlined operations. For instance, integrating the WMS with an ecommerce platform ensures that stock levels are updated in real-time, preventing stockouts or overselling, while connection to a CRM can provide customer service reps with up-to-date order status information.
5. The Rise of AI and Robotics in Order Fulfillment Processes
Adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and robotics is on the rise in modern fulfillment centers, helping automate various processes:
- Picking Robots: These robots are designed to navigate warehouse aisles and select items for orders, significantly reducing human labor and minimizing errors.
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS): These systems automatically place and retrieve loads from defined storage locations, increasing efficiency and reducing labor costs.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Drones and self-driving carts can move items within the warehouse or perform last-mile deliveries.
- AI-Powered Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze data to predict future order volumes, necessary inventory levels, and potential supply chain disruptions, allowing businesses to adjust strategies.
These technologies not only speed up the order fulfillment process but also enhance accuracy, improve worker safety by automating more dangerous tasks, and ultimately lead to greater customer satisfaction through faster and more reliable order processing.
The future of order fulfillment is one where humans and technology collaborate, with AI and robotics handling repetitive tasks, and humans managing more complex or creative responsibilities. This synergy promises a more efficient, accurate, and scalable order fulfillment process, prepared to meet the evolving demands of the modern consumer.
Order Fulfillment Metrics and Performance Indicators
To optimize order fulfillment, businesses must track specific metrics and performance indicators. These numbers offer valuable insights into the efficiency of your operations and warehouse KPIs , highlighting areas for improvement and measuring the impact of changes.
Key Fulfillment Metrics
- Order Accuracy Rate: This measures the number of orders shipped correctly versus the total orders shipped. A high accuracy rate indicates effectiveness in picking, packing, and shipping processes.
- Order Turnaround Time: This is the time taken from when an order is placed to when it's shipped. Speedy order fulfillment is a key metric, especially in the age of same-day and one-day delivery expectations.
- Return Rate: It reflects the percentage of sold items that are returned by the end consumer. A high return rate can indicate issues with product quality, order accuracy, or customer expectations not being met.
Performance Indicators
- Fulfillment Cost Per Order: This involves the total cost associated with fulfilling and shipping an order. Keeping this cost low while maintaining high service levels is crucial for profitability.
- Inventory Turnover: The inventory turnover ratio shows how many times a company's inventory is sold and replaced over a period. A low turnover rate may point to overstocking, obsolescence, or sales issues, while a high rate may indicate strong sales or ineffective buying.
- Backorder Rate: Backorders reflect the number of orders that cannot be filled at the time of purchase. A high backorder rate can signal inventory and order fulfillment management issues and can negatively impact customer satisfaction and retention.
- Average Order Value (AOV): This metric tracks the average dollar amount spent each time a customer places an order. By understanding this metric, businesses can strategize ways to increase revenue.
- Carrying Cost of Inventory: Carrying costs includes all costs related to storing unsold goods. Lowering these costs without affecting order fulfillment efficiency can directly increase net profit.
Each of these metrics plays a vital role in assessing the effectiveness and efficiency of an order fulfillment system. They provide actionable insights that companies can use to streamline operations, reduce order fulfillment costs, and enhance customer service.
The Future of Order Fulfillment
As we look ahead, several trends are poised to shape the future of order fulfillment, driven by technological advancements, evolving consumer preferences, and the overarching necessity for sustainable practices.
Sustainability as a Standard, Not an Option
Increasing environmental concerns are pushing companies to adopt sustainable practices in their order fulfillment processes. This means increased use of eco-friendly packaging, optimization of delivery routes to reduce carbon emissions, and warehousing operations powered by renewable energy. Consumers are progressively favoring brands that demonstrate environmental responsibility, making sustainability a competitive differentiator
Drone Deliveries and Autonomous Vehicles
Drone deliveries are gaining popularity as a viable option for order fulfillment, especially for last-mile delivery. They reduce the overall time from the warehouse shelf to the customer's doorstep and significantly cut down on carbon emissions compared to traditional delivery vehicles.
Similarly, autonomous delivery vehicles are no longer just a concept but are entering real-world testing phases. These technologies promise faster, more cost-effective, and environmentally friendly delivery options.
Smart Warehousing
The warehouses of the future will be highly automated to increase efficiency and reduce reliance on human labor. Advancements in robotics, AI, and machine learning will lead to smart warehouses that can predict, adapt, and respond to changes in order fulfillment demands in real time.
Hyper-Personalized Customer Experiences
Beyond just getting orders right, the future will see an emphasis on bespoke customer experiences. From personalized packaging to products tailored to the individual's preferences and needs, order fulfillment will become a significant part of the brand experience and customer satisfaction.
With the retail landscape evolving rapidly, companies must be ready to pivot quickly, adopting new technologies and methodologies to meet changing consumer demands. This requires an investment in continuous learning, data-driven decision-making, and agile business models.
The future of order fulfillment will offer new avenues for companies to differentiate themselves with a steadfast commitment to innovation and sustainability. With Hopstack’s smart Warehouse Management System, businesses can leverage data-driven insights to streamline fulfillment processes and ensure maximum efficiency.
