Advertisement

The Simple Difference Between Ballistic Missiles and Cruise Missiles
- Share Content on Facebook
- Share Content on LinkedIn
- Share Content on Flipboard
- Share Content on Reddit
- Share Content via Email
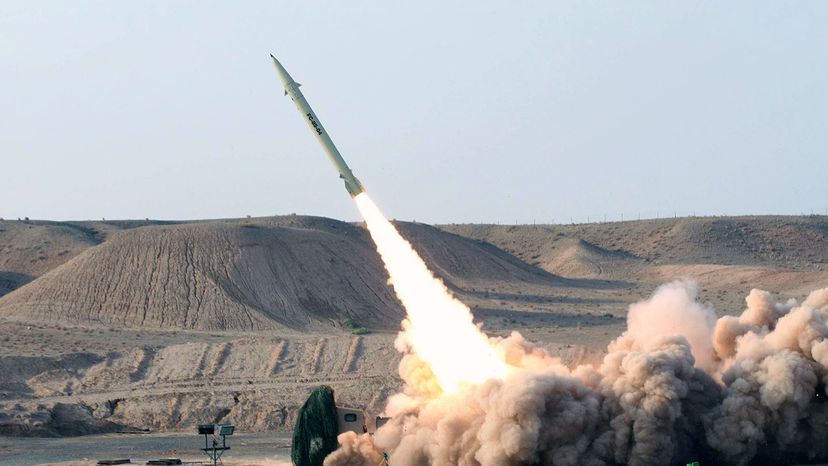

In 2017, North Korea unexpectedly staged a test launch of what was then a new ballistic missile , the Pukguksong-2. The launch took place when Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe was on a state visit to the United States . There have been many more test launches of ballistic missiles by North Korea since. Between May and October 2019, North Korea launched as many as 12 ballistic missiles or other projectiles. But they have all been just test launches.
Things got real, though, on Jan. 7, 2020, when Iran launched more than a dozen ballistic missiles at two Iraqi military bases housing U.S. troops. This was not a test launch. It was Iran's retaliation for the U.S. drone strike that killed Iran Gen. Qassem Soleimani on Jan. 3, 2020. There were no casualties and Iran's Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif defended the missile strike on the U.S. bases in Iraq, saying it was an act of "self-defense."
But for the non-military minded among us, these ballistic missile launches — both the constant test launches in North Korea and the intentional strikes on U.S. bases in Iraq — may raise a good question: What exactly is a ballistic missile, anyway? Is there something about the ballistic part that makes a missile even more dangerous? After all, when someone freaks out we say they've "gone ballistic."
According to the Federation of American Scientists , a ballistic missile is one that has a ballistic trajectory over most of its flight path. What that means is that once the missile burns up the fuel that propels it, the missile keeps moving, the same way that a bullet does after it's been fired out of a gun. Once the fuel is gone, the missile's direction can't be altered. It follows a path determined by the speed of its launch and the force of gravity trying to pull it back toward the Earth's surface. Eventually, gravity guides the missile — and its payload, which might be an explosive, a chemical or biological weapon, or a nuclear device — down toward its target.
Ballistic missiles are different than cruise missiles. Cruise missiles are self-propelled for the majority of their time in the air, flying in a relatively straight line and at lower altitudes thanks to a rocket propellant. Think of a ballistic missile's flight path as a large arc up and back down again, while that of a cruise missile — fired from a warship, for instance — is closer to a straight line.
Ballistic missiles first came into use during World War II, when the Germans used a ballistic missile called the V-2 to attack London. British air defenses designed to stop aircraft couldn't stop the V-2s, because the rockets traveled too high into the upper atmosphere and moved too fast.
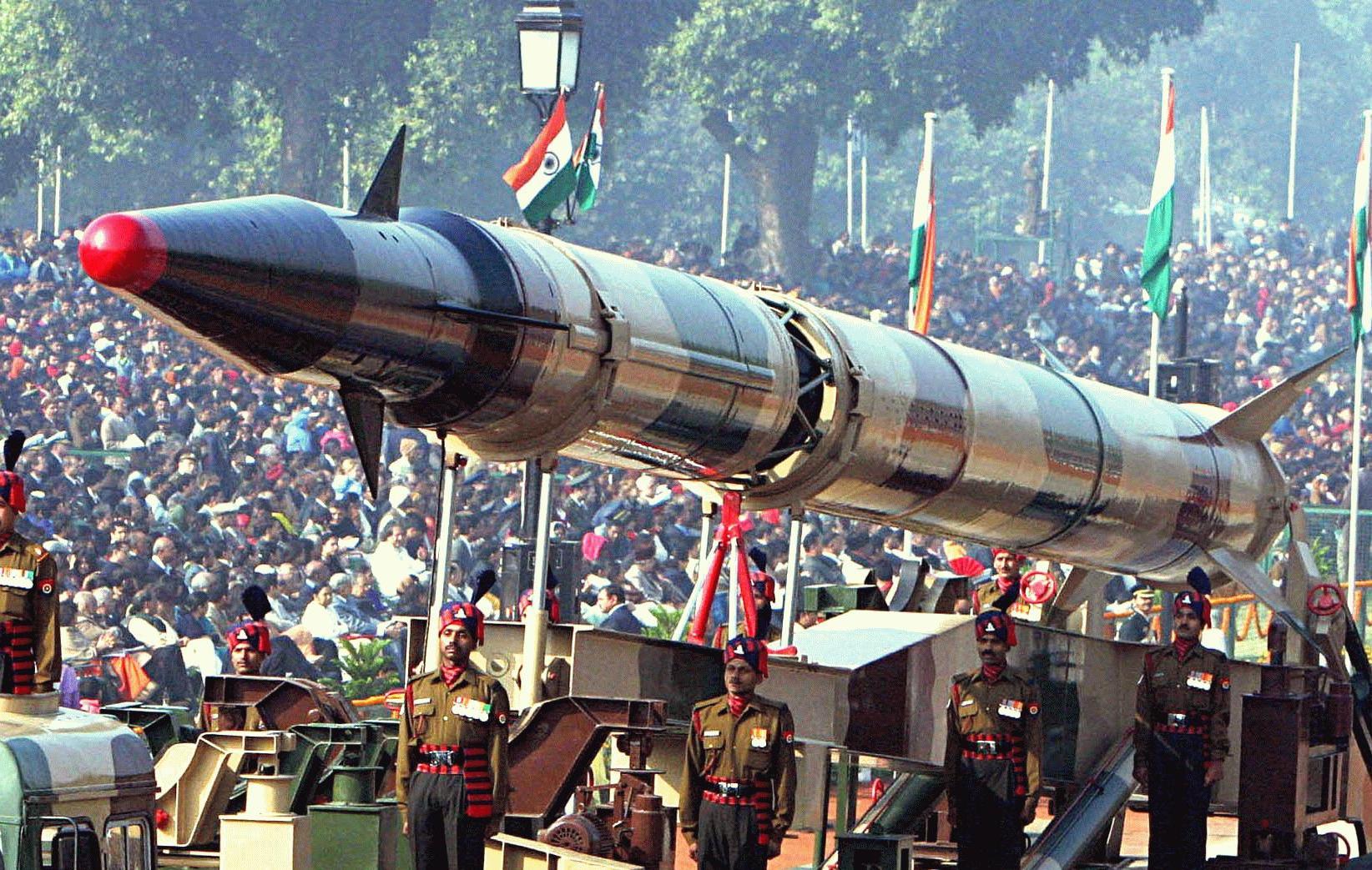
After the war, the U.S., with the help of captured German technology and scientists, built its own arsenal of even more powerful intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) capable of unleashing nuclear destruction upon targets on the other side of the world. The Soviet Union and China built ICBMs as well, setting up a world where a nuclear war was deterred by the prospect of mutual assured destruction.
The North Korean regime successfully tested intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM) in July and November 2017. Its Hwasong-15 ICBM reached an altitude of 2,780 miles (4,475 kilometers) and flew about 590 miles (1,000 kilometers) before landing in the sea off the coast of Japan. Analysts estimate the Hwasong-15 has a potential range of 8,100 miles (13,000 kilometers). If it's fired on a flatter trajectory, it could reach potentially reach anywhere on the U.S. mainland.
Which countries have intercontinental ballistic missiles?
What is meant by ballistic trajectory, what is difference between a ballistic and a cruise missile, how high do ballistic missiles fly, are ballistic missiles nuclear.
Please copy/paste the following text to properly cite this HowStuffWorks.com article:

- Afghanistan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Special Forces
- Weapons & Tech

Pakistan Navy launches first Hangor-class submarine in China.

The second Chinese overseas base is “fully operational.”

China’s new H-20 stealth bomber is of little concern to the…

India transfers ‘ship killer’ missiles to the Philippines

Ukraine cannot defeat Russia alone on the battlefield

The US is developing an unmanned submarine that resembles a stingray

The US National Guard owes more than 13,000 people pensions

Russia displays Abrams tanks and $4 million mine-clearing vehicles in Moscow.

Top 5 Weapons of India’s Elite Para Special Forces

Top 7 Israeli Special Forces Units

Delta Force vs SEAL Team Six: Comparison of the Two Elite…

Inside the United States Army Special Operations Command and Its Special…

United States Special Forces: A Guide to US Navy Special Operations…

MS Agamemnon: The Royal Navy’s New Submarine

The USAF E-3 Sentry Military Aircraft Radar in Detail

Carrier Based Aircraft: Which Countries Operate Them?

Derya ZY9: The Turkish Close Combat Solution

The Rockwell B-1 Lancer: A Key US Air Force Bomber

5 Notable Boeing Military Aircraft: From Air Force One to Maritime…

Top 10 Chinese Weapons Used by Guinean Military

8 Major Close-in weapon system (CIWS) in the World

Top 8 Fighter Jets in the World

4 Most Anticipated Weapons of China in 2024

Tejas Mk 1A vs. JF-17 – A Brief Comparison

German Leopard 2 vs. Russian T-90 Tank – The Ultimate Tank…

F-35 vs. F-22: Comparison of Lockheed Martin fighters

A Comparison of Top Naval Aviation Forces: China vs USA vs…

Comparing Battleships, Cruisers, Destroyers, and Frigates: What Are the Differences?
What are the differences between a ballistic missile and a cruise missile.

Many countries choose missiles because they may be deployed efficiently against an enemy with a strong air defense system , making the use of human aircraft in such an attack impossible or too expensive. There is less need for personnel, supplies, and upkeep when using missiles instead of manned aircraft.
So, What are the Differences between a Ballistic Missile and a Cruise Missile?
When a missile test is being reported, the terms “ballistic missile” and “cruise missile” are frequently used. Ballistic and cruise missile systems are seen as emblems of national power and a cost-effective armament by many governments. Cruise and ballistic missiles are widely used by many countries, both offensively and defensively.
How do cruise missiles and ballistic missiles maneuver, and what are the differences between the basic principles of these maneuvers?
Guided cruise and ballistic missiles were first used when Germany attacked targets in England and Northern Europe with V1 cruise missiles and V2 ballistic missiles during World War II . Although these missiles were inaccurate, their use resulted in tens of thousands of Allied casualties.
The Federation of American Scientists says that a ballistic weapon follows a ballistic path for most of its flight. That means once the rocket’s fuel is gone, it will keep moving, just like a bullet does after being shot out of a gun.
Ballistic missiles climb very high, exiting the atmosphere. According to Wikipedia, short-range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth’s atmosphere, while intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are launched on a sub-orbital trajectory.