If you’re looking to improve your existing order fulfillment pipeline and increase investment into your supply chain operations, schedule a call with our product specialist today.
- Improve Order Accuracy
- Scale Your Fulfillment
- Boost Efficiency & Profits
Unlock Your Warehouse’s Full Potential
See how Hopstack can help you transform your warehouse operations

Annotation Services
Bpm analytics, business process as a service (bpaas), business transformation, customer service, digital interactive services, education technology services, finance & accounting, financial services, geospatial data services, human resource outsourcing, learning and development, legal process outsourcing, manufacturing, master data management, robotic process automation, retail, cpg and logistics, sales and fulfillment, sourcing and procurement, infosys bpm.

Communication Service Providers
Maximising ROI by streamlining the lead-to-cash process in communication services
Every business relies on cash flow and quality sales to survive. But how can you turn up the sales in communication services and drive customer attention? This brings lead-to-cash into play. By leveraging lead-to-cash in communication services , companies can boost ROI and create a seamless customer experience that encourages new customers to buy.
According to reports, around 65% of businesses feel lead generation is their biggest challenge. With the best lead-to-cash strategies, you can address these challenges on the go and raise your sales game in the telecommunications service industry.
When you utilise a well-thought telecommunications lead-to-cash process, you can contribute effectively to business growth and profitability. Here is everything you need to know about lead-to-cash to improve your business performance and increase sales.
What is lead-to-cash?
Lead-to-cash (L2C) is integrating all lead-generation practices to convert prospects into customers. It includes every element of improving the customer relationship, such as lead generation, branding, sales, customer service, and billing.
Optimising L2C requires understanding how the customer wants to be treated during purchase. By automating certain steps in the workflow, businesses can streamline the lead-to-cash process, making sales transactions more accurate and timely and decreasing human error. By integrating lead-to-cash, you will increase revenue and productivity while increasing customer retention.
Challenges in the lead-to-cash process
Communication service businesses face many challenges within the L2C process that can negatively impact their success. Customers’ needs and preferences are understood thoroughly, revenue streams are accurately forecasted, data is accurate across all systems and processes, and customer support is provided timely.
Companies must have strategies to address these key challenges before maximising efficiency and minimising costs in the lead-to-cash process. Here are the top challenges that businesses need to address on the go to drive the most revenue:
- Data quality concerns
- Complicated pricing
- Ineffective data capture
- Uncertain customer journeys
- An unclear target audience
Lead-to-cash boosts performance
Lead-to-cash optimisation can benefit your telecommunications services in many industries by eliminating challenges and enhancing customer journeys, starting with initial contact and progressing to contract drafting, invoicing, and closing. Lead to cash processes add value to your business in the following aspects:
Customer experience
The lead-to-cash process improves customer experience by improving team communication and response times. Additionally, it ensures that sales operations are aligned with customer needs. Artificial Intelligence (AI) solutions can be integrated into the L2C process to automate things like searching for customer information and email follow-ups.
Bottom line
With an optimised lead-to-cash process, organisations can operate more efficiently and accurately. Automated processes such as order management, invoice processing, and payment processing can reduce businesses' manual workload to a great extent. In addition to increasing profitability, employees can focus on more valuable tasks.
Data accuracy
Optimised L2C processes usually result in more accurate data since they reduce the possibilities of human error or inaccurate data entry. Furthermore, automating data processes ensures adherence to internal policies, legal requirements, and other external guidelines.
Lead-to-cash strategies can also help organisations track their customers' orders better. Having this information is helpful to them in gauging their products' performance in various markets and forecasting future trends.
End-to-end lead-to-cash process
Lead-to-cash strategies require the best process in place to deliver the best results within communication services and other industries. Here are some lead-to-cash processes that will take your business to great leads and thrive in a competitive market:
Generating leads
The lead generation process initiates the lead-to-cash process. This is the process of building interest in your product or service in potential customers. Generating quality leads is essential to the success of a sales funnel, as it attracts potential customers.
Managing leads
Upon generating leads, they enter the lead management phase. During this phase, leads need to be qualified and prepared for sales.
Quote to order
It is now time to turn potential leads into sales prospects. Your sales team’s effectiveness is put to the test here. The quotations are precisely prepared with detailed information about prices, discounts, and proposals.
Managing orders
Managing orders involves processing and fulfilling them. An essential step in meeting customer needs and increasing efficiency in operations.
Invoicing and billing
Invoicing and billing are the steps that result in revenue for a business. A business’s cash flow depends on it.
Payment management
To maintain a healthy cash flow, it is essential that customer payments are received and processed correctly.
Recognising revenue
The final step is revenue recognition, in which revenue is accurately reported in the financial statements. This is essential to comply with financial reporting regulations. A properly managed lead-to-cash process can enhance efficiency, customer service, and business revenue growth.
How can Infosys BPM lead-to-cash solution help you?
Infosys BPM next gen services allow communication service businesses to boost their sales game. With our next-gen communication solutions, you can streamline the customer journey and bring the perfect sales plan to life.