According to one definition, a sub-orbital space flight reaches an altitude greater than 100 kilometers above the Earth’s surface. At this altitude, known as the Kármán line, once the fuel runs out, the missile’s direction cannot be altered; it follows a path based on the speed of its launch and the force of gravity attempting to pull it back to the Earth’s surface. Gravity eventually guides the missile and its payload toward its intended target, which could be a chemical or biological weapon or a nuclear device.
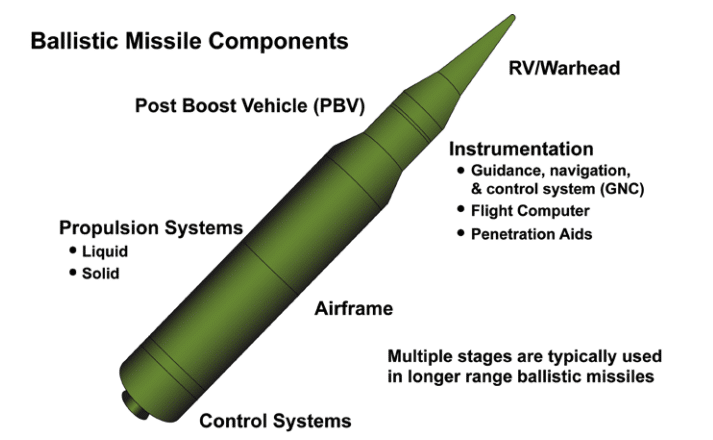
Ballistic missiles are broadly categorized into four groups based on their range:
- Short-range ballistic missiles cover distances less than 1,000 kilometers (approximately 620 miles).
- Medium-range ballistic missiles spanning 1,000 to 3,000 kilometers (approximately 620 to 1860 miles).
- Intermediate-range ballistic missiles range from 3,000 to 5,500 kilometers (approximately 1860 to 3410 miles).
- Intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are capable of traveling over 5,500 kilometers, thus posing a threat to targets across the globe.
Top 10 Short Range Ballistic Missiles (SRBMs)
Short- and medium-range ballistic missiles are called theatre ballistic missiles, while ICBMs and long-range ballistic missiles are referred to as strategic ballistic missiles. On their flight path, ballistic missiles are capable of traveling at a high rate of speed. With terminal velocities of over 5,000 meters per second, an ICBM can strike a target within a range of 10,000 kilometers in approximately 30 to 35 minutes. Due to the limited time available, ballistic missiles are significantly more difficult to intercept than cruise missiles.

For example, the Russian RS-28 Sarmat ICBM can reach almost 25,000 kilometers per hour or over 15,000 miles per hour. To further complicate matters, most ICBMs carry not a unitary large warhead but several smaller and fully independent nuclear missiles called MIRVs (Multiple Independently Targeted Re-entry Vehicle).
The Sarmat can carry up to 24 MIRVs; each MIRV carries nuclear warheads with yields ranging anywhere from hundreds of kilotons to a few megatons. Each MIRV can hit a target hundreds of kilometers away from each other, and some MIRVs will carry decoys and countermeasures, putting additional stress on defensive systems.
Even though cruise missiles are cheaper, more mobile, and more versatile, ballistic missiles are among the most feared armaments in existence. No nation has launched an ICBM as an act of war against another nation, although some nations have tested these missiles during training exercises.

Cruise missiles are unmanned vehicles that are propelled by jet engines, much like an airplane with turbofan engines, in particular being preferred due to their greater efficiency at low altitudes. They range in speed from subsonic to hypersonic, while less common supersonic and hypersonic cruise missiles utilize ramjet and scramjet engines. They can be launched from ground, airplane, and sea platforms like submarines and surface warships.
They tend to have shorter ranges than ballistic missiles. Unlike ballistic missiles, cruise missiles are usually categorized by intended missions and launch mode instead of maximum range. The two broadest categories are land attack cruise missiles (LACMs ) and anti-shipping cruise missiles (ASCMs) . The success of U.S. Tomahawk cruise missiles during the Persian Gulf War has heightened interest in cruise missile acquisition in many countries.
Cruise missiles can reach their objectives from a variety of altitudes so long as they remain within the atmosphere. The trajectory of the vast majority of objects remains close to the Earth’s surface, occasionally hovering just meters above the ground. Their low flight path makes it difficult for most radar and sensor systems to detect the missile unless the radar or sensor system is airborne and directed toward the ground.
Some cruise missiles can only fly at extremely high altitudes, and then they descend steeply once they’ve reached their destination. Higher-altitude flight uses less fuel than lower-altitude flight, allowing the missile to travel further. Unfortunately, modern radars and sensors are often set up to identify and track threats at high altitudes, making the missile more vulnerable to missile defense systems.
Altitude Variation for Tactical Advantage
Cruise missiles are renowned for dynamically altering their flight trajectory, capitalizing on both high and low altitudes. This strategic maneuver enhances their overall performance by combining the advantages of different altitudes. Typically, these missiles initiate their journey at high altitudes to extend their operational range.
However, as they near their target or potential missile defenses, they adeptly descend to lower altitudes, skimming the sea or terrain. This transition serves to elude detection and countermeasures, highlighting the adaptability of cruise missiles in various operational scenarios.
Precision Strikes Defined
The hallmark characteristic of cruise missiles lies in their remarkable precision. Often boasting ranges under 300 kilometers, with the most extended variants reaching approximately 1600 kilometers, these missiles exhibit extraordinary accuracy.
A frequently cited example underscores this accuracy, asserting that cruise missiles can cover a thousand miles and hit a target as compact as a single-car garage. This precision opens avenues for surgical strikes and minimizes collateral damage in contemporary warfare.
Guidance Mechanisms for Pinpoint Accuracy
Cruise missiles harness a repertoire of guidance methods to ensure the impeccable placement of their payloads on intended targets while outmaneuvering missile defense systems. Among these methods, inertial guidance stands as a foundational approach, relying on a pre-programmed flight path set before launch.
Terrain Contour Matching (TERCOM): Navigating with Terrain
Another pivotal guidance method is Terrain Contour Matching (TERCOM) . This intricate mechanism involves the comparison of an onboard terrain map with the actual topography over which the missile traverses. This technique guarantees the missile’s adherence to the designated path, further reinforcing its accuracy and operational efficacy.
Precision Through Global Positioning: GPS and GLONASS
Several cruise missiles integrate GPS systems to achieve pinpoint accuracy. These systems necessitate connectivity with the GPS or GLONASS satellite networks and facilitate adherence to predetermined flight paths. Cruise missiles can strike designated targets with unparalleled precision by leveraging specific coordinates, augmenting their role in modern warfare.
Enhancing Terminal Phase Precision
Cruise missiles deploy advanced guidance methods in the terminal phase of flight to elevate their accuracy.
Laser-Guided Precision: Target Painting
Laser-guided systems emerge as a crucial asset in this phase. Equipped with sensors, these systems detect targets designated by laser markers. While immensely accurate, this method can be vulnerable to interference from environmental factors such as dust and smoke, potentially hindering target acquisition.
TV Guidance: Human Intervention
Terminal guidance can also involve TV guidance, where an operator employs a nose-mounted camera to identify the target and manually guide the missile visually. This dynamic approach allows operators to abort the strike if anomalies are detected, underscoring the human element in precision warfare.
Radar Seekers: Radar-Equipped Accuracy
Certain cruise missiles integrate radar seekers in their nose sections to identify and remain on course toward their targets during the terminal phase. These seekers may utilize passive radar to detect emissions from the target’s radar or active radar to emit signals for target detection.
Infrared (IR) Guidance: Homing in on Heat
Infrared (IR) guidance presents yet another terminal phase technique, steering missiles toward heat-emitting sources like engines. Despite its efficacy, IR guidance’s simplicity renders it incapable of distinguishing between friendly, adversarial, or extraneous IR signals in crowded battlefields. Consequently, it is often employed alongside other guidance systems.
Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC): Image-Reliant Precision
Among the diverse guidance methods, Digital Scene Matching Area Correlation (DSMAC) relies on an onboard camera to identify the target. This image is then compared to a stored reference image using an image correlator, accentuating the missile’s ability to refine target identification during the terminal phase.
Cruise Missiles: Transformative Force in Modern Warfare
Cruise missiles hold a pivotal role across all military branches, reshaping the landscape of modern warfare. Their effective utilization in contemporary conflicts has the potential to sway the outcome without resorting to nuclear options.
As technology advances, the horizon holds promises of more intelligent, self-managing, and hypersonic cruise missiles entering the global market. Irrespective of these changes, cruise missiles are poised to endure as one of the most dependable weapons in the foreseeable future.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Worth reading.

6 interesting facts about the flagship of the Russian Navy, Admiral...

How Important is the Nuclear Submarine?

How the CIA Supported Ukraine During the Conflict

Israel’s F-35I Adir : The Best version of the stealth fighter...

What Defines Fifth Generation Fighters?

What other aircraft fly with US President’s Air Force One?

Can any aircraft beat the F-22 Raptor?

How many aircraft carriers will China build?

The Reasons Behind Iran’s Attack on Israel

How the Israeli Air Force could bring Iran to its knees

Who are the leading suppliers to the Israeli army?

Israel-Iran tensions expose America’s difficult position in the Middle East.
- February 2024
- January 2024
- December 2023
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy
POPULAR CATEGORIES
- Weapons & Tech 559
- Worth Reading 243
Copyright©Militaryview.com 2023
After 30 years of dedicated service, the US Navy has decided...

Hi, what are you looking for?
19FortyFive
- Submissions
- Meet Our Editorial Team
- Contact Information for 19FortyFive
- Editorial Guidelines and Publishing Standards
- Privacy Policy
Uncategorized
Crusie missiles vs. ballistic missiles: what’s the difference.
These rocket motors carry the ballistic missile to a high altitude (boost phase) until the rocket fuel is entirely expended. At that point, known as the midcourse phase, the missile reaches its highest altitude before it begins to travel back down its arced flight path. For ICBMs, this phase can last up to 20 minutes, with the weapon itself traveling at speeds of around 15,000 miles per hour.
Cruise Basics
Cruise missiles don’t leave the atmosphere at any point during their flight, nor do they travel unpowered for any significant duration. Rather than rocket engines, cruise missiles are powered by turbofans just like many tactical aircraft, and most often, even have wings that deploy after they’ve launched. Some cruise missiles can even be guided into their target by remote operators using cameras on the weapon’s nose, again, not unlike piloting a drone or UAV.

Sandboxx News is a digital and print military media outlet focused on the lives, experiences, and challenges facing today’s service members and America’s defense apparatus. Built on the simple premise that service members and their supporters need a reliable news outlet free of partisan politics and sensationalism, Sandboxx News delivers stories from around the world and insights into the U.S. Military’s past, present, and future– delivered through the lens of real veterans, service members, military spouses, and professional journalists.

Recent Posts
- Can Russia Successfully Occupy Ukraine?
- Paris 2024 Summer Olympics: The Terrorism Threat Is Real
- 450,000 Dead or Wounded (Or More): Russian Losses in Ukraine are Truly Historic
- Russia and China Could Be at War Before the 2020s End
- Peace Activists Should Pressure Hamas, Not Just Israel

- PUBLICATIONS
- GRAPHICS WAREHOUSE
- SCRUTINY TOOLBOX
Key characteristics of ballistic and cruise missiles

Ballistic missiles present key advantages (See Table 1) compared with cruise missiles (the latter are propelled until impact and include a guidance system). Ballistic missiles can reach a longer range with lower fuel in a relatively short time (around 30 minutes for an ICBM). Their very high speed in the ballistic phase also makes them harder to intercept and destroy, even if they are easily detected. For these reasons, cruise missiles have not replaced ballistic missiles for carrying nuclear weapons at long range even if cruise missiles provide better precision and are harder to detect due to their low altitude trajectory. Nevertheless, the cost of developing ballistic missiles and the infrastructure they require make them much more expensive than cruise missiles.
European Parliamentary Research Service
How has parliament protected eu values and our fundamental rights, when eu temporary protection for displaced people from ukraine ends: possible scenarios, free movement rights of rainbow families, what europe does for filmmakers, choosing europe’s future: the 2024 espas report.
Be the first to write a comment.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
- What Europe does for me

EU legislation in progress

Download the EPRS App

- EP Plenary Sessions
- Cost of Non-Europe reports
- Latest Media
- Climate Change
- Russia's war on Ukraine
We write about
- Replies to campaigns from citizens
- What Europe does for you
- Economic and Social Policies
- EU Financing / Budgetary Affairs
- Institutional and Legal Affairs
- International Relations
- Policy Cycle
- Structural and Cohesion Policies
Social Media
- EP Think Tank
- Write to the European Parliament
- EP Library catalogue
Disclaimer and Copyright statement
The content of all documents (and articles) contained in this blog is the sole responsibility of the author and any opinions expressed therein do not necessarily represent the official position of the European Parliament. It is addressed to the Members and staff of the EP for their parliamentary work. Reproduction and translation for non-commercial purposes are authorised, provided the source is acknowledged and the European Parliament is given prior notice and sent a copy. For a comprehensive description of our cookie and data protection policies, please visit Terms and Conditions page. Copyright © European Union, 2014-2024. All rights reserved.