Automate & Bring Efficiency by Leveraging Our Cloud-Powered Communication Solutions >>
Recent Posts

Opt in for marketing communication Privacy Statement
Thank you for connecting with us. We will respond to you shortly.
Thank you for subscription.

Published: 30 May 2024 Contributors: Teaganne Finn, Amanda Downie
Order to cash, also known as O2C or OTC, is the entirety of a company’s order processing system. The business process begins the second a customer places an order and goes until payment is made and logged to account receivables.
The O2C system is a critical part of getting and maintaining a healthy cash flow. As the process aims to cut down on the time between when an order is received and when the business is paid. Activities within the O2C system can directly impact supply chain management and inventory management procedures.
The order to cash process shouldn’t be confused with quote to cash (Q2C or QTC), which is a broader, end-to-end business process. The Q2C, as its name infers, starts before point of sales and includes initial steps, such as quote preparation and tailors offers to meet customers needs.
A better way to differentiate the two is that the O2C processes are within the Q2C process. Q2C begins with customer purchase intent and ends at the final pricing decision. Which is where O2C then picks up. The order to cash system should be analyzed to ensure that the business is seeking out constant optimization and improvement.
This report from the IBM Institute for Business Value provides insights on why finance transformation through AI propels business value.
The order to cash process differs slightly depending on what type of business it is, such as through an ecommerce platform or direct sales. But fundamentally it will remain the same from start to finish.
Below is the step-by-step process of the order to cash cycle:
The tracking system of an order from inception to fulfillment, along with all of the information and processes. The order management system (OMS) manages the order and provides transparency to the business and the buyer.
If the business is doing sales on credit, it’s important to have a customer financial risk assessment or approval process. This might include a credit check on a new customer or require references from them before extending credit payment terms.
This step entails actually picking the ordered items and then packing and shipping it to the customer. If the business is dealing with physical products, then inventory management and the fulfillment process will be involved.
The shipping process can be complex and will vary depending on product logistics. A regular audit should be done to ensure that regulations and performance standards are met. It’s important that all data from the purchase order and fulfillment side of things is updated for the shipping team so that carrier pickup and delivery is done in a timely manner.
Invoice generation and payment is a critical step in O2C. Customers receive invoices for their order, which should include line items, details on cost per item, taxes and any discounts applied to the order. This step launches the payment process. Accurate invoicing systems start from staff collecting correct information from the point of sale, such as order notes, costs, credit terms, order date, etc.
Following the invoice generation and the order has been sent to the customer comes the accounts receivable team. This step ensures that payment is collected and is most efficient through implementing an automation process that alerts the team to outstanding invoices at predetermined times. The automated accounting system can detect when errors are made and accounts receivable professionals can then quickly review the data and revise the invoice in a timely manner.
The way a customer pays the business for an order should be determined at the time of purchase and spelled out in the invoice clearly. The customer payment is then collected through online payment, bank transfer, a written check or any other format accepted by the business. To ensure that payment is made, an order reference number is given to the customer and correctly matched to the physical order. This limits confusion and helps with customer satisfaction and further limits issues with accounts payable or the general ledger. Other payment reminders can be made like mobile notifications.
By using integrated software, businesses can analyze every step of the O2C cycle in real-time and monitor where inefficiencies are and where in the process they are having the most success. An integrated data management system, such as enterprise resource planning or ERP systems, is important for reporting and analyzing data so that adjustments to the O2C workflow can be done. By tracking key metrics, a business can streamline its O2C process, remove bottlenecks and fulfill more customer orders.
A business' growth and development rely heavily on a several factors, especially strong customer relationships. With a robust order to cash process it ensures that customers are being served in an optimal way that is both effective and efficient. An O2C system can improve cash flow and working capital, while simultaneously enhance the customer experience as long as all parts of the O2C process are working together.
Separately, the O2C process is key to customer satisfaction. It is one of the most direct ways that a customer interacts with a business and directly related to overall profitability. A successful order to cash cycle will allow customers to easily place an order, receive an invoice for how much they owe and when, and monitor the ETA for order delivery through notifications. Satisfied customers are a major part of any successful business and an efficient order system that streamlines the order to cash process is optimal.
The current business environment requires CFOs, finance professionals and the finance functions they lead to be open to learning new approaches to financial management. This includes adopting and harnessing the power of artificial intelligence (AI) . The AI-driven innovations on offer can improve order to cash system credit scoring, pricing decisions and aid in the prevention of fraudulent payments.
Leaders should consider new technology tools like AI and generative AI (gen AI) as a way to improve finance processes and optimize operational costs for their business. Specific to order to cash, generative AI can recover cash by validating customer claims and deductions, which can result in a cut to revenue loss by 60 to 70%. A performance improvement such as this can be a major boost to a company’s bottom line if finance teams are trained to use the technology responsibly.
Enhancing the order to cash process is important for cash inflows and the overall success of all sales orders. Here are four best practices to optimize your O2C cycle.