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- Cookie Policy
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.
More information about our Cookie Policy .
The present website is hosted by WordPress.com, a service by Automattic. Automattic is a global company with thousands of servers located in several separate data centres around the world. While Automattic takes care of the security of the platform , we, the European Parliamentary Research Service, own the content of the blog. For more detailed information about the compliance of Automattic products and services with the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), please see their dedicated page .
Data collected
We do not collect any personal data that could identify an individual user. The users that are registered in WordPress.com should consult wordpress.com terms of service . We do collect anonymised aggregate data for statistical purposes. The data collected for this purposes include: number of visits/visitors per page, the country of the user, and aggregate numbers of incoming and outgoing clicks.
We determine unique page counts by using a “hashed” version of the visitor’s IP address. The visitor’s full IP address is deleted from our logs after a little over a month. That timeframe is how long the data is needed in order to allow us to calculate your stats on a monthly basis and no longer.
We collect your email address only if you proactively requested to be notified about the updates on the blog. You can always contact us to remove your email address from our records or unsubscribe from the notification service.
We can also see your name and email address if you made a comment to one of our posts. We do not make the email address visible on the comment. Nevertheless, on request, we can delete your comments.
We collect cookies only to facilitate your browsing experience, such as enabling you to share our posts via social media or comment on the post. The majority of cookies will be used only if you are a registered WordPress.com user. In this case, you are bound to WordPress.com terms of service .
Some pages embed content from third parties. In this case, you will need to actively consent to their terms in order to see the content.
We do not collect cookies to show advertisement nor resell any information collected with cookies to third parties. Read more about the wordpress.com cookie policy and the way to control cookies on their dedicated page .
- Sandboxx News Home
What’s the difference between a cruise missile and a ballistic missile?
- By Alex Hollings
- January 7, 2022
Share This Article
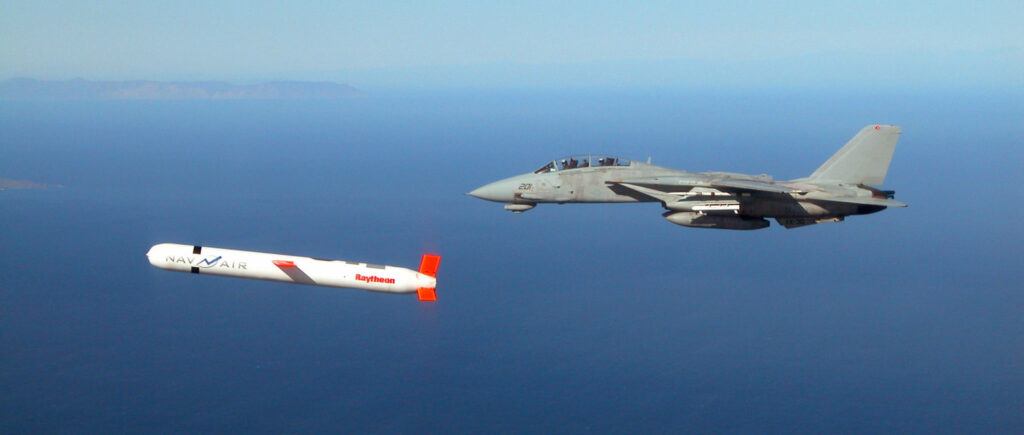

It’s not at all uncommon to see news stories featuring discussions about missile platforms and their capabilities, from Darpa’s recent test of a hypersonic cruise missile to discussions about the destructive power of Russia’s latest intercontinental ballistic missile, the RS-28 Sarmat . As a result, you may have found yourself wondering… what exactly is the difference between a ballistic missile and a cruise missile ?
In the interest of brevity, you can really sum up the difference between these types of weapons with the trajectory that they follow. A ballistic missile follows a “ballistic flight path,” which often includes traveling along a long arc, whereas a cruise missile tends to follow a straighter, lower altitude trajectory. Another easy (if not exactly precise) way to think about them is that ballistic missiles are more like rockets, while cruise missiles are more like aircraft or drones.
Ballistic missile basics
While both ballistic and cruise missiles can carry nuclear payloads, the most commonly understood (and feared) nuclear weapon delivery vehicle of the modern era falls under the ballistic category: the ICBM. And while there are many variations in the employment of different sorts of ballistic missiles, the ICBM model offers a simple way to appreciate the concept behind a “ballistic flight path.”
A ballistic missile is propelled into the air by a rocket motor, or often (as is the case with ICBMs) multiple staged rocket motors. ICBMs bear a striking resemblance to the rockets that take astronauts into space for good reason, other than the payloads these platforms carry, they are mechanically very similar.
Related: What exactly is America’s nuclear triad?
These rocket motors carry the ballistic missile to a high altitude (boost phase) until the rocket fuel is entirely expended. At that point, known as the midcourse phase, the missile reaches its highest altitude before it begins to travel back down its arced flight path. For ICBMs, this phase can last up to 20 minutes, with the missile itself traveling at speeds of around 15,000 miles per hour.
It then begins its unpowered descent, known as the terminal phase, traveling at speeds of nearly 2,000 miles per hour until it collides with its target.
Related: How do America’s nuclear submarines get resupplied at sea?
Cruise missile basics

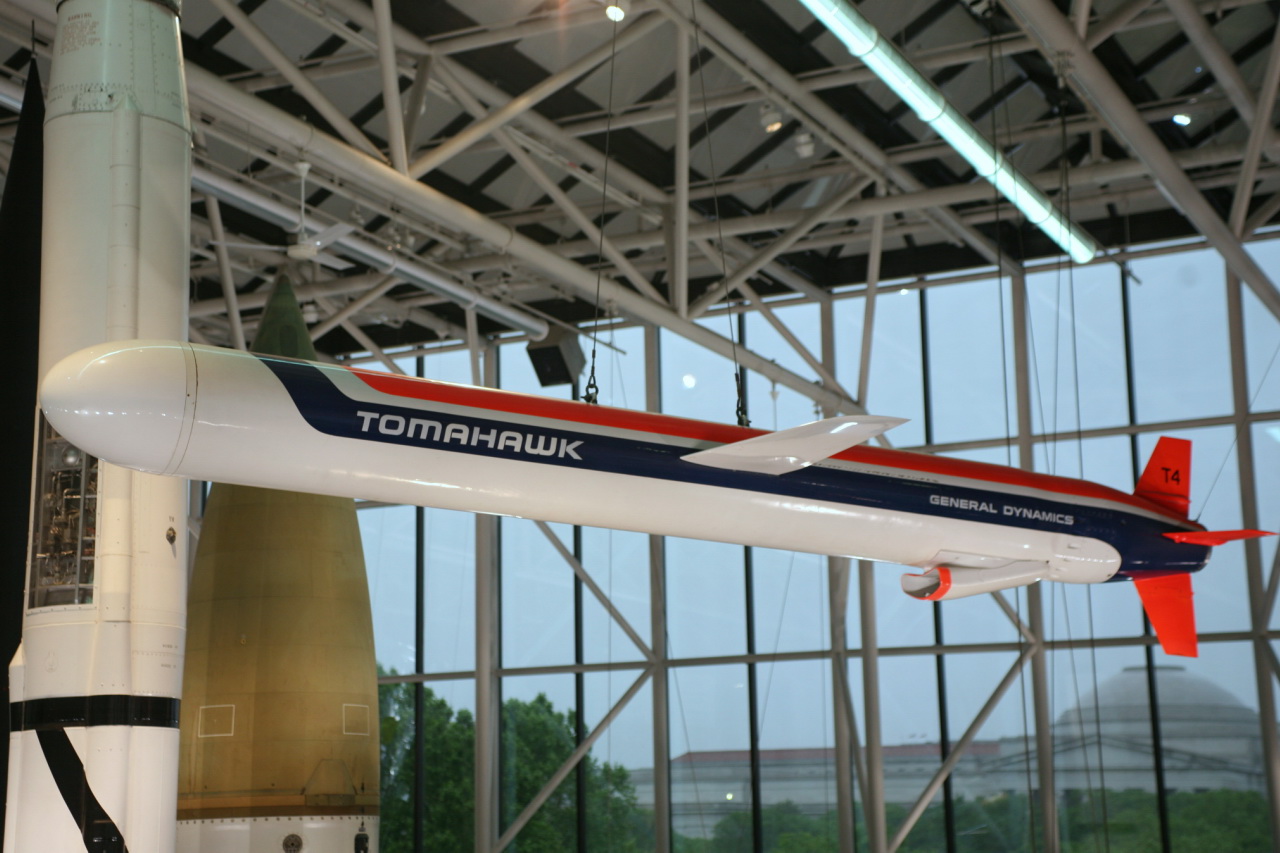
Unlike the long arcing trajectory of a ballistic missile, a cruise missile travels at lower altitudes and on far straighter trajectories. In fact, it might be easiest to think of a cruise missile as a drone of sorts that flies on its own to its intended target and then proceeds to crash into it. Perhaps the most commonly discussed cruise missile in modern use is the Tomahawk, which has become America’s weapon of choice for engaging targets at fairly long distances without deploying troops to a conflict.

Cruise missiles don’t leave the atmosphere at any point during their flight, nor do they travel unpowered for any significant duration. Rather than rocket engines, cruise missiles are powered by turbofans just like many tactical aircraft, and most often, even have wings that deploy after they’ve launched. Some cruise missiles can even be guided into their target by remote operators using cameras on the weapon’s nose, again, not unlike piloting a drone or UAV.
Modern cruise missiles are known for their range and excellent accuracy. In fact, the common rule of thumb regarding these weapons is, “It can fly 1,000 miles and hit a target the size of a single-car garage.”
Read more from Sandboxx News:
- 3 training basics every soldier needs to remember
- How do America’s nuclear submarines get resupplied at sea?
- A missile race is heating up all across Asia
- America’s plan to build 747 arsenal ships packed with cruise missiles
- America really launched an ICBM from the back of a C-5 cargo plane
Feature image: U.S. Navy
Related Posts
The air force’s dogfighting ai is already roughly equal in skill to career pilots.

Alex Hollings
Alex Hollings is a writer, dad, and Marine veteran.
Read More From Alex Hollings

- Fighter Aircraft
- Bomber Aircraft
- Interceptor aircraft
- Attack Aircraft
- Transport Aircraft
- Trainer Aircraft
- Maritime Patrol and ASW Aircraft
- Reconnaissance Aircraft
- Airborne early warning and control
- Electronic Warfare Aircraft
- Aerial Refueling Aircraft
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles
- Attack Helicopter
- Reconnaissance Helicopter
- Utility and Transport Helicopter
- Anti-Submarine Warfare Helicopter
- Aircraft Carrier
- Amphibious Ship
- Patrol Vessel
- Command Ship
- Main Battle Tank
- Armored vehicle
- Air Defense System
- Anti-ship Missiles
- Ballistic missile

Indonesia’s Harimau Tank Commissioned: Revolutionizing Modern Warfare

TAM 2C: Argentina’s Next-Gen Medium Tank Upgrade!

SAMI 155mm Self-Propelled Howitzer: Saudi Arabia’s Artillery Innovation

Sea Viper With Value Upgrade Package – Enhances Fleet’s Air Defense

Alsace Enters The Red Sea – Watch The Weapon Configuration Of…
- Missiles & Bombs
Difference Between Ballistic Missiles And Cruise Missiles
The most important advantage of a ballistic missile is its extremely high speed, extremely large range and can carry many warheads.
Ballistic missiles are generally divided into two categories, short-range ballistic missiles and long-range ballistic missiles (also known as intercontinental ballistic missiles). While short-range ballistic missiles have maximum altitude under the atmosphere, long-range ballistic missiles can reach space altitude before “falling” back to earth.
Due to its extremely high speed and high trajectory, ballistic missiles are extremely difficult to intercept. However, this type of missile is very easy to detect immediately after launch.

The second type of missile is more modern and also much more accurate, the cruise missile. Cruise missiles typically have a shorter range than long-range ballistic missiles, but their accuracy is extremely high.
Basically, a cruise missile is like a jet, it will use an engine to continuously maintain speed, can “glide” in the air, change the trajectory even on the fly. This gives cruise missiles a great deal of flexibility, able to fly at low or high altitudes. It can change its target while in flight, and change its altitude through each phase to ensure secrecy and surprise.
Thanks to its high accuracy, cruise missiles can hit even moving targets, such as enemy warships. Most anti-ship missiles today are cruise missiles. However, due to the need for fuel during flight, the cruise missile has a limited range, and its weight and number of warheads are also limited, often with a single warhead.
The maximum speed of the cruise missile is also not too high, usually only from Mach 0.8 like the Nirbhay missile to Mach 3 like the BrahMos missile. With hypersonic missiles, the speed is no more than Mach 5.
Due to its high accuracy, cruise missiles are often equipped with conventional warheads. Meanwhile, ballistic missiles are often equipped with nuclear warheads, enough to destroy the target even though the accuracy is not high.
RELATED ARTICLES MORE FROM AUTHOR
Alsace enters the red sea – watch the weapon configuration of french frigate.

China SH11 – 155mm SPH For Shoot And Scoot Role

Uragan-1M Entered The War – Russia’s Answer To HIMARS Attacks

China HHQ-10 – Similar To The US RAM RIM-116, The Final Shield Of Warships

China Type 054B – PLA Navy Next-Gen Frigate

Bushmaster 25mm – Weapons Make Up Bradley’s Strength

Ukraine’s Su-24 – More Powerful With AASM Hammer 1000 And SCALP-EG
Russian su-30k – ethiopia is the latest customer.

T-90M Proryv was defeated by M2 Bradleys – Revealing Fatal Weakness
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Follow me on socials
Recent posts, js atago ddg-177 – the power of japan’s most prestigious destroyer in asia, ee-9 cascavel – six-wheeled brazilian armoured car, lockheed u-2 dragon lady – the iconic spy plane of the us air force, short c-23 sherpa – once a us army valuable asset, landing where the c-130..., why did the ch-47 chinook become a symbol of withdrawal.

POPULAR POSTS

The POWER of Russia’s Murmansk-BN electronic warfare complex

Mikoyan Mig-41 – Russia’s top-secret 6th generation fighter frightens the US

USS Theodore Roosevelt has arrived in Philippine waters
Popular category.
- The Land 945
- The Air 888
- The Sea 498
- Fighter Aircraft 410
- Ukraine Conflict 305
- Armored vehicle 301
- Main Battle Tank 249
- Frigate 124

Surprised: Croatia Chooses Expensive 2hand Rafale Rather Than Buying F-35

UPPSC Exam 2024 UPPSC Syllabus UPPSC Application Form 2024 UPPSC Eligibility Criteria UPPSC Admit Card UPPSC Study Plan & Strategy UPPSC Previous Year Questions UPPSC Cut Off Marks UPPSC Salary And Posts
UPPSC RO ARO Qualification UPPSC RO ARO Exam 2023 UPPSC RO ARO Post and Salary UPPSC RO ARO Previous Year Paper
BPSC 69th Notification BPSC 69th Prelims Result BPSC 69th Cut Off 69th BPSC Prelims Answer Key BPSC Syllabus BPSC Exam Pattern BPSC Cut Off Marks 67th BPSC Mains Admit Card 2022 67th BPSC Mains Exam Date 2022
Bihar APO Mock Interview
APSC CCE Exam Notification APSC CCE Prelims Answer Key 2023 APSC CCE Syllabus & Exam Pattern APSC CCE Prelims Result 2023 APSC CCE Admit Card 2023 APSC CCE Eligibility Criteria APSC CCE Previous Year Papers APSC CCE Cut Off 2023 APSC CCE Salary & Job Profile
MPPSC Calendar 2024 MPPSC Syllabus MPPSC Exam Pattern MPPSC Admit Card 2023 MPPSC Eligibility Criteria MPPSC Previous Year Paper MPPSC Cut Off MPPSC Salary And Job Profile
HPSC Notification HPSC Syllabus HPSC Exam Pattern HPSC Admit Card HPSC Cut Off HPSC Previous Year Paper HPSC Salary And Job Profile
WBPSC Syllabus WBPSC Eligibility Criteria WBPSC Application Form WBPSC Previous Year Questions WBPSC Salary & Job Profile
MPSC Notification MPSC Syllabus And Exam Pattern MPSC Application Form MPSC Eligibility Criteria MPSC Age Limit
CGPSC Syllabus And Exam Pattern CGPSC Question Paper 2023 CGPSC Answer Key 2023 CGPSC Admit Card 2023 CGPSC Eligibility Criteria CGPSC Salary And Job Profile
UKPSC Notification UKPSC Exam Calendar 2023 UKPSC Syllabus And Exam Pattern UKPSC Eligibility Criteria UKPSC Application Form 2023
JPSC Syllabus & Exam Pattern JPSC Eligibility Criteria JPSC Previous Year Papers
JKPSC Notification JKSC Syllabus And Exam Pattern JKSC Eligibility Criteria
RPSC RAS Syllabus RPSC RAS Exam Pattern RPSC RAS Eligibility Criteria RPSC RAS Cut Off
HPPSC Syllabus And Exam Pattern HPPSC Eligibility Criteria HPPSC Previous Year Question Papers and cut off
End of Content.
- Why IAS NEXT ?
- How to Choose Best IAS Coaching ?
- How to Choose Best Judiciary Coaching ?
- Admission Procedure
- Download Brochure
Clear Prelims 2024
- Sociology Optional
- Geography Optional
- UPSC Mentorship Program
- IAS With Graduation Degree
- UPPSC Mentorship Program
- Sociology by Sudhanshu Mishra
- Intensive IAS Program (Prelim + Mains)
- Intensive PCS Program (Prelim + Mains)
- Intensive PCS-J / Judicial Services Program
- UPSC IAS Mock Interview
- Interview Guidelines
- Interview Transcripts
- Interview Material PCS - J
- Civil Services Test Series
- NCERT TEST SERIES
- Sociology Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series 2024
- UPSC Mains Test Series 2024
- UP PCS Mains Test Series 2024
- Judiciary Test Series
- PCS-J Test Series
- DJS Preliminary Exam
- Latest Current Affair Blogs
- Daily Current Affairs 2024
- March Current Affairs
- Daily Current Affairs 2023
- December Current Affairs
- November Current Affairs
- October Current Affairs
- September Current Affairs
- August Current Affairs
- July Current Affairs
- June Current Affairs
- May Current Affairs
- April Current Affairs
- February Current Affairs
- Down to Earth Summary
- Prelims Special
- UPSC Topper's Notes
- Previous Year Question
History
Geography
Indian Polity
Indian Economy
Science & Technology
Indian Culture and Heritage
Art & Culture
Psychology
Chemistry
Political Science
About Civil Services
CSE Prelims Syllabus
GS Prelims Strategy
UPSC Preparation Strategy
Civil Services Aptitude Test
Previous Year Questions
- Study Materials
Indian Heritage & Culture
Ancient Indian History
Medieval Indian History
Modern Indian History
World History
World Geography
Indian Geography
Geography by Maps
Internal Security
Social Justice
Indian Polity
International Relations
Agriculture
Environment & Ecology
Science Technology
Disaster Management
World History
Ancient History
Medieval History
Modern History
Indian Society
Art and Culture
Indian Geography
World Geography
Indian Polity
Governance
International Relations
Social Justice
Social Issues
Agriculture
Security Issues
Disaster Management
Environment & Ecology
Cruise Missiles vs Ballistic Missiles

- General Studies- Paper III , UPSC Examination
- Tap For Tech
A Cruise Missile is a guided missile that flies with constant speed to deliver a warhead at specified target over long distance with high accuracy. A Ballistic Missile is lift off directly into the high layers of the earth’s atmosphere.

Cruise Missiles
Cruise missiles are unmanned vehicles that are propelled by jet engines, much like an airplane . They can be launched from ground, air, or sea platforms. Cruise missiles remain within the atmosphere for the duration of their flight and can fly as low as a few meters off the ground. Flying low to the surface of the earth expends more fuel but makes a cruise missile very difficult to detect. Cruise missiles are self-guided and use multiple methods to accurately deliver their payload, including terrain mapping, global positioning systems (GPS) and inertial guidance, which uses motion sensors and gyroscopes to keep the missile on a pre-programmed flight path. As advanced cruise missiles approach their target, remote operators can use a camera in the nose of the missile to see what the missile sees. This gives them the option to manually guide the missile to its target or to abort the strike.
- A cruise missile is a guided missile (target has to be pre-set) used against terrestrial targets.
- It remains in the atmosphere throughout its flight.
- It flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed.
- Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
- Modern cruise missiles are capable of travelling at supersonic or high subsonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory.
Types of cruise missiles based on speed
- Hypersonic (Mach 5): These missiles would travel at least five times the speed of sound (Mach 5). E.g. BrahMos-II.
- Supersonic (Mach 2-3): These missiles travel faster than the speed of sound. E.g. BrahMos.
- Subsonic (Mach 0.8): These missiles travel slower than the speed of sound. E.g. Nirbhay.
Ballistic Missile
Ballistic missiles are powered initially by a rocket or series of rockets in stages, but then follow an unpowered trajectory that arches upwards before descending to reach its intended target . Ballistic missiles can carry either nuclear or conventional warheads. There are four general classifications of ballistic missiles based on their range, or the maximum distance the missile can travel:
- A ballistic missile follows a ballistic trajectory to deliver one or more warheads on a predetermined target.
- A ballistic trajectory is the path of an object that is lift of but has no active propulsion during its actual flight (these weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods of flight).
- Consequently, the trajectory is fully determined by a given initial velocity, effects of gravity, air resistance, and motion of the earth ( Coriolis Force ).
- Shorter range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Long-range intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), are lift off on a sub-orbital flight trajectory and spend most of their flight out of the atmosphere.
Also read : petaFLOP Supercomputers
Types of ballistic missiles based on the range
- Short-range (tactical) ballistic missile (SRBM): Range between 300 km and 1,000 km.
- Medium-range (theatre) ballistic missile (MRBM): 1,000 km to 3,500 km.
- Intermediate-range (Long-Range) ballistic missile (IRBM or LRBM): 3,500 km and 5,500 km.
- Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM): 5,500 km +

How Cruise Missiles different from Ballistic Missiles?
Cruise missiles are unmanned vehicles that are propelled by jet engines, much like an airplane. They can be lift off from ground, air, sea or submarine platforms . Cruise missiles remain within the atmosphere for the duration of their flight and can fly as low as a few meters off the ground. Flying low to the surface of the earth expends more fuel but makes a cruise missile very difficult to detect . Cruise missiles are self-guided and use multiple methods to accurately deliver their payload, including terrain mapping, global positioning systems (GPS) and inertial guidance.

Also Read: Solid Fuel Ducted Ramjet Technology
Read more: missiles, indian missiles, missiles of india, ballistic meaning, ballistic missile, ballistic, cruise missiles of india
- Ballistic Missiles , Cruise Missiles
Demo Class/Enquiries
Clear pcs-j program ( pre + mains ), clear prelims - cap for upsc 2024, weekend programme for upsc- ias, upsc mains answer writing program, weekly pcs-j answer writing, current affairs magazine.

Green Hydrogen

Key Biodiversity Areas

World Anti-Doping Report 2022

Right To Information Act

Black Carbon

Digital Governance in India

The Ultimate Guide to Voting Green in the Indian Elections

Bone Grafting Technology in India

Schemes under Ministry of Women and Child Development
Upsc study materials.
- Answer Writing
- Career Guidance
- Current Affairs
- Down to Earth
- General Studies- Paper I
- General Studies- Paper II
- General Studies- Paper III
- General Studies- Paper IV
- Indian Penal code
- Landmark Judgements
- Law Entrance Exams
- LEGAL TERMS
- Legal Updates
- Miscellaneous
- Notification
- Other Topics
- PCS J Examination
- PCS-J STUDY MATERIALS
- Reports & Indices Current Affairs
- Sucess Story
- UGC NET Law
- UPPSC Examination
- UPPSC SYLLABUS
- UPSC Examination
- UPSC Prelims

Ancient India -for UPSC and other State PCS Examination

Art &Culture : for UPSC & State PCS (Mains)

Environment and Ecology : for UPSC and state PCS

Geography: Hand book for UPSC & State PCS

Indian Economy (GS) for IAS Prelims and Mains

Indian Constitution and Polity

Medieval History : For UPSC & State PCS

Medieval India : For UPSC & State PCS

Science & Technology for UPSC & State PCS

Modern History : For UPSC & State PCS

- General Enquiry : +91 9454721860
- Admin Enquiry : +91 7991861111
- Alternate Number : 05224241011
- [email protected]
- Monday to Friday: 9.00am - 8.00pm
- Free Download
- Test Series
- Study Material
- Topper's Notes
- Previous Year Questions
- IAS Next Franchise
- Web Stories
Copyright © C S NEXT EDUCATION. All Rights Reserved


Difference Between Cruise and Ballistic Missiles
Cruise missiles are guided, low-altitude, and precise. Ballistic missiles are unguided, high-speed, long-range, and follow a high trajectory. Check Difference between Cruise and Ballistic Missiles.