Rather than taking a macro approach to the O2C cycle, try analyzing it step-by-step. See how each step in the cycle is working and how it functions as it relates to the entire process.
Begin with the low-hanging fruit or common problem areas first in the O2C cycle. Start to target the areas that have the highest return with the least amount of effort necessary.
The customers and staff of your business are a crucial part of the success of your O2C process. Listen to the complaints coming from customers and see whether patterns arise, or pay attention to reoccurring issues warehouse staff might be facing.
New technology, such as software as a service (SaaS) , can automate managing business processes like an O2C cycle. This can result in better cashflow and operational efficiency. While ERP software can provide a unified platform for all business applications, streamlining the entire O2C process.
What is the difference between order to cash and quote to cash?
Quote to cash is a broader system with more initial steps leading up to the order. Whereas O2C begins at the point of sale.
What is billing in O2C?
The billing step in O2C refers to the request of payment from the customer. This is typically done through an invoice.
What are the steps in O2C?
The typical steps include order management, credit management, order fulfillment, order shipping, customer invoicing, accounts receivable, payment collection and reporting and data management.
What is the difference between order to cash versus procure-to-pay?
Procure to pay and order to cash both manage purchase or service requests. However, procure-to-pay is specifically focused on processing orders placed by the business for within the organization.
What is the difference between order to cash and accounts receivable?
Accounts receivable is the step within the O2C process focused on documenting customer purchase and ensuring payment is collected.
What are some challenges with order to cash?
The O2C process becomes more complex as the sales volume goes up and requires a business to stay on top of each step in the process. The snowball effect is very much at play when it comes to the success of an O2C process. An example is if a customer is late to pay an invoice, which might take capital away from a business, which could then trickle down to an impact to employee payroll.
What are the benefits of an effective order to cash system?
Customers want to trust the business they are buying from and vice versa. A transparent and efficient O2C process can ensure an almost-seamless buying experience and a streamlined customer service process. Aside from customers, employees can also benefit from an automated O2C system that relieves them from mundane tasks and gives them more time to work on strategic projects.
Reimagine your finance operation with data, AI and automation by partnering with the FAO team at IBM Consulting®.
Accelerate your digital transformation by simplifying technology integrations and implementing a complete omnichannel order fulfillment solution.
Enhance your order management system with a platform that uses generative AI and machine learning to help ensure order accuracy and boost profitability.
Here are extra resources as you begin your order to cash journey.
Learn how senior finance leaders use AI for concrete improvements in process quality, cost and efficiency.
Learn how IBM® Procurement BPO cognitive solution helps enterprises transform their procurement and financial processes.
Explore the challenges banks around the globe are facing as they try to make payments more efficient.
Learn how IBM watsonx Orders, an AI-powered voice agent for drive-thrus of quick-service restaurants helps with labor challenges.
Join the IBM webinar to explore trends, industry-specific AI-first operating models, AI-powered insights, growth through process and enterprise transformation.
Better understand new generative AI solutions and unique AI foundation models for the future of Finance and Accounting (F&A).
Accelerate end-to-end transformation by working with a single partner that can help you unlock new levels of productivity and reimagine your finance operations. IBM Finance and Accounting Business Process Outsourcing (FAO) brings together advanced data, AI and automation technologies, intelligent workflows, and cost-mindedness.
In an OSS, what are O2A, T2R, U2C, P2O and DBA?
Let’s start with the last one first – DBA.
In the context of OSS/BSS, DBA has multiple meanings but I think the most relevant is Death By Acronym (don’t worry all you Database Administrators out there, I haven’t forgotten about you). Our industry is awash with TLAs (Three-Letter Acronyms) that lead to DBA.
Having said that, today’s article is about six that are commonly used in relation to end to end workflows through our OSS/BSS stacks. They often traverse different products, possibly even multiple different vendors’ products. They are as follows:
- P2O – Prospect to Order – This workflow operates across the boundary between the customer and the customer-facing staff at the service provider, particularly salespeople. It allows staff to generate and sustain sales as well as checking what products can be offered to a customer. This includes service qualification (SQ), feasibility checks, then design, assign and reserve resources.