Table of Contents
Cruise missiles are guided, jet or propeller-driven projectiles that can fly at low altitudes, follow a flexible path, and are capable of precision strikes. Ballistic missiles, on the other hand, are unguided, rocket-powered weapons that follow a high, arching trajectory before descending toward their target. They are typically much faster and have longer ranges, but they lack the in-flight manoeuvrability of cruise missiles, making them more suitable for long-range and strategic strikes.
Recently North Korea continued its weapons testing, firing cruise missiles amidst escalating tensions and “war preparations” against South Korea. Know the Difference between Cruise and Ballistic Missiles in This article.
Cruise Missiles
Cruise missiles are self-propelled, guided weapons that can be launched from various platforms, including aircraft, ships, or ground-based launchers. They are designed to fly at low altitudes and can be programmed to follow a specific flight path, often hugging the terrain, which makes them difficult to detect and intercept. Cruise missiles can carry various types of warheads and are used for precise, long-range strikes on specific targets, such as military installations, infrastructure, or high-value targets. Their ability to navigate and adapt during flight provides them with a high degree of accuracy.
Examples of Cruise missiles
- Tomahawk: The United States Navy’s Tomahawk cruise missile is one of the most well-known examples. It’s used for long-range precision strikes and can be launched from ships and submarines.
- BrahMos: A joint venture between India and Russia, the BrahMos cruise missile is one of the fastest supersonic cruise missiles in the world.
- AGM-86 ALCM: The United States Air Force employs the AGM-86 Air-Launched Cruise Missile as a nuclear-armed cruise missile.
- Storm Shadow / SCALP: Developed by France and the UK, this air-launched cruise missile is used for precision strikes against high-value targets.
- Kalibr: A family of cruise missiles used by Russia, including anti-ship, land-attack, and anti-submarine variants.
- JASSM: The Joint Air-to-Surface Standoff Missile, used by the United States and several other countries, is designed for precision strikes against high-value, well-defended targets.
We’re now on WhatsApp . Click to Join
Ballistic Missiles
Ballistic missiles are unguided rockets that follow a high, parabolic trajectory when launched, ascending into space and then descending rapidly toward their target. They can carry nuclear or conventional warheads and are categorized based on their range: short-range, medium-range, intermediate-range, and intercontinental-range missiles.
Ballistic missiles are known for their high speed and long-range capabilities, making them suitable for delivering strategic or long-range strikes. Unlike cruise missiles, they lack in-flight manoeuvrability but rely on their high velocity and trajectory to reach their intended targets. They are a key component of many countries’ military arsenals.
Examples of Ballistic Missiles
- Intercontinental Ballistic Missile (ICBM): The Minuteman III ICBM used by the United States is a prime example, designed for delivering nuclear payloads over intercontinental distances.
- Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile (SLBM): The Trident II D5, used by the U.S. Navy, is an example of an SLBM capable of being launched from submarines.
- Medium-Range Ballistic Missile (MRBM): The Russian Iskander-M is an MRBM used for shorter-range precision strikes.
- Short-Range Ballistic Missile (SRBM): The North Korean Hwasong-15 is an example of a SRBM with an extended range, designed for regional threats.
- Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missile (IRBM): The Chinese DF-26 is an example of an IRBM designed for regional and strategic purposes.
Here you can check the major Differences Between Cruise and Ballistic Missiles:
Ballistic vs. Cruise Missiles

Sharing is caring!
Difference Between Cruise and Ballistic Missiles FAQs
What's the main difference between cruise and ballistic missiles.
Cruise missiles are guided, air-breathing, and offer in-flight maneuverability, while ballistic missiles are unguided, rocket-powered, and follow a high-arching trajectory.
Is cruise missile better than ballistic missile?
The suitability of cruise or ballistic missiles depends on the mission. Cruise missiles excel at precision strikes, while ballistic missiles offer long-range and high-speed capabilities for strategic objectives.
Which is faster ballistic or cruise?
Ballistic missiles are generally faster than cruise missiles. Ballistic missiles can travel at supersonic to hypersonic speeds, while cruise missiles are typically subsonic or supersonic but slower than ballistic missiles.
Is the BrahMos cruise or ballistic?
The BrahMos is a cruise missile. It is a supersonic cruise missile developed jointly by India and Russia and is known for its high speed and precision in striking targets.
Greetings! I'm Piyush, a content writer at StudyIQ. I specialize in creating enlightening content focused on UPSC and State PSC exams. Let's embark on a journey of discovery, where we unravel the intricacies of these exams and transform aspirations into triumphant achievements together!
- science and tech

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Exam 2024
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form

Recent Posts
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
IB ACIO Exam
- IB ACIO Salary
- IB ACIO Syllabus
CSIR SO ASO Exam
- CSIR SO ASO Exam 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Result 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date
- CSIR SO ASO Question Paper
- CSIR SO ASO Answer key 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Exam Date 2024
- CSIR SO ASO Syllabus 2024
Study Material Categories
- Daily The Hindu Analysis
- Daily Practice Quiz for Prelims
- Daily Answer Writing
- Daily Current Affairs
- Indian Polity
- Environment and Ecology
- Art and Culture
- General Knowledge
- Biographies
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
Why it’s so hard to defend against cruise missiles
A recent conference raises the question: What kind of threat does this type of weapon pose to the United States?
By Kelsey D. Atherton | Published Jul 25, 2022 7:00 AM EDT

On July 14, the Center for Strategic and International Studies in Washington, DC held a one-day conference premised on a specific threat: What if, in the future, war comes to the United States via cruise missile? Pointing to new developments in cruise missile technology, and the limitations of existing early warning systems that are focused on the high arcing trajectories of ballistic missiles, the CSIS conference and accompanying report suggests that to defend the continental United States from such a threat, the military should adapt and deploy the kind of cruise missile defenses presently used as regional weapons.
Unlike ballistic missiles, which arc up into space before traveling back down towards earth, cruise missiles fly close to the ground, making it hard for radar on the ground that’s pointed up at space to see them.
The perceived threat from new cruise missiles is driven by tech developments occurring across the globe, as new materials, better aerodynamics, and sophisticated sensors and guidance systems make possible the fielding of weapons, like hypersonic missiles , that had mostly been just theoretical decades ago.
For the United States, the development of long-range bombers in the 1940s, followed by the development of intercontinental ballistic missiles, shattered the notion that the enormous distances of the Atlantic and Pacific oceans were enough to protect the continental US from direct attack. (During World War II, US territories in the Pacific came under direct attack, but the only long-range assault on the 48 states came in the form of incendiary-carrying balloons launched by Japan into the jet stream and carried over to the US.)
With atomic and then thermonuclear payloads, bombers and long-range missiles threatened devastation on an unprecedented scale, and the United States built an elaborate system of early warning sensors focused on detecting early signs of launch, and expanded its first-in-the-world nuclear arsenal to deter attack. North American Aerospace Defense Command (NORAD) is run by both Canada and the United States, and maintains a series of radars and other sensors designed to detect early attacks across the Arctic or elsewhere. (Every December, NORAD highlights its existence by tracking Santa Claus, turning a system designed to detect oblivion into a kid-friendly Christmas tradition .)
At the conference held by CSIS, the threat from cruise missiles was discussed as a way that other countries could attack the United States that is hard to detect by employing existing, ICBM-focused measures. It is also considered hard to deter through threat of nuclear retaliation, operating on the assumption that if a cruise missile with a conventional warhead destroyed a building or killed people in the United States, the President would not immediately respond with a nuclear strike.
“You know, our adversaries are building diverse, expansive ranges of modern offensive missile systems, and we see them – we see them in the news every day,” Stan Stafira, Chief Architect of the Pentagon’s Missile Defense Agency, told the panel. “They’re capable of maneuvering in the midcourse and the terminal phases of their flight, like maneuvering reentry vehicles, multiple independent reentry vehicles, hypersonic glide vehicles, and cruise missiles.”
Part of the broader appeal of hypersonic weapons to nations like Russia, China, and the United States is that the speed and trajectories of the missiles make them harder to detect than ICBMs. The ballistic arc of ICBMs means the launch is visible to radar while it is still ascending, once it clears the horizon line. Meanwhile, both hypersonic glide vehicles and hypersonic cruise missiles, which travel at Mach 5 or above, are designed to fly below that radar horizon, with the cruise missile keeping a close trajectory to earth and the glide vehicle flying in the high atmosphere.
“I want to state that we absolutely believe that nuclear deterrence is the foundation of homeland defense,” said Lieutenant General AC Roper, deputy commander of Northern Command, the part of the US military responsible for North America. “However, we also must have credible deterrence options below the nuclear thresholds, options which allow for a balanced approach of deterrence by denial and deterrence by punishment or cost imposition.”
Deterrence, at its most straightforward, is a strategy of making a big threat on a condition: One country publicly declares it will launch nukes at another if it launches nukes at it, with the intended effect that neither country launches nukes. But because the payload of a cruise missile—it could be nuclear or conventional, unlike ICBMs, which are always nuclear—is unlikely to be known until impact, generals like Roper would prefer to have a range of weapons with which to respond.
Missile defense is one of those options, and the US already employs a few forms. Part of any missile defense system is the sensors, like specially focused radar, that can detect incoming attacks, and then track those weapons as they travel. These radars then send that tracking information to interceptors, which are missiles launched to fly and destroy the incoming attacking missile. Shooting missiles at other missiles is a hard problem because an incoming threat arrives at great speed, and because the cost calculus can favor an attacker. Interceptors, like shorter-ranged Patriot missiles or longer-ranged ballistic interceptors , are often more expensive than the missiles they are intercepting. And unlike interceptors, which have to hit precisely to work, missiles launched in attack can deploy decoys or countermeasures to redirect interceptors away, or can instead be fired in a greater volume, overwhelming interceptors through sheer numerical advantage.
“The resulting 20-year cost to provide even a light defense of a vast area ranged from $77 billion to $466 billion,” reads the CSIS report , citing an analysis from the Congressional Budget Office studying a range of cruise missile defense options. “The considerable cost variation is due to alternative combinations of sensors and interceptors and varying desired warning times of 5 or 15 minutes.”

Kelsey D. Atherton is a military technology journalist who has contributed to Popular Science since 2013. He covers uncrewed robotics and other drones, communications systems, the nuclear enterprise, and the technologies that go into planning, waging, and mitigating war.
Like science, tech, and DIY projects?
Sign up to receive Popular Science's emails and get the highlights.
Difference Between Ballistic And Cruise Missile With Examples
A missile is one of the most important technological advanced projectile which is used for various purpose like scientific, military and space exploration. Missiles are guided and self propelled vehicles that can carry payload such as explosive warheads. In this article we are going to study about different types of missiles and difference between ballistic and cruise missile , cruise missile vs ballistic missile.
Table of Contents
Ballistic Missile Meaning
These are based on rocket technology, to maximize range they are fired at 45 degree, the long range ballistic missile are known as re-entry vehicles because they complete their journey in endo and exo atmosphere. They have three phases to take off midcourse, race and termination.
Classification of Ballistic missile
These are classified on various parameters i.e. Nature and Range.
- Nature – on the basis of nature they are surface to surface, surface to air, and air to air missiles.
- Short-Range Ballistic Missiles (SRBMs ) : These missiles range up to 700 km, it is a single stage solid fuel based. Examples : Iskander Missile (Russia), DF21 (China), LORA (Israel), Ghaznavi (Pakistan), Prithvi missile (India).
- Medium-Range Ballistic Missiles (MRBMs) : These missiles range range between approximately 1,000 and 3,000 kilometres (620 to 1,860 miles). Example Hwasong-12 (North Korea), Agni 1 (India), Khoramshahr 4 (Iran).
- Intermediate-Range Ballistic Missiles (IRBMs) : IRBMs missiles have a range between around 3,000 and 5,500 kilometres (1,860 to 3,420 miles). Example : Agni missile 2, 3, 4.
- Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) : ICBMs have the longest range exceeding 5,500 kilometres (3,420 miles). They are designed to travel across continents or even around the world. Example : RS 28 Sarmat (Russia), Minuteman III (United States), Dongfeng-41 (China), Hwasong-15 (North Korea) Agni 5 (India).
- Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs) : These missiles are launched from submarines.
- Hypersonic Ballistic Missiles : missiles travel at speeds greater than Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound).
- Anti-Ship Ballistic Missiles (ASBMs) : ASBMs are designed to target ships, particularly aircraft carriers and other naval vessels.
Cruise missile
Cruise Missile is based on jet technology. Travels only in endo atmosphere, and move parallel to earth’s surface therefore airborne radars are completely effective in detecting them. These missiles are equipped with guidance systems.
Classification of Cruise missile
- Subsonic : These are guided missile that travels at speeds slower than the speed of sound, which is approximately 343 meters per second (or 1,125 feet per second). Example Nirbhay, Tomahawk, Harpoon Missile.
- Supersonic Missile : travels at speed which is more than speed of sound. Example Brahmos, kh 47m2 Kinzhal.
- Hypersonic : Travels at speeds which is greater than the speed of sound. Speeds are generally considered to be Mach 5 (five times the speed of sound) or faster. Example : Brahmos 2, Kh-47M2 Kinzhal.
Nirbhay Missile

- It is India’s subsonic cruise missile with speed of 0.7 mach with range of 1100- 1300 km.
- It is nuclear capable and operated on principle of fire and forget.
- Nirbhay missile is not a stalled missile but to avoid detection from radar if enemy, it follows tree top trajectory.
- It is that uncomfortable fight for enemies’ radar which makes it difficult for them to detect consignment.
Tomahawk Missile

- It is a USA subsonic cruise missile with speed of 0.74 mach with range of approximately 2400 km.
- Tomahawk is a long range, all weather missile, primarily used by the United States of America Navy.
- It has an Inertial Navigation System , flies at very low altitude and during flight it can be reprogrammed to change target.
Brahmos Missile
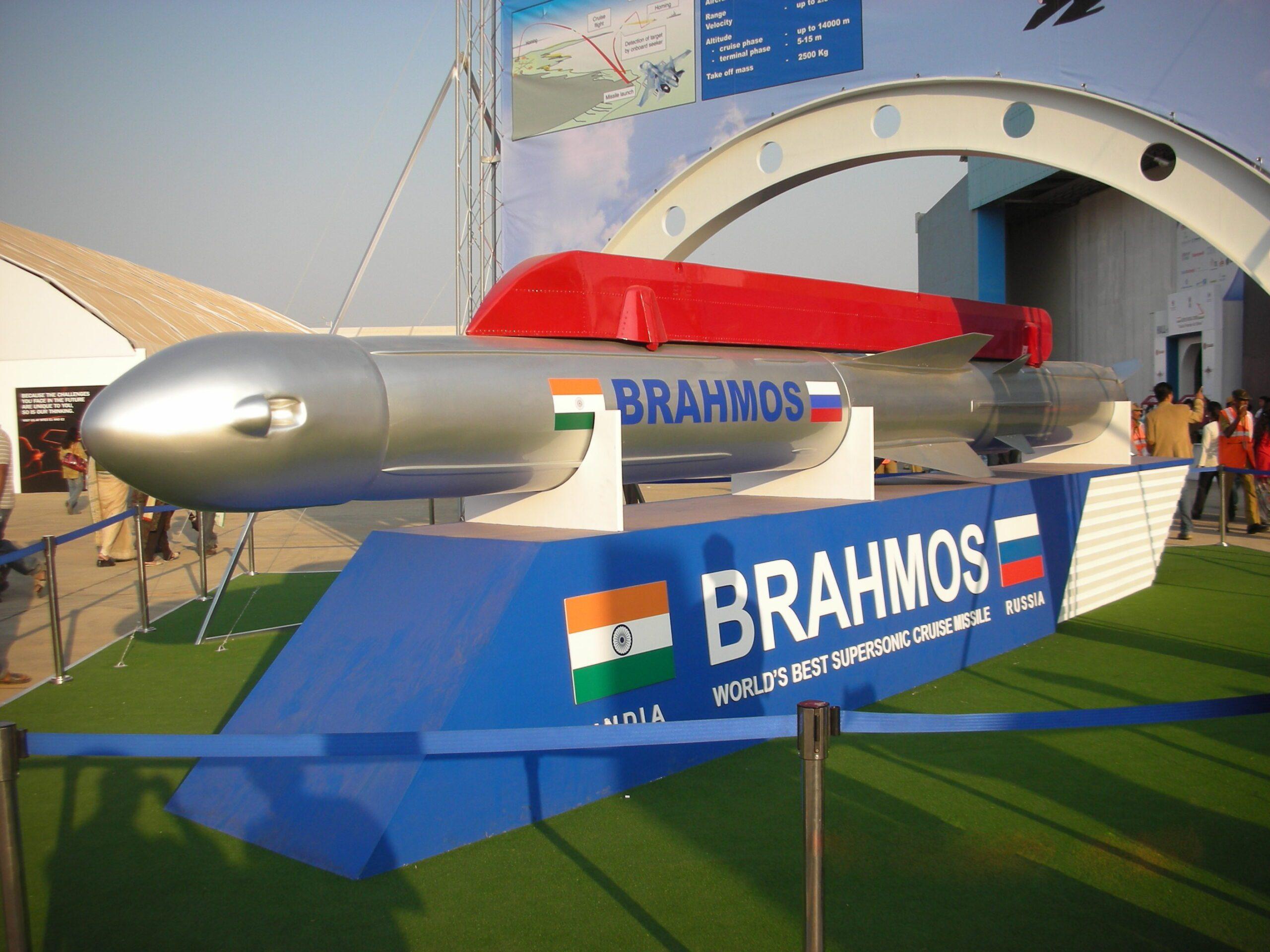

- Fastest cruise missile in the world in its category.
- The Brahmos missile speed is Mach 2.8 and has a range of 290 kilometres, or approximately three times the speed of sound.
- The Brahmaputra and Moskva rivers in Russia inspired the its name, which was jointly developed with Russia.
Difference Between Ballistic And Cruise Missile
Also Read :
- Indian Ballistic Missile Defence Programme And System
Are ballistic missiles better than cruise?
Yes ballistic missiles are better than cruise, ballistic are not restricted to atmosphere they can travel both above it and into the outer space.
Is BrahMos a cruise or ballistic missile?
It is Supersonic Cruise Missile.
Is Agni a ballistic missile?
Yes, Agni is a ballistic missile.
Arshil Iqbal
A BCA graduate, Web developer, Technophile and a reading enthusiast who likes to research and explore. Now professionally utilising my technical skills in blogging to create information and engaging content.
Related Posts
Application Of Computer Graphics In Different Fields (2024)
10 Advantages Of Computer In Daily Life
Third Generation Of Computer With Examples (Simple Terms)
What Is Electrostatic Precipitator, Working With Diagram ?
What Is Fog Computing In IoT VS Edge Computing ?
- Bihar Board
RBSE Result 2024
Srm university.
- Goa Board Result 2024
- Maharashtra HSC Result
- Maharashtra SSC Result
- RBSE 10th Result 2024
- RBSE 12th Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
- general knowledge
What is the difference between Ballistic Missile and Cruise Missile?
There are two major types of missiles- ballistic and cruise. the article below enlists the difference between the two categories and details it. take a look at the difference between cruise missile and ballistic missile below. .

Ballistic Missiles vs Cruise Missiles: About
Ballistic Missile:
Any missile is called Ballistic when the trajectory it follows is ballistic. It is used to deliver one or more warheads on a predetermined target.
A ballistic trajectory is the path of any object that is launched but with no active propulsion during its actual flight. Thus in such missiles the trajectory has to be fully determined by a given initial velocity, effects of gravity, air resistance and earth's motion.
Cruise Missile:
It is a guided missile where the target is pre-set. It is basically used against terrestrial targets.
Such missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
Difference between Ballistic Missile and Cruise Missile:
Cruise Missiles type:
Hypersonic (Mach 5): These travel at least five times the speed of sound (Mach 5).
Supersonic (Mach 2-3): These missiles travel faster than the speed of sound.
Subsonic (Mach 0.8): These missiles travel slower than the speed of sound.
Ballistic Missile Type:
Short-range (tactical) ballistic missile (SRBM): 300 km to 1,000 km range
Medium-range (theatre) ballistic missile (MRBM): 1,000 km to 3,500 km range
Intermediate-range (Long-Range) ballistic missile (IRBM or LRBM): 3,500 km to 5,500 km range
Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM): Above 5,500 km range
Also Read| GK Quiz on Election Commission of India (ECI)
Get here current GK and GK quiz questions in English and Hindi for India , World, Sports and Competitive exam preparation. Download the Jagran Josh Current Affairs App .
- Which countries have intercontinental ballistic missiles? + Russia, the United States, China, France, India, North Korea and the United Kingdom
- How high do ballistic missiles fly? + It can fly almost 4500 kilometres before it reaches back to Earth.
- Are ballistic missiles nuclear? + Almost all longer-range ballistic missiles and various types of cruise missiles carry nuclear warheads.
- IPL Schedule 2024
- Fastest 50 in IPL 2024
- National Dengue Day
- India T20 World Cup Squad 2024
- Buddha Purnima 2024
- IPL 2024 Points Table
- Mother's Day Quotes, Wishes
- Ram Navami 2024
- Purple Cap in IPL 2024
- WB HS Result 2024
Latest Education News
RBSE 12th Result 2024 LIVE: Check Rajasthan Board Arts, Commerce and Science Result Online at rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, Jagran Josh with Roll Number
Indian Army TES 52 Notification 2024: Registration Begins from May 13 on joinindianarmy.nic.in
Indian Air Force Agniveer Recruitment 2024: Apply Online for Agniveervayu Posts at agnipathvayu.cdac.in
[Fast Update] IPL Points Table 2024: आईपीएल 2024 अपडेटेड पॉइंट टेबल यहां देखें, KKR और RR, SRH, RCB Qualify
IPL 2024 Qualifier, Eliminator: कब, कहां और किसके बीच होगा क्वालीफायर और एलिमिनेटर, Tickets और Live Streaming कैसे देखें
IPL 2024 Playoffs Teams: इन 4 टीमों का प्लेऑफ टिकट कन्फर्म! KKR, SRH और RR के बाद किसका नंबर
Maharashtra Board Result 2024: MSBSHSE HSC, SSC Result at mahresult.nic.in, mahahsscboard.in
Maharashtra Board 12th Result 2024: MSBSHSE HSC Result at mahresult.nic.in, mahahsscboard.in
Most Sixes In IPL 2024: आईपीएल में चौकों-छक्कों की रेस में कौन सबसे आगे? Sharma जी ऑन Top
RBSE Vrishth Upadhyay Result 2024: राजस्थान वरिष्ठ उपाध्याय रिजल्ट Link at Jagran Josh, rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, rajresults.nic.in
MBSE 12th Result 2024: Mizoram Board Class 12 Result Date And Time at mbse.edu.in
MBSE Result 2024: Check Mizoram Board Result at mbse.edu.in
Optical Illusion Eye Test: Find the nobleman’s hat in the picture in 5 seconds!
RBSE Result 2024 Kab Aayega: कल 12.15 PM पर जारी होगा राजस्थान बोर्ड 12वीं का रिजल्ट, rajresults.nic.in पर मिलेगा Result Link
RBSE 12th Result 2024 Science: राजस्थान 12वीं विज्ञान रिजल्ट Link at Jagran Josh, rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, rajresults.nic.in
RBSE 12th Result 2024 Commerce: राजस्थान 12वीं वाणिज्य रिजल्ट Link at Jagran Josh, rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, rajresults.nic.in
Maharashtra HSC Result 2024 soon at hscresult.mahahsscboard.in; How to Check MSBSHSE Class 12 Online
RBSE 12th Result 2024 Arts: राजस्थान 12वीं कला रिजल्ट Link at Jagran Josh, rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, rajresults.nic.in
RBSE 12th Result 2024: राजस्थान 12वीं रिजल्ट Link at Jagran Josh, rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, rajresults.nic.in
RBSE Result 2024: राजस्थान बोर्ड रिजल्ट Link at Jagran Josh, rajeduboard.rajasthan.gov.in, rajresults.nic.in
Listen Live
Know the difference – rockets versus missiles
The terms 'rocket' and 'missile' are often used interchangeably, which is understandable for anyone without a working knowledge of the subject as they are both varieties of weapons systems that deliver explosive warheads to their targets by rocket propulsion.
Even some in military fields – without naming names – have occasionally struggled to give a confident answer to the question of the difference between a rocket and a missile.
Meanwhile, members of the Armed Forces have been quick to call out some media organisations on social media when it is reported that "rockets have been fired" in news reports when, in fact, the weapons being referred to are missiles, or vice versa.
- Know Your Missiles – the UK's most high-tech firepower
- Britain to send multiple-launch rocket systems to Ukraine
- In pictures: Up close with weapons being used on Ukraine frontline
Coverage of the conflict in Ukraine, for example, has been known to mistakenly refer to one or the other of rockets or missiles with apparent confusion over which is which.
To the undiscerning eye, the two can look remarkably similar – both are launched at distant targets, both propel themselves through the air, and both deliver explosive charges.
What follows is a look at these similar, but distinct, weapon systems, with a basic explanation of the differences for those who remain unsure.
Although they look like missiles, rockets are technologically simpler and were therefore developed far earlier than missiles.
The first rockets date back to the 13th Century and were used in medieval China.
The Chinese also developed early forms of multiple-launch rocket systems, which were rudimentary wooden launchers containing multiple arrows propelled by and carrying explosive batches of gunpowder.
Early rocket technology spread via the Mongols to Europe, where they were used in sieges as a kind of incendiary projectile.
Europeans themselves, and specifically soldiers of Britain's East India Company (EIC), or Honourable East India Company (HEIC), encountered rockets during the Battle of Pollilur in 1780.
Encountered, in this instance, meant being on the receiving end of them, and as A Bowdoin van Riper points out in 'Rockets and Missiles: The Life Story of a Technology', these rockets were a step-up from earlier types.
Rather than being made of bamboo or pasteboard, as rockets had been for centuries, they instead consisted of iron tubes packed with flammable and explosive materials. Although weightier than earlier variants, they also packed in more propellant and had greater thrust and range, apparently able to travel 1.5 miles.
According to van Riper, one factor in the defeat of the British was that the Mysorean rockets caused their ammunition wagon to catch fire, and a painting depicting the battle suggests they exploded with immense force.
Jump forward in time about 150 years and the pattern for modern rockets was being established. This essentially consisted of substituting the long metallic rocket tubes filled with propellant and payloads for long metallic launchers filled with smaller rockets.
This is the main concept behind the first anti-tank rocket launchers of World War 2 such as the American Bazooka, the British PIAT and the German Panzerfaust and Panzerschreck.
An even more recent equivalent is the AT4, which works in a similar fashion. Essentially, rockets, be they NASA space rockets or anti-tank rockets, work by using momentum – that is, the momentum of the thrust they generate being used to propel them through the air.
That thrust comes from propellant, which is a reactive fuel like gunpowder in early rockets, or nitroglycerine, that is ignited by pulling the trigger on a launcher.
Once it leaves the launcher, the shape of a rocket is designed to cut down on air resistance and thereby make it travel on a trajectory that is as smooth and predictable as possible, an important feature given that rockets must be aimed at their intended targets.
An explosive charge in the top of the rocket then goes off, either when it has struck its target, or when an internal fuse detonates it after a certain period of time, such as five seconds.
The thrust from rockets can cause a certain amount danger since the propellant creates a back blast that can burn the firer or adjacent personnel. They must therefore not only be aimed carefully at their intended targets but also positioned correctly to avoid injuring those who are near the rocket when it is launched.