- O2A – Order to Activate – This workflow includes all activities to manage customer services across entire life-cycles – from when the customer places the order, to when they start utilising the service/s. That is, not just the initial activation of a service, but in-flight changes during activation and post-activation changes as well (see more here )
- U2C – Usage to Cash – This workflow allows customers or staff to evaluate the usage or consumption (or credits remaining) of a service (or services) that has already been activated for a customer
- T2R – Trouble to Resolve – This “workflow” is more like a bundle of workflows that relate to assuring health of the services (and the network that carries them). They can be categorised as reactive (ie a customer triggers a resolution workflow by flagging an issue to the service provider) or a proactive (ie the service provider identifies and issue, degradation or potential for issue and triggers a resolution workflow internally). (see more here )
- CPQ – Configure, Price, Quote – This “workflow” or tool allows an organisation to efficiently, accurately and consistently generate offers / proposals to customers. Offers may need to incorporate specific customisations or designs as well as calculating quantities, rates, discounts, product features and more. CPQ is a sub-set of Q2C that follows (see more on CPQ here )
- Q2C – Quote to Cash – Starts with lead / opportunity management, goes through the CPQ steps above, but then also includes order fulfilment and billing / invoicing (see more here )
TM Forum has produced GB921E (Addendum E to its eTOM framework) to help define some of the end-to-end process flows used by telcos. These include:
- Request to Answer (R2A)
- Order to Payment (O2P)
- Usage to Payment (U2P)
- Request to Change (R2C)
- Termination to Confirmation (T2C)
- Complaint to Solution (C2S)
- Order to Acceptance
- Ticket to Solution
- Activation to Usage
- Capacity Management
- Service Lifecycle Management
- Resource Lifecycle Management
- Idea to Business Plan
- Idea to Business Proposal
- Business Proposal to Launch
- Assessment to Relaunch
- Assessment to Retirement
- Market Strategy to Campaign
- Procurement Using Engaged Party
If you’re interested in seeing how these workflows relate to the TM Forum APIs and specifically to NaaS (Network as a Service) designs , there’s a great document (TMF 909A v1.5) that can be found at the provided link. It shows the sub-elements (and associated APIs) that each of these workflows rely on. However, also note that this comes from an outdated version of the Open API suite for NaaS. Version 3 can be found here .
PS. I recently read a vendor document that described additional flows:- I2I (Idea to Implementation – service onboarding, through a catalog presumably), P2P (Plan to Production – resource provisioning) and O2S (Order to Service). There’s also C2M (Concept to Market), C2L (Concept to Launch), D2G (Demand to Grow), L2C (Lead to Cash), O2C (Order to Cash), M2I (Measure to Improve) and I’m sure I’m forgetting a number of others. Are there any additional TLAs that I should be listing here to describe end-to-end workflows?
Follow this link for further information on how to Design Telecommunication Business Process Flows Using eTOM . In addition, if you wish to document, benchmark and optimise operational processes , we can assist. Our approach uses activity logs from your OSS / BSS to help capture current-state process flows in BPMN format (see sample below) and identify optimsation / automation opportunities.

- June 17, 2019
If this article was helpful, subscribe to the Passionate About OSS Blog to get each new post sent directly to your inbox. 100% free of charge and free of spam.
Our solutions.

- Publications
The Most Exciting OSS/BSS Innovations of 2022 (eBook)

- Market Analysis
AIOps of the Future: A Definitive Guide (digital whitepaper)

Mastering Your OSS – Operational Support System Implementation Tips and Techniques

OSS/BSS Use-Cases
Most recent articles, when it comes to oss, are you a tigger or an eeyore.
I was listening to a group of telco experts on a podcast the other day. As they were talking, I kept picturing the image of
Closing the OSS Buyer / Seller chasm – When the most expensive thing about your OSS product isn’t your price (part 7)
Earlier in the year, we wrote a series of articles about the chasm that exists between OSS/BSS buyers and sellers (pt1, pt2, pt3, pt4, pt5, pt6). “The chasm” is
A question for my OSS developer friends
Actually, maybe a few related questions. As you’ve seen from recent articles such as this, I’m increasingly interested in the cross-over worlds of comms and
A novel OSS/BSS idea? Or is it?
I’d like to share an idea with you. I think it’s a novel idea. However, I’m still trying to work through the possible pros /
Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Here at Passionate About OSS, we are exactly that – Passionate About OSS (Operational Support Systems). We’re also passionate about BSS, NMS, or any other names you call the tools that help to operationalise your network.
- @PassionateaboutOSS
- Passionate About OSS
Did you still not find what you are looking for?
Passionate About OSS © All rights reserved
Designed and developed by inqiludio digital.
40 politely-worded templates to get invoices paid
What does order to cash (or O2C) mean in B2B payments? | Chaser

Share this article

The order to cash ('O2C' or 'OTC') process is a critical function of any business that sells goods or services to other businesses. It is a series of steps that are designed to ensure that a company receives payment for the products or services it provides to its customers.
To better understand the order to cash process and how it benefits aspects of your business such as outstanding invoices, accounts receivable, cash flow, and customer satisfaction, we'll be diving into the O2C process and explaining how it works in B2B payments delivered.
O2C meaning and how it affects business processes
The order-to-cash process, also known as O2C, is a series of steps that a company takes to fulfill a customer order and receive payment for the goods or services provided. The process begins when a customer places an order and ends when payment is received for the order. The OTC process includes a variety of steps, including order processing, invoicing, payment, and fulfillment.
The O2C process is an essential aspect of B2B customer payments as it enables businesses to manage their cash flow effectively. It is critical to streamline the order to cash cycle to ensure that there are no delays in receiving payments, which if left undealt with, can have a significant impact on the company's financial health.
In addition to improving cash flow and other business processes involved, it can also help to improve customer satisfaction. From payment reminders that assist in payment reminders to a smoother invoicing system, optimizing the O2C process can offer a number of benefits to your customers. It's a major business process that finance teams can greatly improve given the right resources.