Although they look very similar to rockets, missiles are a step up technologically.
While they also have propellant and use thrust to reach their targets, and have explosive warheads just like rockets, there is a crucial difference: rockets rely on accurate aiming, but every individual missile has its own guidance system.
More complex flight paths over longer distances also mean that missiles tend to have more in the way of aerodynamic external elements, such as larger tail fins and wings.
In terms of predecessors, there was an early form of rocket in medieval China known as the Huolongchushui, which roughly translates as 'fire dragon out of water'. This weapon has been likened to a kind of ancestor of modern ballistic missiles.
It was initially propelled towards its target by downward-facing rockets packed with gunpowder, and then, apparently, by arrow rockets contained within its bamboo body.
The fuses on these would be automatically lit when those on the external rockets burnt out.
However, since the Huolongchushui did not have a guidance system, it was more akin to an early two-stage rocket than a modern missile.
The earliest true missiles were the V-1 flying bomb and the misnamed V-2 rocket, both of which were developed by Nazi Germany and fired at London and other targets.
The guidance system of the V-1 consisted of two gyroscopes designed to keep it on a level flight path and counteract air resistance or wind, which might have caused side-to-side or tilting motions liable to send the missile off its intended path.
V-1s also contained internal compasses and barometric devices to help them maintain direction and altitude.
V-2 rockets had guidance systems that worked similarly, although they also had accelerometers that controlled their speed, and both missiles had technologies that cut off their engines at pre-programmed moments, causing them to, effectively, dive on their target areas.
Modern missiles can be far smaller than their Second World War-era predecessors, and systems such as the NLAW and Javelin are good examples.

Like the AT4, both are anti-tank weapons, although a telltale difference is the nature of the projectile's flight path.
The rocket fired out of the AT4 launcher travels in a continuous trajectory towards its intended target.
Missiles launched out of Javelin or NLAW systems, on the other hand, first head towards their targets, then shift direction by climbing up, before arcing downwards.
This is their internal guidance systems kicking in, since both weapon systems are designed to travel towards and hit what they are aimed at – usually a tank – but they do so by travelling up and over onto the top of the target.
The reason for this is that tank armour is weaker on top than it is on the front or sides of the vehicle, a feature that makes anti-tank missiles more deadly to tanks than more rudimentary rocket systems like the AT4.
As well as varying in size, missiles can also vary considerably in the type of guidance system they use. Some examples are heat-seeking systems, like the air-to-air missiles fighter jets use to shoot each other down, and laser-guided systems and satellite systems, like those used by some cruise missiles.
Inter-Continental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) use rocket technology, as in fuel as a propellant, to get airborne, as well as momentum to remain in flight. Guidance is provided mid-flight, perhaps by satellite, before gravity brings the missile down on its target.
Since ICBMs carry nuclear weapons, it is important to point out that none has ever been used in anger, although the potential threat of nuclear strike and counterstrike still lingers from the Cold War era.
Rockets have a long history, from the earliest medieval incendiary siege weapons to today's shoulder-fired anti-tank weapons. They differ from bombs because bombs do not propel themselves through the air, while rockets do.
Yet they also differ from missiles in that they do not have internal guidance systems of any kind to help direct them to their intended targets.
Missiles do have this feature, and, being more advanced, are a more recent technology, with the earliest types only going back to the Second World War.
Both weapon systems are commonly used as anti-tank weapons, and both are being used in Ukraine.
The AT4 is a good example of an anti-tank rocket system with a range of 300 to 500 metres.
It must be aimed but its rockets use internally generated thrust to drive themselves towards targets.
Javelins and NLAWs are good examples of comparable missile systems that also perform an anti-tank function but do so with missiles that lock onto a target the firer has aimed at, then guide themselves up, over and down onto it, causing maximum damage.

Cover image: Javelin anti-tank missile in flight (Picture: MOD).
Related topics
- Weapons and Kit
Join Our Newsletter
Please select at least one newsletter to subscribe to:
Moving heavy armour across rivers at speed with British Army’s bridging specialists
German helicopters train with us soldiers on nato's exercise swift response, army's new ares ajax variant on the move with royal armoured corps, most popular.

Forces Help To Buy scheme helps around 30,000 military families onto property ladder

Ground broken for new single living accommodation at Royal Military Academy Sandhurst

Watch: Challenger 3's firepower on display as it takes to the range in Germany
Challenger 3: explosive footage shows power of army's new tank, from canine vigilance to surgical precision: inside exercise immediate response, royal navy pull off shocking t20 inter services win over british army, latest stories.

Let Ukraine use Western weapons in Crimea, Shapps urges

Lack of planes for D-Day commemoration highlights need for more cash, Defence Secretary says

British ceremony marking 80th anniversary of the Battle of Monte Cassino takes place in Italy
Editor's picks.

Ukrainians may swap AK for HK as Western arms manufacturer chooses Eastern calibre

RFA's new underwater surveillance vessel snapped as she ties up alongside HMS Belfast

Missing Victoria Crosses safe after being returned to museum anonymously
Browse hundreds of jobs for ex-forces.
- Forces News Catch-up

Prelims 2024 CA | 2024 Test Series | Daily CA | Daily MCQs | Monthly CA
Ballistic Missile vs. Cruise Missile, India’s Missile Systems, IGMDP
- August 2, 2019
Subscribe to Never Miss an Important Update! Assured Discounts on New Products!
Must Join PMF IAS Telegram Channel & PMF IAS History Telegram Channel
We frequently notice news related to ballistic missiles, cruise missiles and various missile systems of India. Memorizing names and salient features of various Indian missiles is hard without having a broader understanding of the concept of ballistic missiles and cruise missiles, and major missile defence systems. It is better to give these concepts a holistic structure rather than learning them in bits and pieces.
Ballistic Missile vs. Cruise Missile
The Hindu | GS3 > indigenization of technology
The terms ‘ballistic missile’ and ‘cruise missile’ appear in news articles wherever there is a missile test. It is essential for us to understand these terms to understand various Indian missile defence systems.
Ballistic Missile
- A ballistic missile follows a ballistic trajectory to deliver one or more warheads on a predetermined target.
- A ballistic trajectory is the path of an object that is launched but has no active propulsion during its actual flight (these weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods of flight).
- Consequently, the trajectory is fully determined by a given initial velocity, effects of gravity, air resistance, and motion of the earth (Coriolis Force).
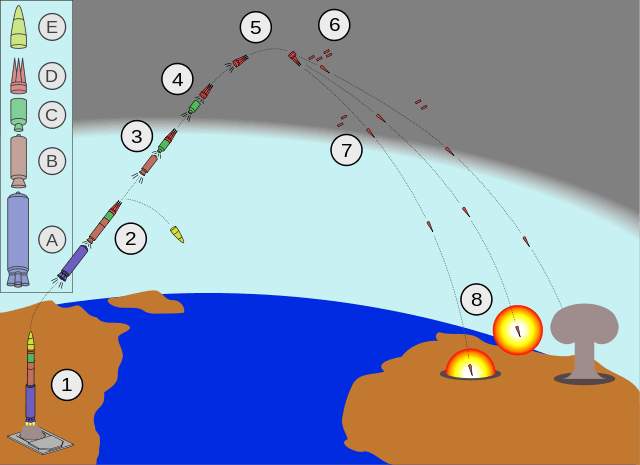
Image Credits: Wikipedia
- Shorter range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth’s atmosphere.
- Longer-ranged intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), are launched on a sub-orbital flight trajectory and spend most of their flight out of the atmosphere.
Types of ballistic missiles based on the range
- Short-range (tactical) ballistic missile (SRBM): Range between 300 km and 1,000 km.
- Medium-range (theatre) ballistic missile (MRBM): 1,000 km to 3,500 km.
- Intermediate-range (Long-Range) ballistic missile (IRBM or LRBM): 3,500 km and 5,500 km.
- Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM): 5,500 km +
Cruise missile
- A cruise missile is a guided missile (target has to be pre-set) used against terrestrial targets.
- It remains in the atmosphere throughout its flight.
- It flies the major portion of its flight path at approximately constant speed.
- Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
- Modern cruise missiles are capable of travelling at supersonic or high subsonic speeds, are self-navigating, and are able to fly on a non-ballistic, extremely low-altitude trajectory.
Types of cruise missiles based on speed
- Hypersonic (Mach 5): these missiles would travel at least five times the speed of sound (Mach 5). E.g. BrahMos-II.
- Supersonic (Mach 2-3): these missiles travel faster than the speed of sound. E.g. BrahMos.
- Subsonic (Mach 0.8): these missiles travel slower than the speed of sound. E.g. Nirbhay.
Differences between Ballistic Missile and Cruise Missile
Integrated guided missile development programme (igmdp).
PIB | Source | The Hindu | 19-06-2019 | GS3 > indigenization of technology
- IGMDP was conceived by Dr. A P J Abdul Kalam to enable India attain self-sufficiency in missile technology.
- IGMDP was conceived in response to the Missile Technology Control Regime that decided to restrict access to any technology that would help India in its missile development program.
- To counter the MTCR, the IGMDP team formed a consortium of DRDO laboratories, industries and academic institutions to build these sub-systems, components and materials.
- IGMDP was started in 1983 and completed in March 2012.
- Keeping in mind the requirements of various types of missiles by the defence forces, the development of five missile systems was taken up.
- Prithvi: Short-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile (Prithivi means Earth Surface to Surface)
- Agni: Intermediate-range surface-to-surface ballistic missile
- Trishul: Short-range low-level surface-to-air missile
- Akash: Medium-range surface-to-air missile (Akash means Sky Surface to Air)
- Nag: Third generation anti-tank missile (Nag means Snake Nag slithers like a Snake to hit a tank!)
- After its success, the Agni missile program was separated from the IGMDP upon realizing its strategic importance.
India’s Missile Systems
PIB | Source | The Hindu | GS3 > indigenization of technology
SLBM: Sub-marine launched ballistic missile
Prithvi Missiles
All the Prithvi variants are surface-to-surface SRBMs.
Agni Missiles
MIRV: Multiple Independently targetable Re-entry Vehicle
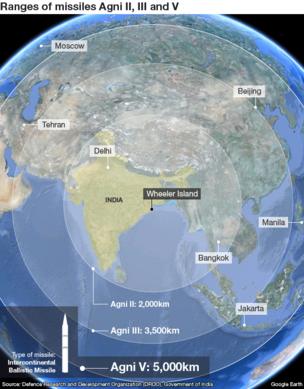
Anti-satellite weapons (ASAT)
- In March 2019, India successfully tested its ASAT missile.
- The ASAT missile destroyed a live satellite in Low Earth orbit (283-kilometre).
- As per DRDO, the missile is capable of shooting down targets moving at a speed of 10 km per second at an altitude as high as 1200 km.
Newsletter Updates
Assured Discounts on our New Products!
Related Posts
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance & Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- May 11, 2021

Kepler’s laws, Satellite Orbits, Launch Vehicles PSLV & GSLV
- December 3, 2020
Uranium & Thorium Distribution across India & World
- April 6, 2020
Nuclear Fission, Components of Nuclear Reactor, Types of Nuclear Reactors
- January 2, 2020

India’s Three-Stage Nuclear Power Programme
- March 21, 2016

Precision Farming, Geoinformatics for Precision Farming
- November 30, 2019
Lithium-ion battery, Internal Combustion Engine vs. Electric Vehicles
- November 9, 2019

Genome, Whole Genome Sequencing, Genome India Project
- June 4, 2021
wonderful sir
Thanks a lot for this fantastic compilation sir!
I was unable to find such complied information on internet, but I found it here. Thanks a lot to PMFIAS
Thanks a lot
What a work sirji. Thank you so much
Thanks for very useful information and systematic content is systematic view of point very fantastic please keep it up latest update by geneon source like Hindu PIB arc etc
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Name *
Email *
Add Comment *
Post Comment
Trending now

Never miss an important update!

Russia to Deploy Submarine-Launched Bulava Ballistic Missiles
Russia has integrated the Bulava intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) into its submarine fleet, a significant upgrade to its strategic nuclear arsenal.
The Bulava missile, designed to be launched from Borei-class submarines, has completed rigorous testing, including a successful test launch from a distance of 3,500 miles.
Yuri Solomonov, the missile's chief designer, confirmed the missile's adoption in a decree dated May 7, coinciding with President Vladimir Putin's commencement of a new six-year term as president.
According to the Missile Defense Project at the Washington-based Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), the Bulava represents "a core component of Russia's future strategic nuclear force." Development of the missile began in the 1990s, with Solomonov also behind the Topol-M and Yars ICBMs.
The three-stage Bulava missile features solid fuel propellant in the first and second stages and a liquid fuel third stage for high maneuverability during warhead separation. Its inclined launch capability allows submarines to launch while in motion.
A recent CSIS assessment highlighted the Bulava's potential to deliver 10 multiple independently targetable re-entry vehicles (MIRVs), each capable of striking different targets. The weapon can carry decoys, and its re-entry vehicles are designed for in-flight maneuverability and re-targeting to evade enemy defenses.
"This capability poses a significant challenge for missile defense systems, potentially overwhelming them with volume and trajectory complexity," CSIS notes.
Russia's Northern and Pacific Fleets operate seven Borei-class submarines, each armed with 16 Bulavas. Last November, the defense ministry reported a successful test launch of the Bulava from one of these submarines.
Launched from under the White Sea on the northwest coast of Russia, the test missile traveled thousands of miles over the Russian mainland to strike a designated target on the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia's Far East region, according to the Russian Defense Ministry.
"Firing a ballistic missile is the final element of state tests, after which a decision will be made to accept the cruiser into the Navy," a ministry statement said in November. With testing complete, the missiles are now considered operational.
The modernization of Russia's submarine-launched missile systems comes amid heightened tensions with the West. Putin has said that NATO intervention in Ukraine could escalate to a nuclear conflict.
In late April, Russian Ambassador to the U.S. Anatoly Antonov issued a stark warning to Washington after President Joe Biden signed a bill providing approximately $61 billion in additional aid to Ukraine. "America has chosen the path of war," Antonov said.
Start your unlimited Newsweek trial


COMMENTS
Ballistic missiles are different than cruise missiles. Cruise missiles are self-propelled for the majority of their time in the air, flying in a relatively straight line and at lower altitudes thanks to a rocket propellant. Think of a ballistic missile's flight path as a large arc up and back down again, while that of a cruise missile — fired from a warship, for instance — is closer to a ...
Ballistic missiles have three stages of flight: Boost Phase begins at launch and lasts until the rocket engine (s) stops firing and the missile begins unpowered flight. Depending on the missile, boost phase can last three to five minutes. Most of this phase takes place in the atmosphere. Midcourse Phase begins after the rocket (s) stops firing.
There are four general classifications of ballistic missiles based on their range, or the maximum distance the missile can travel: Short-range: less than 1,000 kilometers (approximately 620 miles), also known as "tactical" ballistic missiles. Medium-range: between 1,000 and 3,000 kilometers (approximately 620-1,860 miles), also known as ...
Difference between cruise and ballistic missiles. There are some important differences between cruise and ballistic missiles. These are: Ballistic missiles follow an arc-like trajectory and are launched from the land or sea; They usually carry a nuclear warhead and are very heavy; They rely on Earth's gravity to fly down once launched
They can be launched from ground, airplane, and sea platforms like submarines and surface warships. They tend to have shorter ranges than ballistic missiles. Unlike ballistic missiles, cruise missiles are usually categorized by intended missions and launch mode instead of maximum range. The two broadest categories are land attack cruise ...
In the interest of brevity, you can really sum up the difference between these types of weapons with the trajectory that they follow. A ballistic missile follows a "ballistic flight path," which often includes traveling along a long arc, whereas a cruise missile tends to follow a straighter, lower altitude trajectory.
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided vehicle that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path and whose primary mission is to place an ordnance or special payload on a target. [1] Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large warhead over long distances with high precision.
Strategic missiles represent a logical step in the attempt to attack enemy forces at a distance. As such, they can be seen as extensions of either artillery (in the case of ballistic missiles) or military aircraft (in the case of cruise missiles). Ballistic missiles are rocket-propelled weapons that travel by momentum in a high, arcing trajectory after they have been launched into flight by a ...
Guided cruise and ballistic missiles were first used when Germany attacked targets in England and Northern Europe with V-1 cruise missiles and V-2 ballistic missiles during World War II. Although these missiles were inaccurate, their use resulted in tens of thousands of Allied casualties. Ballistic and cruise missiles present a significant ...
Key characteristics of ballistic and cruise missiles. Ballistic missiles present key advantages (See Table 1) compared with cruise missiles (the latter are propelled until impact and include a guidance system). Ballistic missiles can reach a longer range with lower fuel in a relatively short time (around 30 minutes for an ICBM). Their very high ...
While both ballistic and cruise missiles can carry nuclear payloads, the most commonly understood (and feared) nuclear weapon delivery vehicle of the modern era falls under the ballistic category: the ICBM. And while there are many variations in the employment of different sorts of ballistic missiles, the ICBM model offers a simple way to appreciate the concept behind a "ballistic flight ...
A ballistic missile (BM) is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are powered only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles (SRBM) typically stay within the Earth's atmosphere, while most larger missiles are exo-atmospheric. The largest ICBMs are capable of full orbital flight.
Rocket and missile system - Strategic missiles: Strategic missiles represent a logical step in the attempt to attack enemy forces at a distance. As such, they can be seen as extensions of either artillery (in the case of ballistic missiles) or manned aircraft (in the case of cruise missiles). Ballistic missiles are rocket-propelled weapons that travel by momentum in a high, arcing trajectory ...
cruise missile, type of low-flying strategic guided missile.The German V-1 missile used in World War II was a precursor of the cruise missile, which was developed by the United States and the Soviet Union in the 1960s and '70s. Capable of carrying either a nuclear or a conventional warhead, the cruise missile was designed to have a very low radar cross section and to hug the ground while ...
Due to its extremely high speed and high trajectory, ballistic missiles are extremely difficult to intercept. However, this type of missile is very easy to detect immediately after launch. The second type of missile is more modern and also much more accurate, the cruise missile. Cruise missiles typically have a shorter range than long-range ...
A Cruise Missile is a guided missile that flies with constant speed to deliver a warhead at specified target over long distance with high accuracy. A Ballistic Missile is lift off directly into the high layers of the earth's atmosphere.. Cruise Missiles. Cruise missiles are unmanned vehicles that are propelled by jet engines, much like an airplane.They can be launched from ground, air, or ...
Check Difference between Cruise and Ballistic Missiles. Cruise missiles are guided, jet or propeller-driven projectiles that can fly at low altitudes, follow a flexible path, and are capable of precision strikes. Ballistic missiles, on the other hand, are unguided, rocket-powered weapons that follow a high, arching trajectory before descending ...
Unlike ballistic missiles, which arc up into space before traveling back down towards earth, cruise missiles fly close to the ground, making it hard for radar on the ground that's pointed up at ...
Fastest cruise missile in the world in its category. The Brahmos missile speed is Mach 2.8 and has a range of 290 kilometres, or approximately three times the speed of sound. The Brahmaputra and Moskva rivers in Russia inspired the its name, which was jointly developed with Russia. Difference Between Ballistic And Cruise Missile
This missile is self-propelled till the end of its flight. This missile is similar to a rocket engine. The cruise missile shares similarity with a jet engine. Long-range ballistic missiles leave ...
Missiles do have this feature, and, being more advanced, are a more recent technology, with the earliest types only going back to the Second World War. Both weapon systems are commonly used as anti-tank weapons, and both are being used in Ukraine. The AT4 is a good example of an anti-tank rocket system with a range of 300 to 500 metres.
Strategic missiles (weapons designed to strike targets far beyond the battle area) are either of the cruise or ballistic type. Cruise missiles are jet-propelled at subsonic speeds throughout their flights, while ballistic missiles are rocket-powered only in the initial (boost) phase of flight, after which they follow an arcing trajectory to the ...
The principal intended phase of ballistic missile interception is noted. Other phases may be tried, with less effect. The earlier in flight that a missile is intercepted, the greater area a system may defend. Mid-course interception requires an ABM launch position between the ballistic missile launch site and the area defended.
Medium-range (theatre) ballistic missile (MRBM): 1,000 km to 3,500 km. Intermediate-range (Long-Range) ballistic missile (IRBM or LRBM): 3,500 km and 5,500 km. Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM): 5,500 km + Cruise missile. A cruise missile is a guided missile (target has to be pre-set) used against terrestrial targets.
The latest Ukrainian deep-strike weapon isn't a drone, a cruise missile or a ballistic missile. It's a balloon. In a recent speech, Russian defence minister Sergei Shoigu claimed Russian air ...
"Firing a ballistic missile is the final element of state tests, after which a decision will be made to accept the cruiser into the Navy," a ministry statement said in November. With testing ...