In B2B payments, the OTC process is often more complex than in B2C payments. Customer orders tend to be much larger and more complex. This can put a lot more strain on invoice creation, your order management system, and also the speed at which your company is processing customer orders. Without the right system in place, it could lead to inaccurate cash estimates and payment processing difficulties too.
The payment terms for B2B transactions also range from 30 to 90 days. This tends to delay a company's cash inflows and may complicate accounts payable. As a result, it is critical to manage the order-to-cash process effectively to ensure timely payment and avoid any delays that could impact cash flow.
Order to cash process steps
The OTC process involves several steps that are critical to the successful completion of a transaction. Let's take a closer look at each of these steps.
Step 1: Credit management and approval
Before a customer places an order, businesses must determine their customer's creditworthiness and ensure that the customer has the financial capability to pay for the goods or services. This involves conducting a credit check to determine if the customer has a good credit score and a history of paying their bills on time. If the customer passes the credit check, the business can proceed with the order.
A sophisticated credit management system within your company will greatly improve the speed of credit approval. If customer payments are more likely to happen and the approval process is faster, then it can speed up the order to cash cycle. Your business success hinges on ensuring the customer pays, so the last thing you want is to have issues when you collect payment.
Step 2: Order processing
Order processing involves receiving an order from the customer, verifying the order details, and entering the order into the company's system. Once a customer places an order, it's entered into the order management system and sent to the warehouse for fulfillment. It is also essential to ensure that the customer's payment terms are in place to avoid any delays in payment.
Step 3: Fulfillment and delivery
Fulfillment involves delivering the goods or services to the customer as specified in the order management system. Fulfillment management functions can be completed in-house or through a third-party logistics provider. When it comes to fulfilling a product order, the order fulfillment process entails identifying the location of the items, preparing them, and arranging for their shipment. Throughout this process, it's essential to ensure that all delivery details, such as the shipping address and delivery timeframe, are accurate and in order. In the case of a service order, order fulfillment involves scheduling the service delivery date and location and making sure that all services outlined in the order are provided as promised. This may involve coordinating with other teams or external partners to ensure that the service is carried out successfully.
Step 4: Invoicing
Invoicing is the next step in the order to cash process. Once the order has been processed, an invoice is created. The invoice includes details such as the customer name, order details, and the amount owed for the order. See the full list of details that must be included on your invoices
Invoices can be sent to customers via email, SMS payment reminders , or via a payment portal system. In most cases, they should follow a standardized digital format to make them easier to read and understand.
Invoicing is a critical step in the O2C process, as it represents the company's request for payment from the customer. The invoice must be accurate, complete, and easy to understand to ensure that the customer can make a timely payment.
Step 5: Payment
Payment is the step in the order to cash process that involves receiving payment for the goods or services provided. Depending on the payment terms agreed upon by the customer and the company, payment may be due immediately on delivery of the goods or service, or at a later date.
The business must decide which types of payments they will accept and which channels they will use to accept payment.
In B2B payments, payment terms are often set based on the customer's creditworthiness and payment history. For example, a customer with a good payment history may be offered more favorable terms than a new customer with no payment history.
Step 6: Cash application
Once payments have been received via various payment channels, the business needs to apply the cash to the corresponding customer accounts. Cash application is the process of recording and matching the cash received with the corresponding invoice, and marking it as paid. This ensures that the customer's account balance is updated accurately, and the company can reliably use the cash for its operations.
Cash application can be a complex process for companies that receive a high volume of payments each month. Cash application specialists are responsible for matching the cash received with the corresponding invoices, which can be time-consuming and prone to errors. To streamline the process, companies often use payment remittance advice, which is a document that provides details about the payment and the invoices it covers. Some payment methods, such as paper checks and credit card payments, come with remittance advice attached.
Step 7: Accounts receivable
If payment collection isn't possible, then companies must undertake action to recover their accounts receivables or due amount from the customer. This can involve:
- Sending payment reminders
- Calling the customer to discuss when payment will be made
- Creating payment installment plans
- Using debt collections
- Handling customer disputes or queries about paying the invoice
It's important that a system is able to flag outstanding invoices so that they can be followed up. If there are errors or discrepancies, then it's important for everything to be traceable in order to accelerate cash flow and improve the customer experience.
Accounts receivable can be tough to handle, especially if the cause of a late payment is unclear. It might be the fault of late order shipping, or it could be a bug in your invoice system. However, there's always the possibility that a customer just doesn't want to cooperate. In this case, it's best to track performance data to determine worthy customers that you want to work with.
Step 8: Performance data
Data management is another important component of the O2C process. Most companies have interconnected software to perform everything from supply chain management to inventory management. By monitoring this data, a sales department and other related teams can analyze trends to improve a customer relationship, improve cash flow, optimize an order processing system, and even improve credit management for future transactions.
By analyzing this data carefully, order management teams can more accurately determine the impact of your order to cash process and where things can be improved. A company might discover that their accounts receivable process is full of issues that lead to payment collection issues, resulting in poor process management and a bad customer experience. Others may notice that their invoice generation system isn't working correctly, leading to incorrect figures and payment delays.
O2C process challenges in B2B payments
Managing the OTC process can be challenging in B2B payments due to the complex nature of these transactions. Let's take a closer look at some of the challenges that companies face when managing the OTC process.
Delayed cash flow
Delayed payments are a common challenge in B2B payments, as terms can range from 30 to 90 days. In fact, 9 in 10 businesses report that they are typically paid late for their goods or services. This can put a significant strain on a company's cash flow, as they must continue to pay their own bills while waiting for payment from their customers.
To mitigate the risk of delayed payments, it is essential to have clear payment terms in place, and to communicate these terms clearly to customers. It may also be helpful to establish credit checks and payment histories for new customers to ensure that they have a history of making timely payments.
Inaccurate invoicing
Inaccurate invoicing can also be a challenge in the O2C process. If an invoice is incorrect or incomplete, it can lead to delays in payment or disputes between the customer and the company. These are typically handled by the accounts receivable department or team.
To avoid inaccurate invoicing, it is essential to have a clear invoicing process in place . This process should include verifying the accuracy of the order details, ensuring that the correct pricing is applied, and checking that any discounts or promotions are correctly applied. Without a solid accounts receivable process, you may experience delayed payments.
Inefficient order processing
Inefficient order processing can also be a challenge in the O2C process. If it's not processed quickly and accurately when a customer places an order, it can lead to delays in fulfillment and payment. It's vital that your entire organization is on the same page and using company software to its fullest potential.
To improve order processing efficiency, it is essential to have clear processes in place for receiving and entering orders. This may include establishing standard order forms and processes, training employees on the processing procedures, and automating certain aspects of the process where possible. If order fulfillment is slow or inefficient, it will reflect badly on your company.
Lack of visibility
A lack of visibility into the O2C process can also be a challenge for companies. Without visibility into the status of orders, invoices, and payments, it can be difficult to manage the process effectively and identify areas for improvement.
To improve visibility into the O2C process, companies can implement software solutions such as ERPs, Order Management Systems, or CRM tools, that provide real-time data on the status of orders, invoices, and payments. This can help to identify bottlenecks and areas for improvement, and enable companies to make data-driven decisions to improve the OTC process.
Order to cash best practices
To effectively manage the O2C process in B2B payments, there are several best practices that companies can implement. Let's take a closer look at some of these best practices.
Establish clear terms
Establishing clear payment terms is critical to managing the order to cash cycle effectively. This includes establishing payment due dates, late payment fees , and credit limits for customers. Clear terms can help to avoid disputes and delays in payment, and ensure that the company has a healthy cash flow.
Explaining this clearly before a customer places an order will prevent issues with accounts receivable and result in smoother payment collections.
Automate processes where possible
Automating processes where possible can help to improve efficiency in the order to cash process. This may include automating the order processing system, invoicing, and payment processes. Automation can help to reduce errors, speed up processes, and free up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
Enterprise resource planning software is typically used to automate many order to cash processes. Order management software can also supplement this workflow. For example, an invoicing system can automatically produce and send invoices, and a data management system can record performance data. Where possible, it's a good idea to automate an order to cash process to streamline customer orders and quickly process a customer order.
Monitor payment histories
Monitoring payment histories can help to identify potential issues with customers before they become a problem. This includes tracking customer payment behaviour and identifying customers who consistently pay late or have a history of disputes. This can help companies to adjust payment terms for these customers or take other actions to mitigate risks.
Implement a dispute resolution process
Implementing a dispute resolution process can help to resolve issues quickly and prevent them from escalating. This process should include a clear path for customers to report disputes, and a process for resolving disputes in a timely manner. A well-defined dispute resolution process can help to maintain positive relationships with customers and prevent disputes from negatively impacting the order to cash process.
The OTC, O2C, or order-to-cash process is a critical aspect of B2B payments that involves several steps, including order processing, invoicing, payment, and fulfillment. Managing the O2C process can be challenging due to delayed payments, inaccurate invoicing, inefficient order processing, and a lack of visibility into the process. However, by implementing best practices such as establishing clear payment terms, automating processes where possible, monitoring payment histories, and implementing a dispute resolution process, companies can effectively manage the OTC process and improve their financial health.
Related articles

What does remit payment mean in B2B invoice payments? | Chaser
Payment remittance is the process of transferring money from a payer to a payee or one person to another...

Chaser wins B2B Supplier of the Year at the CICM British Credit Awards
I am extremely proud to announce Chaser has won B2B Supplier of the Year at the CICM British Credit Awards...
AVA Digital Awards awards Chaser’s website Gold for B2B websites
With over 2,500 entries a year, the AVA Digital Awards is an international competition that recognizes...
Subscribe to Chaser's monthly newsletter
Our monthly newsletter includes news and resources on accounts receivables management, along with free templates and product innovation updates.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Lead-to-Cash (L2C) process is a comprehensive business workflow that spans from the initial generation of a sales lead to the collection of cash or payment for the goods or services provided. It encompasses various stages of the customer lifecycle and involves multiple departments within an organization. The Lead to Cash process typically ...
Lead-to-cash (L2C) is a business process encompassing all activities and tasks involved in converting potential leads into customers who make purchases. It covers the entire customer lifecycle, from lead generation to marketing, sales processes, customer service and support, billing, and payments. Optimizing L2C requires a deep understanding of ...
It is a critical process for any organization as it involves multiple departments and stakeholders, including sales, marketing, customer service, finance, and operations. The lead to cash process consists of the following areas: Generating, Qualifying and Converting Leads. Creating and Closing Opportunities. Quotes, Proposals, and Contracts.
Lead-to-Cash cycle is a comprehensive business process that encompasses the entire customer acquisition and revenue generation journey within an organization. A well-implemented process can optimize a business's operations, enhance customer satisfaction, and contribute to the overall growth and profitability of the company.
Matt Cheung. Matt co-founded Clarasys in 2011 and ... Lead to Cash (L2C) is a core process that every organisation needs to excel at. Providing your customers with a high quality experience that is able to generate revenue is a critical success factor. If your organisation has multiple departments and you sell a wide range of products, sales ...
Introduction to the Lead to Cash (L2C) Process. The L2C process is integral to business operations. It encompasses the entire journey from the first interaction with a potential customer to finalizing a sale and service delivery. Here's an overview of the critical steps: 1. Lead Generation and Qualification. Businesses kick off the L2C ...
The Bike Company implementation project is currently in the Realization phase, in which the end-to-end processes are tested by the project team. You are already familiar with the detailed structures of the different areas, such as financial accounting, management accounting, human resources, purchasing, production, and sales.
Lead to cash is a comprehensive end-to-end business process that encompasses the entire sales cycle, from initial customer interest to the final receipt of payment. It represents the journey of a lead (potential customer) as it moves through the stages of the sales funnel to become a cash-paying customer. This process is critical for businesses ...
2. Efficient Order Fulfillment: Once the contract is in place, the order fulfillment phase begins. This critical step involves coordinating product delivery or service provision while ensuring adherence to contractual obligations. Streamlining this process reduces delays, boosts customer satisfaction, and prevents revenue leakage. 3.
Lead-to-cash is a comprehensive business process that traverses the entire value chain, commonly known as Revenue Transformation. What is Lead-to-Cash? L2C is essentially a strategic alignment of sales, marketing, and operational functions to enhance the overall efficiency and effectiveness of a company's revenue generation efforts.
Lead-to-cash (L2C) or Order-to-cash (O2C) refers to the processes, technology and capabilities an organisation utilises to enable that customer journey. At Clarasys, we understand how our clients can optimise their lead-to-cash processes to create excellent customer experiences and maximise revenue. We work with you to innovate and transform ...
According to McKinsey, "Outperformers" focus on optimising their Lead-to-Cash (L2C) process by implementing tools and strategies that improve efficiency, customer satisfaction, and connected ...
The lead-to-cash process is a customer's journey from the initial inquiry of a product or service to making the final payment. It includes a variety of activities, both online and offline, that aim to convert leads into paying customers. The lead-to-cash process typically starts with qualifying leads.
Key Benefits of Optimization: Enhances customer satisfaction, accelerates cash conversion cycles, improves data visibility and analytics, reduces operational costs, and supports business growth. Stages of O2C: Includes Order Entry and Validation, Processing and Fulfillment, Shipping and Delivery, Invoicing, Account Receivables Management, Cash ...
Order fulfillment is the process through which businesses manage and fulfill customer orders, from receiving an order to delivering the product to the end customer. The order fulfillment pipeline bridges crucial touchpoints like — inventory management, picking, packing, shipping, and even potential returns. Starting at the factory, goods are ...
The lead-to-cash process improves customer experience by improving team communication and response times. Additionally, it ensures that sales operations are aligned with customer needs. Artificial Intelligence (AI) solutions can be integrated into the L2C process to automate things like searching for customer information and email follow-ups.
What is an order to cash system? The O2C system is a critical part of getting and maintaining a healthy cash flow. As the process aims to cut down on the time between when an order is received and when the business is paid. Activities within the O2C system can directly impact supply chain management and inventory management procedures.
It allows staff to generate and sustain sales as well as checking what products can be offered to a customer. This includes service qualification (SQ), feasibility checks, then design, assign and reserve resources. O2A - Order to Activate - This workflow includes all activities to manage customer services across entire life-cycles - from ...
same time as allowing flexibility where product L2C processes need to be different. Caveat This release does not support the billing and payment areas of the end-to-end Lead-to-Cash processes as these have not yet been fully defined. Later versions may include this functionality or additional documentation may be developed to support them.
Conclusion. The OTC, O2C, or order-to-cash process is a critical aspect of B2B payments that involves several steps, including order processing, invoicing, payment, and fulfillment. Managing the O2C process can be challenging due to delayed payments, inaccurate invoicing, inefficient order processing, and a lack of visibility into the process.